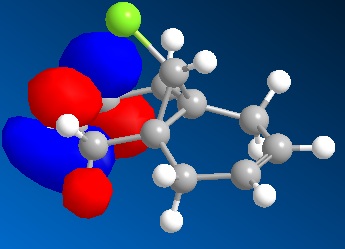
User:St908(module 1)
Method using Molecular Mechanics
The computational modelling operated by related Programs invokes classical machanics approach to solve chemical problem such as optimization of energy with suitable geometry of molecules. The total energy is the combination of stretch, bend, stretch bend, torsion, Non-1,4 VDW, 1,4 VDW and Dipole/Dipole. These components of energy are the function of adjustable parameter such as bond length, bond angle. In absence of quntum mechanics approach, the computer is able to run the calculation in seconds.
The Hydrogenation of Cyclopentadiene Dimer
Program: ChemBio 3D
Method: MM2 Minimization.
Compound 1(Exo cyclopentadiene dimer)
Exo cyclopentadiene dimer |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 109: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 1.2811 Bend: 20.5916 Stretch-Bend: -0.8384 Torsion: 7.6391 Non-1,4 VDW: -1.4066 1,4 VDW: 4.2410 Dipole/Dipole: 0.3771
Total Energy: 31.8848 kcal/mol
Compound 2(Endo cyclopentadiene dimer)
Endo cyclopentadiene dimer |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 103: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 1.2545 Bend: 20.8528 Stretch-Bend: -0.8343 Torsion: 9.5072 Non-1,4 VDW: -1.5216 1,4 VDW: 4.3013 Dipole/Dipole: 0.4457
Total Energy: 34.0056 kcal/mol
The exo dimer has energy 31.8848 kcal/mol which is 2.12 kcal/mol lower than endo dimer in terms of energy quantified by mechanical method. The two double bonds in exo product is more far apart than that in endo product in order to minimise the steric effect. In formation of these two dimer isomers, although exo dimer is the thermodynamic stable form, endo dimer is the major product for more favoured transition state. Therefore this reaction is kinetically controlled.
Compound 3(Hydrogenated dimer3)
Hydrogenated dimer |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 79: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 1.2862 Bend: 19.9637 Stretch-Bend: -0.8404 Torsion: 10.7161 Non-1,4 VDW: -1.2230 1,4 VDW: 5.6252 Dipole/Dipole: 0.1621
Total Energy: 35.6899 kcal/mol
Compound 4(Hydrogenated dimer4)
Hydrogenated dimer |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 59: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 1.0963 Bend: 14.5074 Stretch-Bend: -0.5493 Torsion: 12.4972 Non-1,4 VDW: -1.0507 1,4 VDW: 4.5124 Dipole/Dipole: 0.1407
Total Energy: 31.1540 kcal/mol
Hydrogenated dimer 4 is about 4.5 kcal/mol more stable than dimer 3 from the calculation. Energy of bending is the mojarity contribution of stabilising energy compared to the less stable form. At evaluated temperature with energy far higher than activation energy, the dimer 4 product dominates regardless of kinetic effect.
