Yhy123456
NH3 Molecule
Bond Angle = 105.741°
Bond Length = 1.01798Å
NH3 Optimisation
For the Gaussview Optimisaion:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986278D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
the result of optimisation is:
Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -56.44397188 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.05399560 a.u. Point Group = C3V
NH Molecule |
NH3 Vibration
All of the 6 modes are from 3N-6 rule Mode 2 and 3, 5 and 6 are degenerate Mode 1,2and3 are bond vibration. Mode4,5and6 are bond stretch Mode 1and4 are highly symmetric Mode 1 is the 'umbrella' mode 2 bands will show in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia
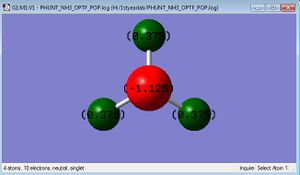
NH3 Charge Analysis
The Nitrogen atom should be negative and hydrogen should be positve due to the electronegativity of the Nitrogen is higher than Hydrogen.
N2 Molecule
Bond Length=1.10550Å
N2 Optimisation
For the Gaussview Optimisaion:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.248809D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
The result of optimisation is:
Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -109.52412868 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000365 a.u. Point Group = D*H
N2 Vibration
N2molecule mole have 1 mode of vibration with frequency 2457.31 and infrared is zero
N2 Charge analysis
N2 molecule as an element the charge on its element should be zero

H2 Molecule
