ZX2015Y101
NH3 Molecule
N-H bond distance = 1.01798 armstrong
H-N-H bond angle = 105.741 degree
Optimisation
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basis Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) : -56.55776873
RMS gradient : 0.00000485
Point group : C3V
Optimised NH |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
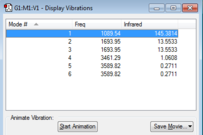
Number of modes expected from the 3N-6 rule : 6 modes
Modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy) : 2&3 ; 5&6
Modes are "bending" vibrations : 1,2,3
Modes are "bond stretch" vibrations : 4,5,6
Mode is highly symmetric : 4
The "Umbrella" mode : 1
Number of bands expected to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia : 2 bands
Charge distribution
Nitrogen in NH3 has small negative charge of -1.125
Hydrogen in NH3 has small positive charge of 0.375
Nitrogen atom is more electronegative than hydrogen atom. So the nitrogen atom pulls the pair of electrons towards itself. Therefore the nitrogen contains negative charge while the hydrogen is relatively positively charged.
Reactivity
Molecule : N2
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basis Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) : -109.52412866
RMS gradient : 0.00012786
Point group : D∞h
Vibration frequency : 2457.98
Optimised NH |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000221 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000221 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000052 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000098 0.001200 YES
Molecule : H2
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basis Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) : -1.17853936
RMS gradient : 0.00002276
Point group : D∞h
Vibration frequency : 4466.46
Optimised NH |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000039 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000039 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000052 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000073 0.001200 YES
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
* E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au * 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au * E(N2)= -109.52412866 au * E(H2)= -1.17853936 au * 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 au * ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579076 au * ΔE= -146.478651538 kj/mol
Therefore the product NH3 is more stable.
O2 Molecule

Dond distance = 1.21602 armstrong
Bond Angle = 180 degree
Optimisation
Calculation Method : RB3LYP
Basis Set : 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) : -150.25742434
RMS gradient : 0.00007502
Point group : D∞h
Vibration frequency : 1642.74
Optimised NH |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Charge Distribution

Covalent Double Bond forms between two oxygen atoms. No charge on neither oxygen atom.
Molecular Orbitals

This MO is a bonding combination of the two 1s core AOs on each oxygen atom. It is filled by two electrons.
Because It is much deeper energy than MO formed by valence shell AOs, it does not involve in chemical bonding.


The 3rd MO is a bonding combination of 2s valence AOs of each oxygen atom while the 4th MO is an anti-bonding combination of 2s valence AOs.
Both of these MOs are occupied. They are higher in energy, so they involve in chemical bonding.

The 5th MO is a bonding combination of 2px valence AOs.MO is occupied.
Sigma 2px bond is formed.
Its energy is higher than MOs formed by 2s AOs.

The 6th MO is a bonding combination of 2py valence AOs. MO is occupied.
Pi 2py bond is formed.
Its energy is even higher than MO gives sigma bond, so it is easier to be broken in a chemical reaction.
