Year1ql
NH3 molecule
General Information
calculation method: RB3LYP
basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -56.55776873
RMS gradient: 0.00000485
point group of your molecule: C3V
N-H bond distance=1.01798
N-H-N bond angle= 109.471
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Jmol 3D Model
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
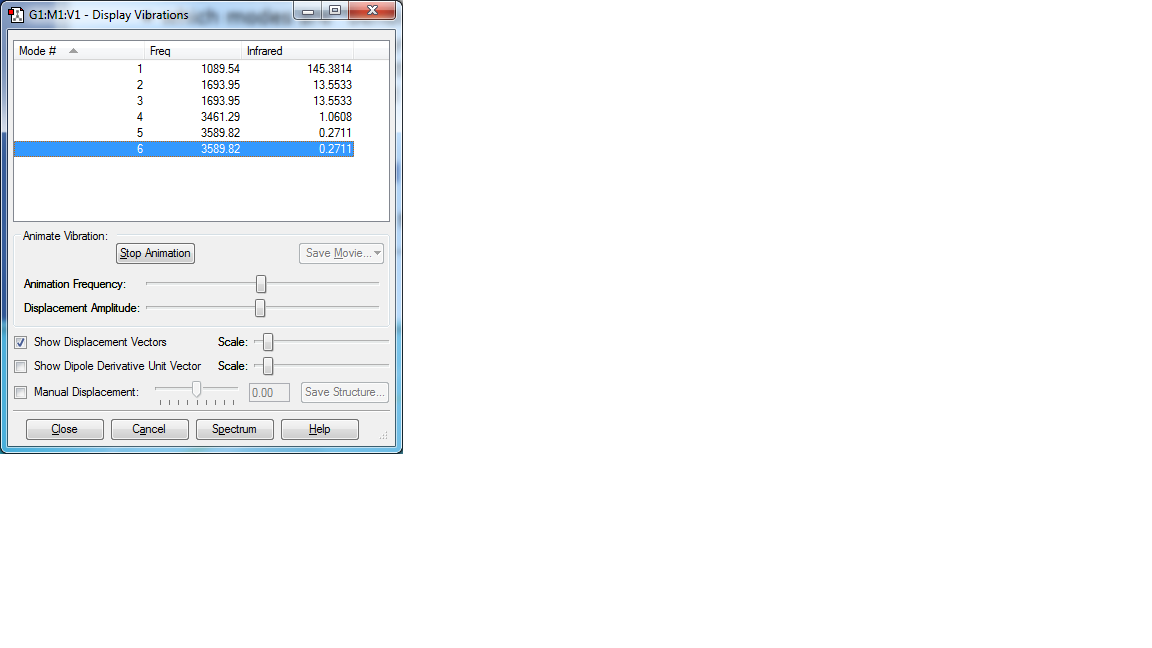
Display Vibrations
Questions about Display Vibrations
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 5 6
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 1 2 3, 4 5 6
which mode is highly symmetric? 4
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 4
charge
charge on the N-atom: -1.125 charge on the H-atoms: 0.375 Since N atom is more electronegative than H atom, the charge on N atom is negative while that on H is positive.