Stereochemistry of Nucleophilic additions to a pyridinium ring
Program: ChemBio3D
Methods: MM2, MOPAC(PM6)
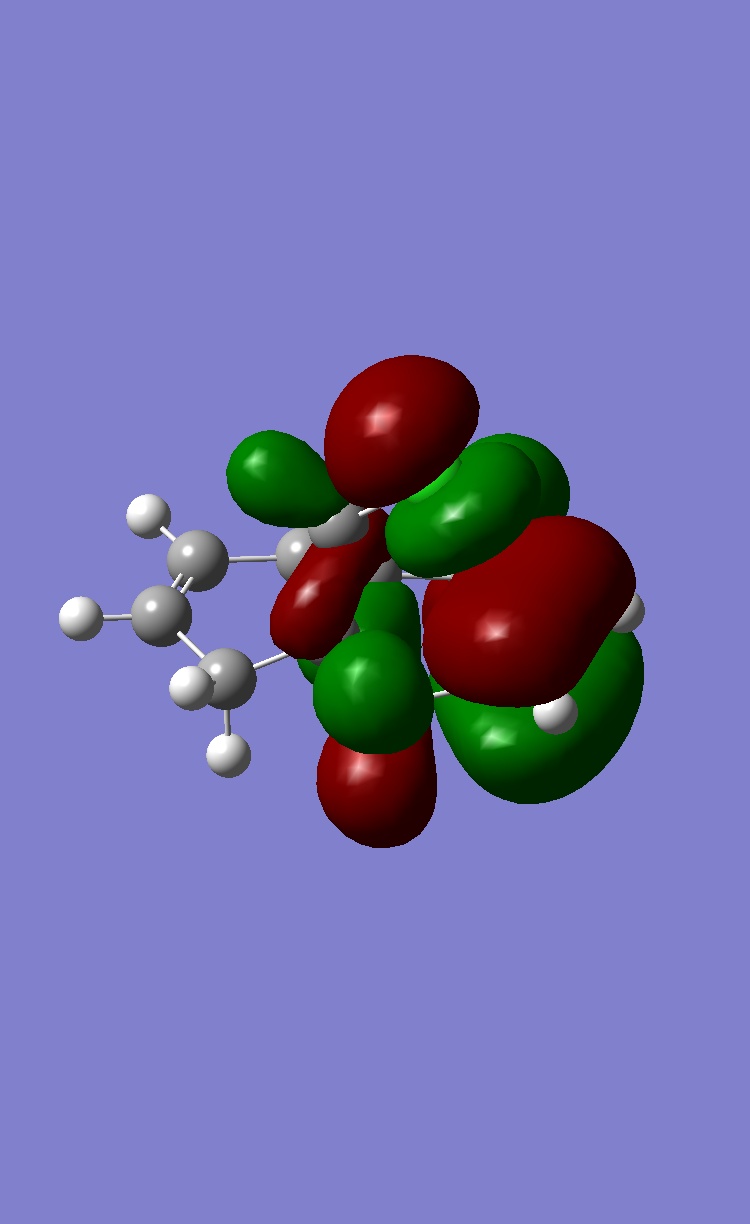
Compound 5&6(prolinol)
Pentahelicene |
MM2 Minimization------------
Pi System: 1 2 3 4 6 5 12 16 Warning: Some parameters are guessed (Quality = 1).
Iteration 203: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 2.0500 Bend: 14.2014 Stretch-Bend: 0.1341 Torsion: 5.1463 Non-1,4 VDW: -0.5697 1,4 VDW: 16.5291 Charge/Dipole: 9.6290 Dipole/Dipole: -3.9975
Total Energy: 43.1226 kcal/mol
Mopac Interface ------------
Model: structure 1
Mopac Job: AUX PM6 CHARGE=1 EF GNORM=0.100 GRAPH SHIFT=80 Finished @ RMS Gradient = 0.09672 (< 0.10000)
Heat of Formation = 93.90897 Kcal/Mol
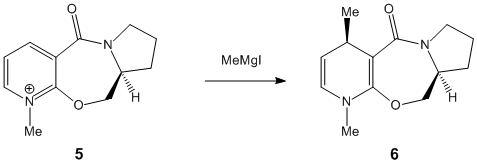
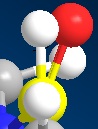 The angle of deviation between β-H and C=O(Hydrogen is in plane of aromatic ring)
The angle of deviation between β-H and C=O(Hydrogen is in plane of aromatic ring)
Minimization of energy is performed using MM2 followed by Moapac interface. Since MM2 has bug in optimization of energy and geometry influenced by postively charged species, MOPAC is introduced to achieve more accurate prediction with electronic calculation and minimise the effect caused by MM2 problem. The optimised model with lowest energy(43.1226kcal/mol) is shown above. With 3D model help, the acidic β hydrogen on pyridinium ring and carbonyl group do not lie on the plane of aromatic ring but slight distortion to the front for carbonyl group. In steric aspect, the oxygen might hinder the attack by nucleophile in transition state. The experimental results shows that methyl group sits on the front face of the ring as shown in compound 6[1] This phenomenon attribute to electronic effect that Mg in grignard reactant tends to bound to electronegative oxygen in the transition state. This mechanism determines the position of the Methyl subsituent by largely dominating the steric effect. In thermodynamic aspects, these two possible conformations of product are similar in energy calculated by MM2 optimization. Therefore this reaction is kinetically controlled reaction which electronic effect dominates.