Bond length: 0.74309Å
H2 Optimisation
For the Gaussview Optimisaion:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.852867D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7431 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The result of optimisation is:
Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Charge = 0 Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -1.17853930 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00012170 a.u. Imaginary Freq = 0 Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye Point Group = D*H
Haber Process
Haber process is the industrial process to make ammonia which has following steps with heterogeneous catalyst involved.[1]
- ↑ Wennerström, Håkan; Lidin, Sven. http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2007/advanced-chemistryprize2007.pdf (PDF). NobelPrize.org. Swedish Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 2015-09-17.
| Step | reaction |
|---|---|
| 1 | N2 (g) → N22 (adsorbed) |
| 2 | N2 (absorbed) → 2 N (absorbed) |
| 3 | H2 (g) → H2 (absorbed) |
| 4 | H2 (g) → 2 H (absorbed) |
| 5 | N (adsorbed) + 3 H(adsorbed)→ NH3 (adsorbed) |
| 6 | NH3 (absorbed) → NH3 (g) |
The energy change of Haber Process can be calculated by this:
| Molecule | Energy/kjmol-1 |
|---|---|
| E(NH3) | -148183.2 |
| 2×E(NH3) | -296374.34 |
| E(N2) | -287544.78 |
| E(H2) | -3098.09 |
| 3×E(H2) | -9294.27 |
| ΔE=2×E(NH3)-E(N2)-3×E(H2) | 464.71 |