H2 molecule
General Information
H-H bond distance = 0.74309
H-H bond angle = 180°
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -1.17853930
RMS gradient: 0.00012170
Point Group: D*H
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
Jmol 3D Model
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
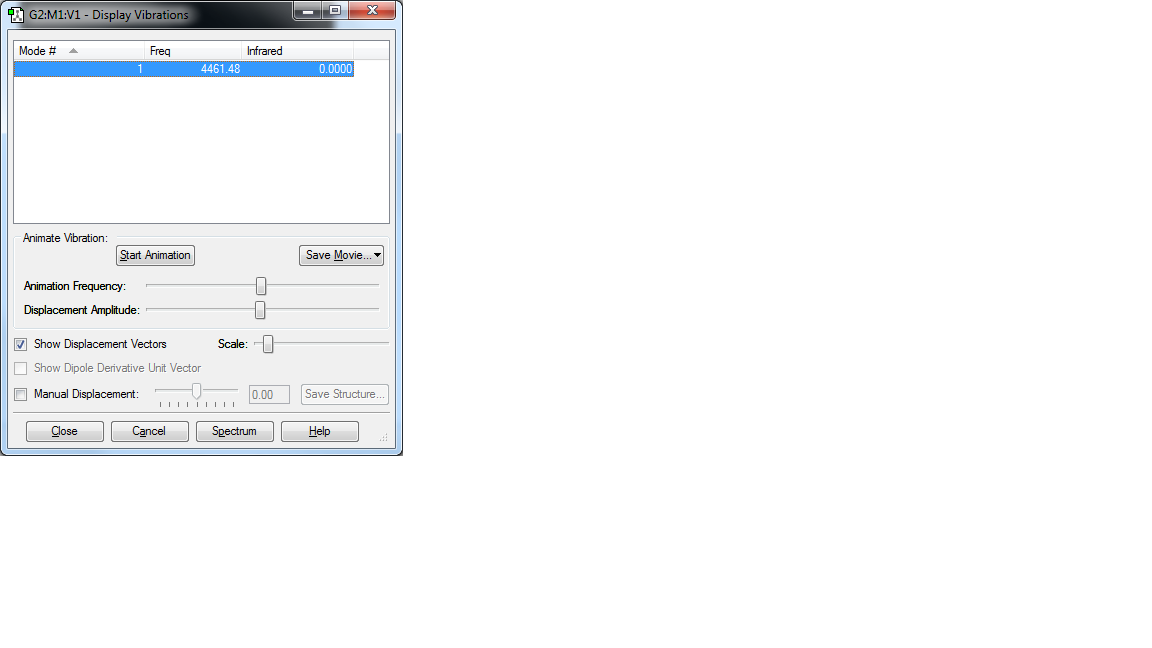
Display Vibrations
N2 molecule
General Information
H-H bond distance = 1.10550
H-H bond angle = 180°
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -109.52412868
RMS gradient: 0.00000365
Point Group: D*H
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES
Jmol 3D Model
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
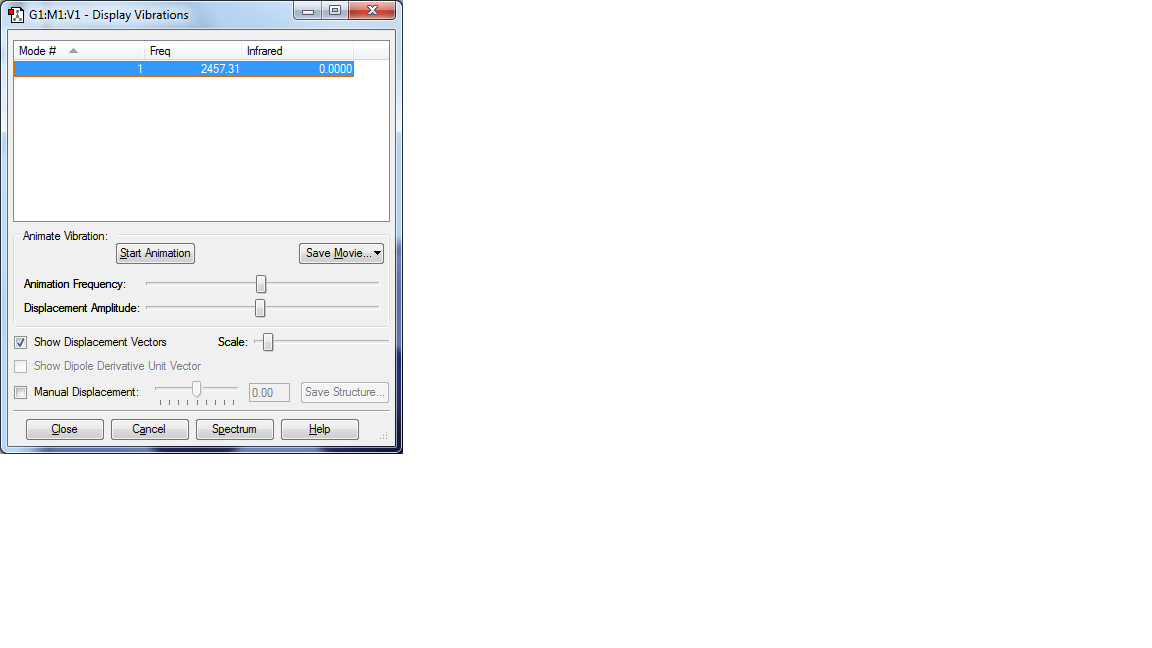
Display Vibrations
Reaction Energies
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u
E(N2)= -109.52412298 a.u
E(H2)= -1.17853930 a.u
3*E(H2)= -3.5356179 a.u
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746-(-109.52412298-3.5356179)=-0.05579658 a.u= -146.50 kJ/mol
Since the energy difference is negative, the ammonia product is more stable.
