User:Sth16
NH3 Moleclue:
NH3 |
Log file :
The optimisation file is linked to here
Molecule name:
Ammonia
Charge distribution:
N:-1.125 H:0.375 N is expected to have negative charge and H is expected to have positive charge because Nitrogen is more electronegative which mean it is going to attract the bonding pairs of electrons towards itself which makes it more negative

Calculation method:
RB3LYP
Basis set:
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP):
-56.55776873 a.u.
Point group:
c3v
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986278D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimised N-H bond distance:
1.01798 Å
The literature value is 101.2pm (1)
Bond angles:
105.741 degree
The literature value is 106.7 degree(1)
Vibrations:
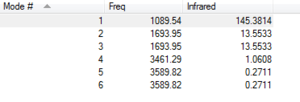
Modes of vibrations: 6
Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate, 5 and 6 are degenerate
Mode 1,2,3 are bending
Mode 4,5,6 are bond stretching
Mode 1 is highly symmetric
Mode 4 is umbrella mode
3 bands are expected to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia
Mode 5 and 6 are being infra-red inreactive because there is no change in electrical dipole moment when it absorbs infra red radiation and vibrates.
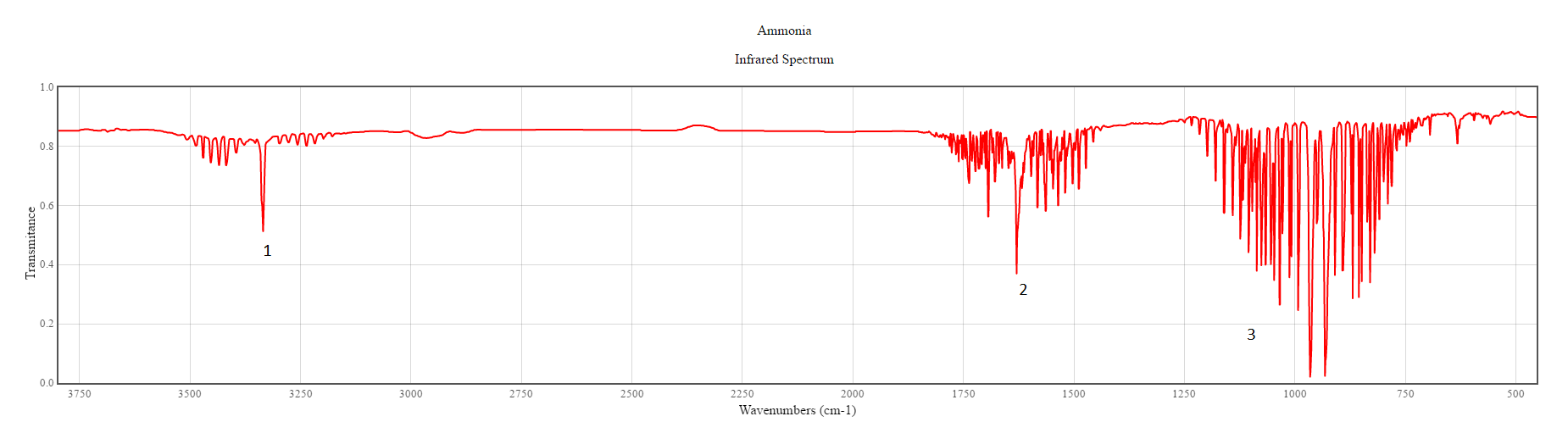
The literature value for IR spectrum of NH3 is shown below(2).The spectrum labelled 1 corresponds to the vibration mode 4 which is at a frequency around 3400 cm-1 and has a relatively weak signal. The spectrum labelled 2 corresponds to the vibration mode 2&3 which is at a frequency around 1700 cm-1 and has a relatively medium signal. The spectrum labelled 3 corresponds to the vibration mode 1 which has a very strong signal and at a frequency around 1000 cm-1
.
N2
N2 |
Log file :
The optimisation file is linked to here
Name:
Nirtrogen
Bond length:
1.092Å
Calculation method:
RB3LYP
Basis set:
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP):
-109.52412868 a.u.
Vibrations:
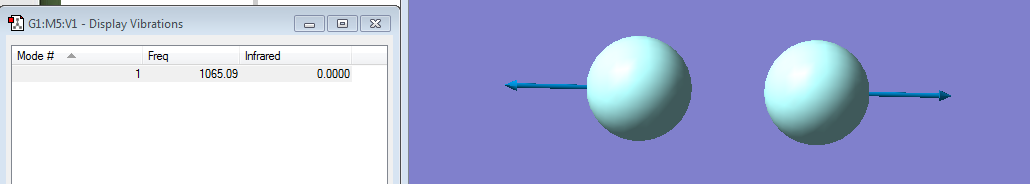
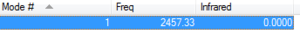
N2 is a diatomic molecule with symmertric bond.There is only one mode of vibration(3N-5)which is symmetrical stretching with frequency shown below
It is infra-red unreactive because there is no change in dipole moment when it absorbs infrared radiation and vibrating.
Point group:
D∞H
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401137D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2
H2 |
Log file :
The optimisation file is linked to here
Name:
Hydrogen
Bond length:
0.6Å
Calculation method:
RB3LYP
Basis set:
6-31G(d,p)
Vibrations:
H2 is a diatomic molecule with symmertric bond.There is only one mode of vibration(3N-5)which is symmetrical stretching with frequency shown below
It is infra-red unreactive because there is no change in dipole moment when it absorbs infrared radiation and vibrating.

