Yukilamys010
EXERCISE 1: H + H2 system
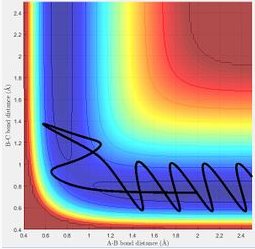
Dynamics from the transition state region
The transition structure is the maximum on the minimum energy path whereas the minimum is at the minimum point on the path. At a minimum and a transition structure, the total gradient of the potential energy surface is 0. On the potential energy surface diagram, the transition structure will be the saddle point which is the local maximum on the path which will have a negative value for the second derivative. Meanwhile, the minimum will be the local minimum on the path which has a positive value for the second derivative. The transition structure will be indicated by negative curvature whereas as the minimum has positive curvature.
Locate the transition state
At this value of r, the system will reach a transition structure which is the maximum point on the minimum energy path. The transition state position is when r1 = r2 so it is expected that on the internuclear distances vs time plot will show that the distances of AB and BC will be the same in the time frame.And the distance AC will be double of that of AB or BC which is the sum of AB and BC.
MEP and Dynamics
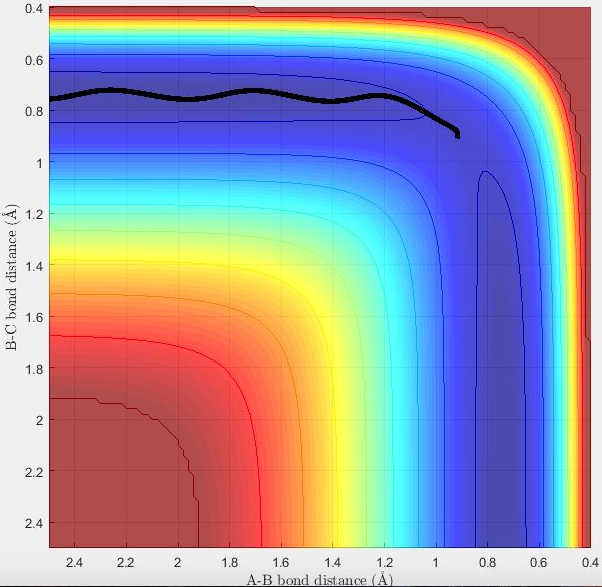
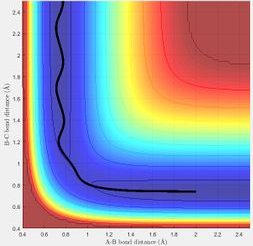
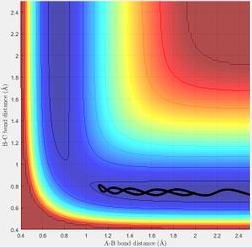
MEP shows the direction of the reaction. For example, the reaction will be forming product if the trajectory of MEP is going towards the direction of the product. The reaction is not forming product if the trajectory is proceeding towards reactants. On MEP, it doesn't show the change in potential energy whereas it will be shown on dynamics plot.
Reactive and unreactive trajectories
Assumptions of Transition State Theory
The transition state theory assumes that there is a quasi-equilibrium between reactants and transition state, and when it reaches the equilibrium, the system will form product. But as it is shown in the example above, this is not necessary the case as indicated in the 4th example that the system has passed through the activation barrier but it bounces back to the reactants channel to reproduce the reactants and the reaction wasn't successful.
EXERCISE 2: F - H - H system
Reaction of F and H2
The reaction of F and H2 to form HF and H. The reaction will be exothermic, because the energy results from bond forming and breaking. In this reaction, H-H bond are being broken which needs to absorb energy and H-F bonds are being formed which will release energy. Since H-F is a stronger bond than H-H, thus energy will be given out which means this reaction is exothermic. The reaction of HF and H to form F and H2. The reaction will be endothermic, because more energy are absorbed than that being released.
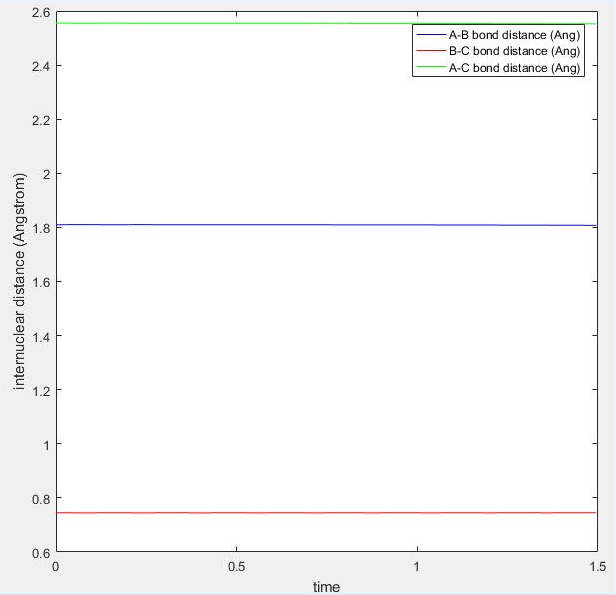
Locate the transition state
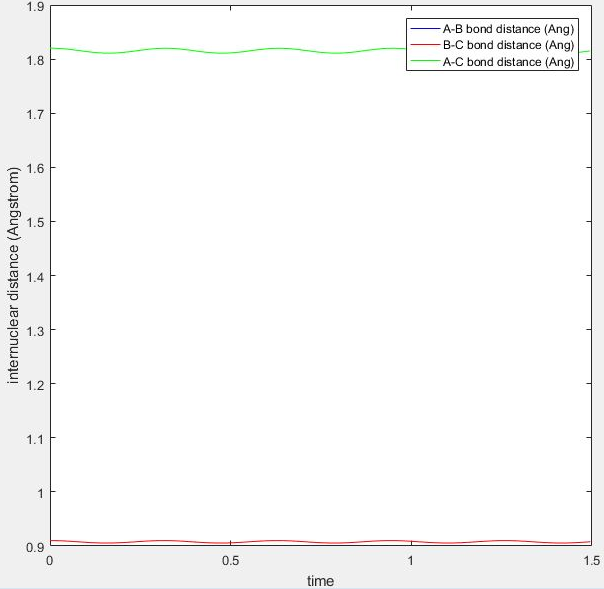
The transition position is when HF has a distance of 1.81 and HH has a distance of 0.745.
Activation Energy
Activation energy (form HF and F)= 0.6kJ/mol Activation energy (form F and H2 )=30.6 kJ/mol
Reaction Dynamics
Transition State Position and Distribution of Energy
The amount of translatinoal and virational energy will affect whether the reaction can be reactive or not.