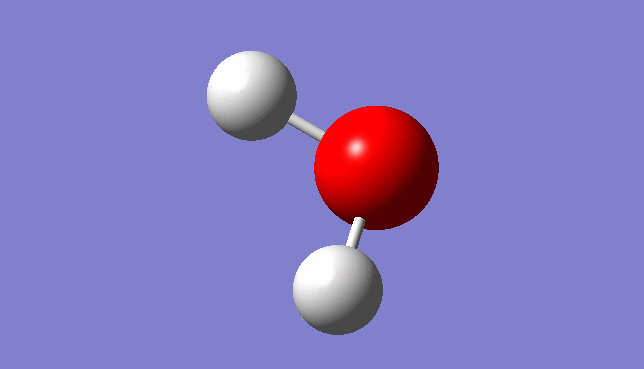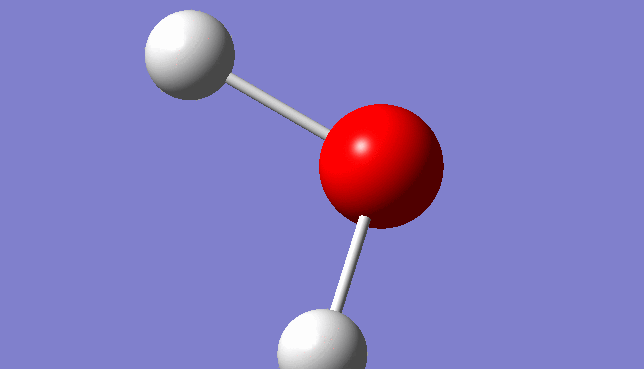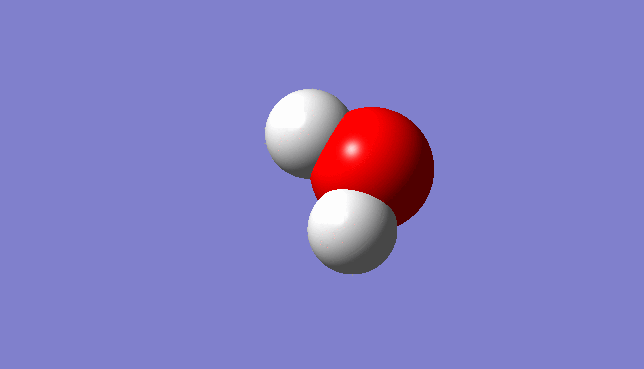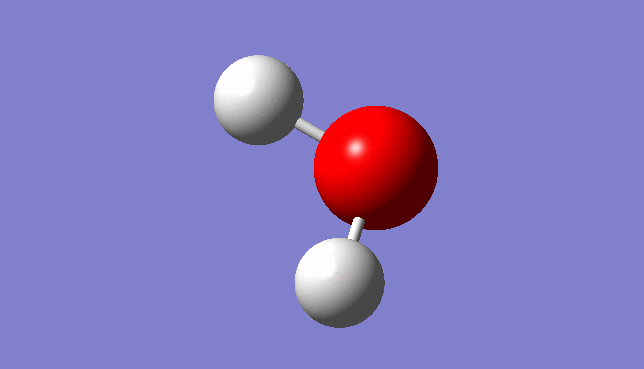
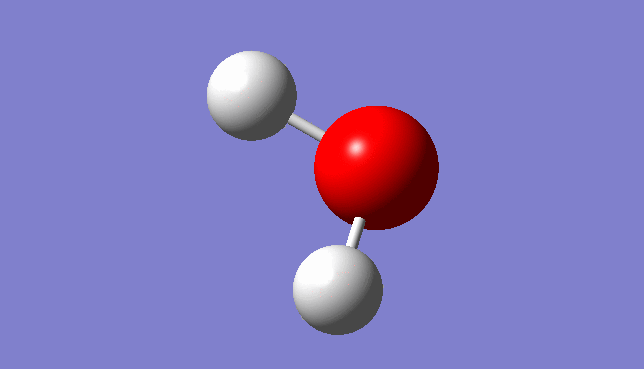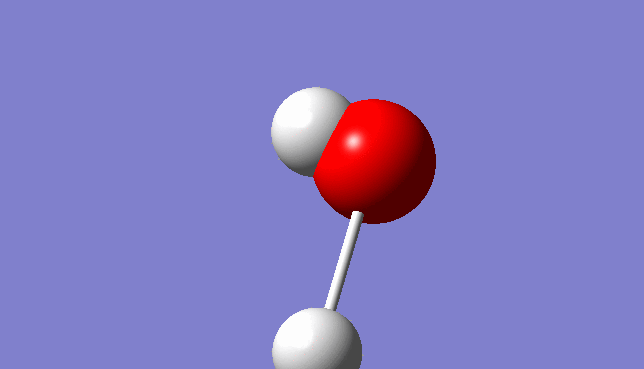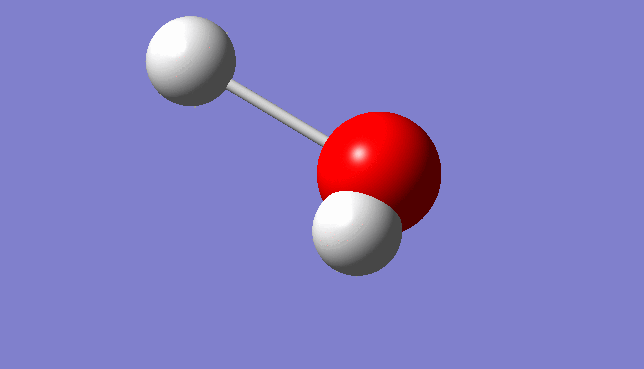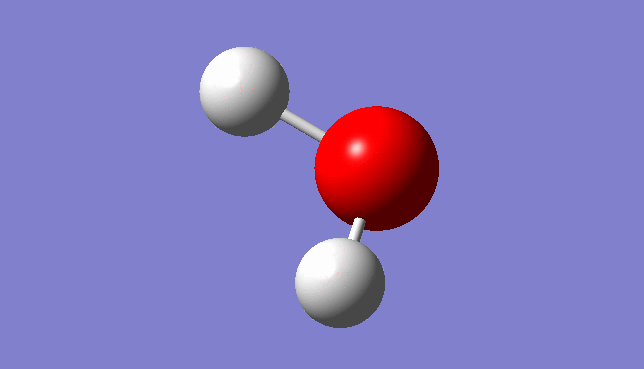
H2O Molecule
Bond length:0.96532Å Bond angle:103.74°
H2O Optimisation
For the Gaussview Optimisaion:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000003 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000002 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000011 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.476162D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.9653 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 0.9653 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 103.7384 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The result of optimisation is:
Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -1.17853930 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00012170 a.u. Point Group = D*H
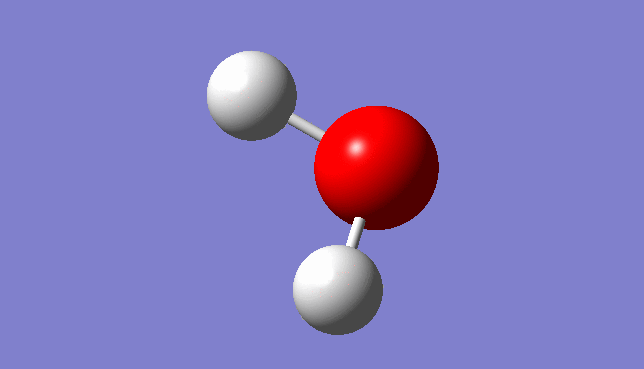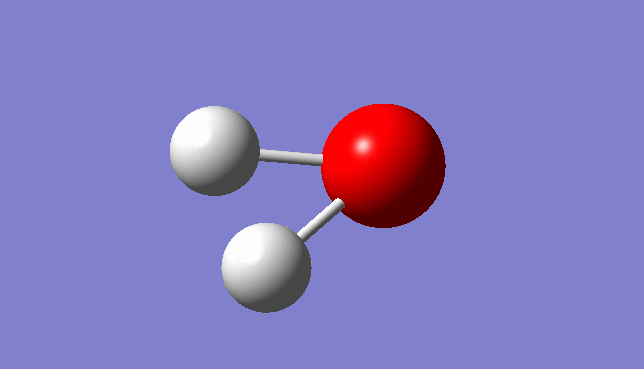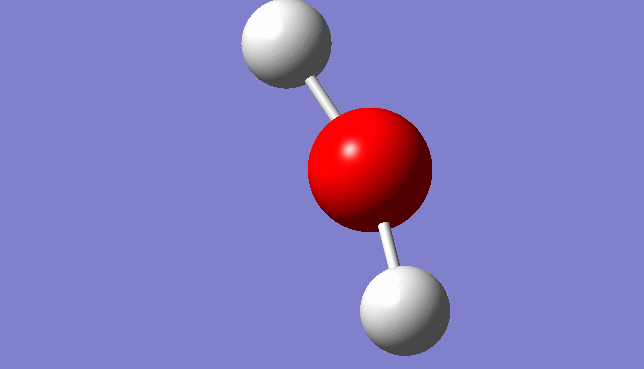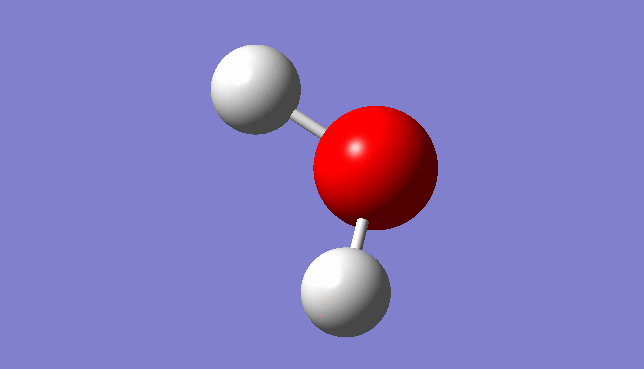
H2O Vibration
Three mode of vibrations are found after the optimisation:
| Mode | Frequency/Hz | infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1665.31 | 70.3173 |
| 2 | 3799.69 | 1.6380 |
| 3 | 3912.81 | 20.2156 |
Vibration Mode 1
Vibration Mode 2
Vibration Mode 3
H2O Charge analysis