Compound 7&8(NAD+)
Pentahelicene |
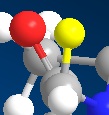 TheC3</sbu>-C=O bond distorted from plane of aromatic ring, yellow atoms is the β-hydrogen.
TheC3</sbu>-C=O bond distorted from plane of aromatic ring, yellow atoms is the β-hydrogen.
MM2 Minimization------------
Pi System: 18 19 20 12 17 6 1 2 3 5 4 7 11 8 10 9 15 22 Warning: Some parameters are guessed (Quality = 1).
Iteration 207: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 3.7757 Bend: 11.2663 Stretch-Bend: 0.3866 Torsion: 11.1014 Non-1,4 VDW: 3.6353 1,4 VDW: 29.3761 Charge/Dipole: 9.0477 Dipole/Dipole: -4.8779
Total Energy: 63.7110 kcal/mol
Mopac Interface ------------
Model: lactam 1
Mopac Job: AUX PM6 CHARGE=1 EF GNORM=0.100 GRAPH SHIFT=80 Finished @ RMS Gradient = 0.09713 (< 0.10000) Heat of Formation = 156.19563 Kcal/Mol
As positive formal charge also exist, MOPAC is used for further optimization. From the most favourable conformation of reactant, we can predict that amine could attack to the opposite face of C=O on lactam with less steric effect. This prediction coincide with the literal experimental results[2]
If we compare the optimized energy of these two possible conformational product, as shown below:
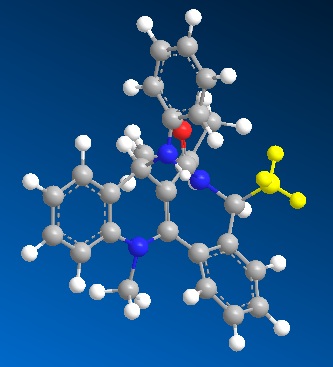 Literature conformation, MM2 energy: 77.6781 kcal/mol
Literature conformation, MM2 energy: 77.6781 kcal/mol
 Amine attack at same face of C=O, MM2 energy: 80.5456 kcal/mol
Amine attack at same face of C=O, MM2 energy: 80.5456 kcal/mol
The possible resultant conformation of product shown above possess slightly higher energy than the experimental product. This reaction is not only kinetically controlled, probably also infuenced by thermodynamic conformation. If the methyl group on the lactam swap the position with adjacent hydrogen on the same carbon it attaches to, both of the conformations becomes even more stable(about 20 kcal/mol lower) and similar in energy(both around 50kcal/mol). But change of conformation to the more stable form require certain amount of activation energy. according to the X-ray structure study, the change of conformation predicted by MM2 is not thermally accessible. Therefore reaction is also thermodynamically controlled but its contribution is not as important as kinetic factor.
Stereochemistry and Reactivity of an Intermediate in the Synthesis of Taxol
Programs:ChemBio 3D Methods: MM2 MMFF94
Compound 9(intermediate of total sythesis of taxol)
Pentahelicene |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 199: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 3.0685 Bend: 19.1710 Stretch-Bend: 0.2771 Torsion: 20.4337 Non-1,4 VDW: 0.2916 1,4 VDW: 14.9224 Dipole/Dipole: 0.0355
Total Energy: 58.2000 kcal/mol
Calculation completed
Iteration 81: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm
Final Energy: 81.3249 kcal/mol
Compound 10(intermediate of total sythesis of taxol)
Pentahelicene |
MM2 Minimization------------
Note: All parameters used are finalized (Quality = 4).
Iteration 298: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 2.6736 Bend: 13.3462 Stretch-Bend: 0.3291 Torsion: 19.9511 Non-1,4 VDW: -0.0786 1,4 VDW: 13.4436 Dipole/Dipole: 0.2921
Total Energy: 49.9571 kcal/mol
MMFF94 Minimization------------
Iteration 241: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm
Final Energy: 66.6298 kcal/mol
The compound 10 has lower energy optimised by both MM2 and MMFF94 compared to compound 9. This is because in compound 9, the C=O is closer to the bridged iso propyl group than compound 10 where the steric hindrance is released. Thermodynamically, compound 10 is more favourable intermediate. The magnitude of the energy produced by MMFF94 is higher than produced from MM2.
Modelling Using Semi-empirical Molecular Orbital Theory
Instead of using classical mechanical approach, to refine the modelling, quantum mechanics is introduced to account the electronic interaction.