F2 molecule
General Information
F-F bond distance = 1.16000 Å
F-F bond angle = 180°
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Total Energy: -199.42620785 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.23253407 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Jmol 3D Model
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
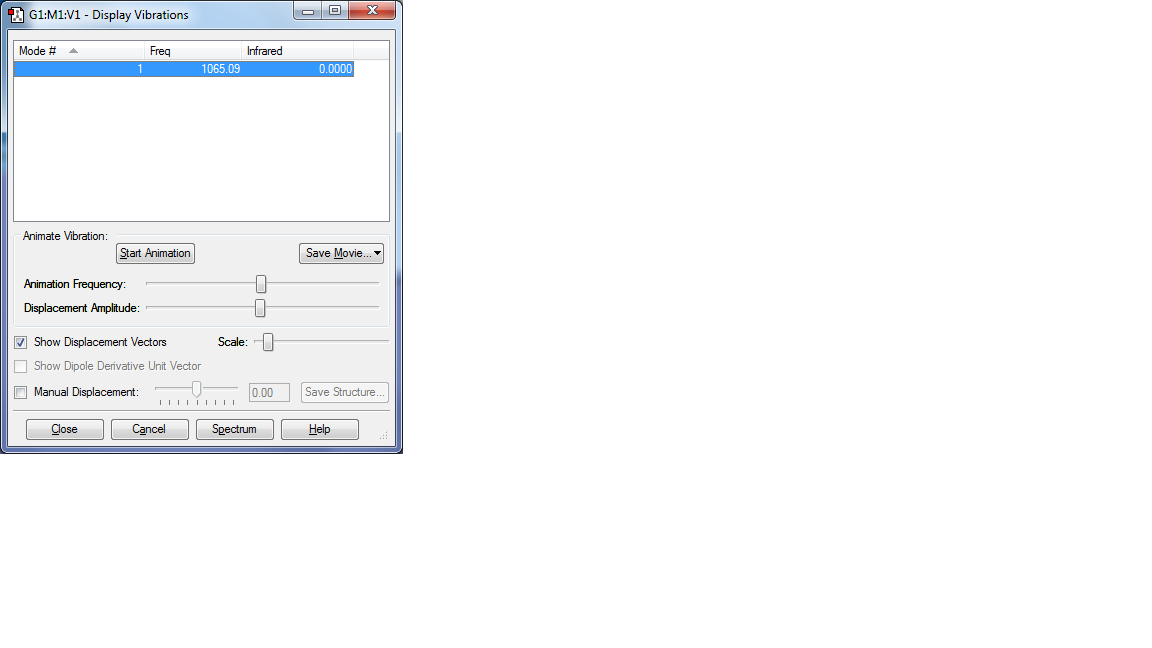
Display Vibrations
charge
There is the same charge on 2 F atoms and F2 molecule does not carry on a overall charge.
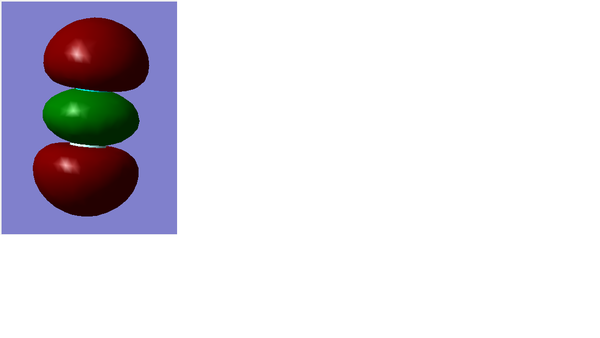
Molecular Orbital
MO1
MO2
MO3
MO4
MO5
Summary
MO1 and MO2 are bonding and anti-bonding orbitals respectively formed by 2s AOs of each F atom. Both of them are sigma bonds.
2p AOs of F atom contribute to the formation of MO3, MO4 and MO5. MO3 and MO4 are occupied and bonding while MO5 is anti-bonding orbital. MO3 and MO5 are sigma MOs formed by 2 pz AOs and, MO4 is pi MOs which is formed by 2 Px AOs.
MO3 and MO4 are bonding orbitals, they have relatively lower energy in HOMO region, at -0.58753 a.u. and -0.52332 a.u.
Also, MO5 is the LUMO with energy (-0.12679 a.u.)