Water is a polar Molecule, so the Oxygen atom should be negative and Hydrogen atoms should be posivtve.

Molecular Orbital Analysis
there are 5 molecular orbitals in H2O that are occupied with electron.

Molecular Orbital 1
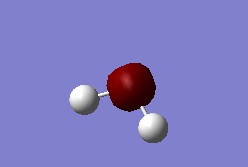 This Orbital is the atomic orbital of 1s2 of Oxygen(1a1).
This Orbital is the atomic orbital of 1s2 of Oxygen(1a1).
Molecular Orbital 2
 This Molecular orbital is attribute to 2s orbital of Oxygen. Consequently it is like a spherical shape.
This Molecular orbital is attribute to 2s orbital of Oxygen. Consequently it is like a spherical shape.
Molecular Orbital 3
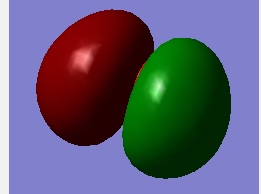 This Molecular orbital is from O—H bonding,which is a σ bonding between 2px of Oxygen and 1s orbital of Hydrogen.
This Molecular orbital is from O—H bonding,which is a σ bonding between 2px of Oxygen and 1s orbital of Hydrogen.
Molecular Orbital 4
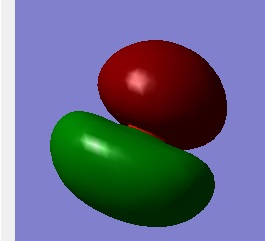 This Molecular orbital is from O—H bonding,which is a σ bonding between 2py of Oxygen and 1s orbital of Hydrogen.
This Molecular orbital is from O—H bonding,which is a σ bonding between 2py of Oxygen and 1s orbital of Hydrogen.
Molecular Orbital 5
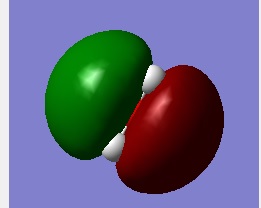 This is an anti-bonding orbital of H2O which is the atomic orbital of 2pz. This contribute the most the effect of lone pairs.
This is an anti-bonding orbital of H2O which is the atomic orbital of 2pz. This contribute the most the effect of lone pairs.