Final energy E(RB3LYP):
-1.17853936 a.u.
Point group:
D∞H
Item table:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Reaction energies
Haber process:
This process describe how to manufacture ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas.
N2 + 3 H2 → 2 NH3
To achieve higher yield and rate of reaction, iron with potassium hydroxide added to it is used as catalyst and pressure is set at around 200 atm and a compromise temperature 400-450 celsius degree is used.
- E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
- 2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375 a.u.
- E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
- E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
- 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579074 a.u.=-146.48 kJ/mol
- The literature value is -92kJ/mol (3)
- The reaction energy is negative which indicates that the reaction is exothermic and releasing energy.This means gaseous reactants have higher energy so ammonia is the more stable one.
Molecule of own choice: F2
F2 |
Log file :
The optimisation file is liked to here
Name:
fluorine
Bond length:
1.16Å
Calculation method:
RB3LYP
Basis set:
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy:
-199.49825218 a.u.
Point group:
D∞H
Vibrations:
Fluorine is a symmetric diatomic molecule and by applying the 3N-5 rule it is supposed to have 1 mode of vibration which is stretching. There is no net change in dipole moment so it is infra-red unreactive
Item table:
Variable Old X -DE/DX Delta X Delta X Delta X New X
(Linear) (Quad) (Total)
R1 2.65093 0.00013 0.00000 0.00031 0.00031 2.65124
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.995024D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4028 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
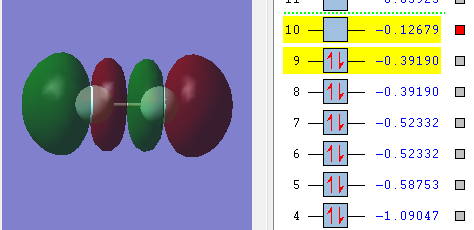
Molecular orbitals:
For fluorine molecule, the valence electrons are in the two 2s orbitals and 3 2p orbitals.
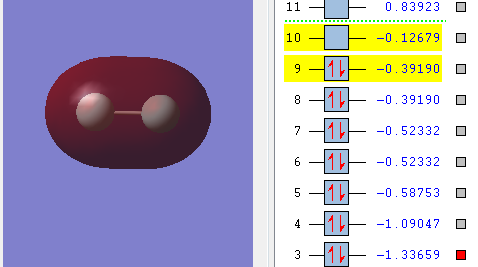
This diagram shows overlap of the 2s orbitals of the two F atom. The two orbitals are in phase and symmetric with respect to the inversion center and if the M.O. is rotated around the internuclear axis it stays unchanged. This means the 2s orbitals from both F atom linearly combine to give a bonding of σ-symmetry and symmetry label g. Also the electrons in 2s oribtals have the lowest energy among these valence electrons so it overlaps to give the M.O. with the lowest energy.(2σg)
This diagram shows overlap of the 2s orbitals of the two F atom. The two orbitals are not in phase and asymmetric with respect to the inversion center and if the M.O. is rotated around the internuclear axis 180 degree it stays unchaged. This means the 2s orbitals from both F atom linearly combine to give an anti-bonding of σ-symmetry and symmetry label u. (2σu*) This orbital is low in energy.
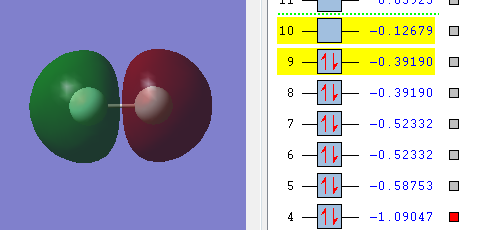
This diagram shows overlap of the 2pz orbitals of the two F atom. The two orbitals are in phase and symmetric with respect to the inversion center and if the M.O. is rotated around the internuclear axis 180 degree it stays unchange. This means the 2pz orbitals from both F atom linearly combine to give a bonding of σ-symmetry and symmetry label g. (3σg)
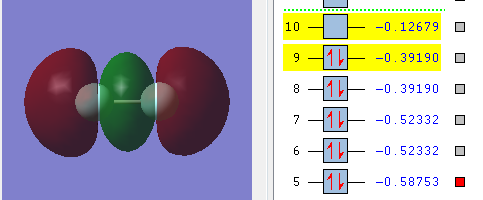
This diagram shows overlap of the 2py orbitals of the two F atom. The two orbitals are in phase and asymmetric with respect to the inversion center and if the M.O. is rotated around the internuclear axis 180 degree it changes sign. This means the 2py orbitals from both F atom combine to give a bonding of π-symmetry and symmetry label u. (1πu)
This diagram shows overlap of the 2pz orbitals of the two F atom. The two orbitals are not in phase and asymmetric with respect to the inversion center and if the M.O. is rotated around the internuclear axis 180 degree it stays unchanged. This means the 2pz orbitals from both F atom combine to give an anti-bonding of σ-symmetry and symmetry label u. (3σu*) These anti-bonding orbiatls are unoccupied so it is the LUMO
Charge distribution:
F2 is a diatomic molecule consists of the same type of element. The atoms in the F2 are identical so the charge distribution is going to be uniform and same for each atom.
Refrence:
1 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th ed. http://www.hbcpnetbase.com. Page 9-26. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
2 http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C7664417&Type=IR-SPEC&Index=1