Regioselective Addition of Dichlorocarbene
Program: ChemBio3D
Methods: MM2, MOPAC(PM6), Guassian interface(B3LYP)
Part 1
Compound 12
Pentahelicene |
MM2 Minimization------------
Warning: Some parameters are guessed (Quality = 1).
Iteration 98: Minimization terminated normally because the gradient norm is less than the minimum gradient norm Stretch: 0.6129 Bend: 4.8462 Stretch-Bend: 0.0415 Torsion: 7.5971 Non-1,4 VDW: -1.0849 1,4 VDW: 5.7885 Dipole/Dipole: 0.1113
Total Energy: 17.9126 kcal/mol
Mopac Interface ------------
Model: MM2
Mopac Job: AUX PM6 CHARGE=0 EF GNORM=0.100 GRAPH SHIFT=80 Finished @ RMS Gradient = 0.09750 (< 0.10000) Heat of Formation = 19.74037 Kcal/Mol
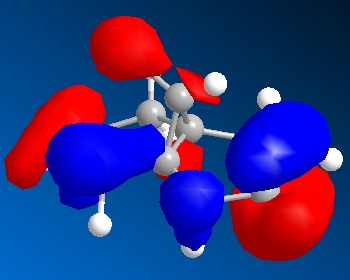
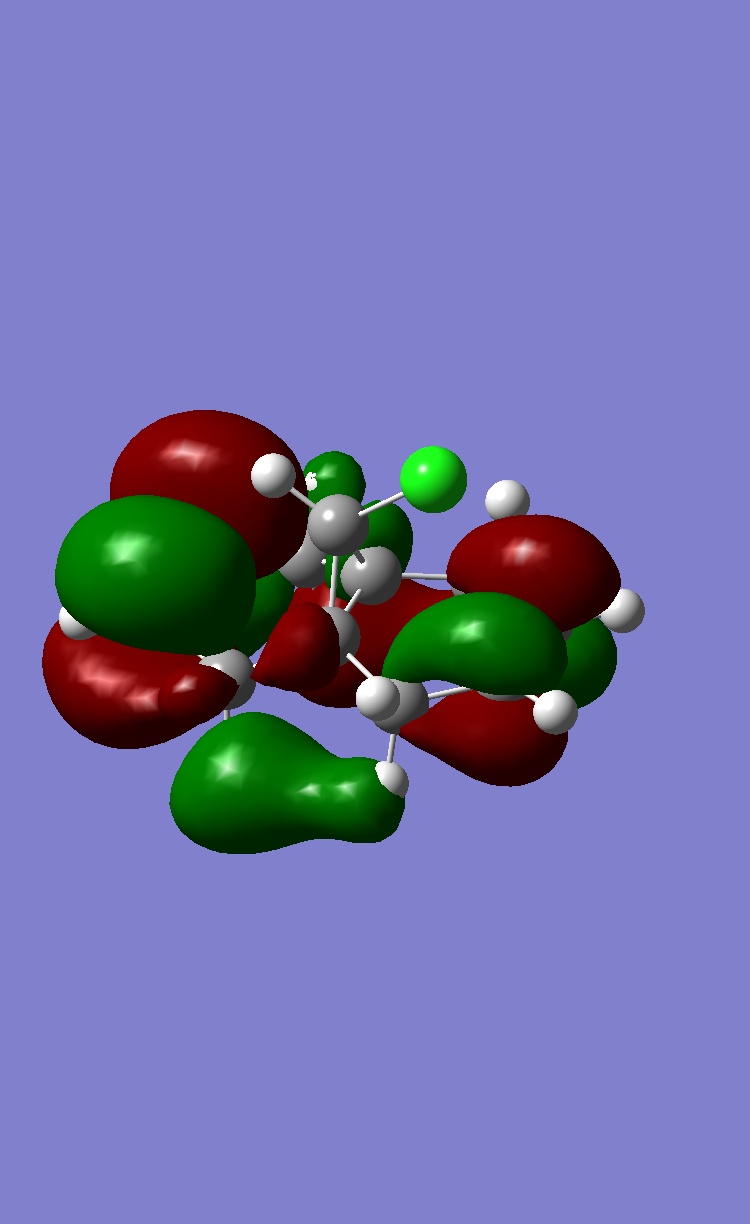
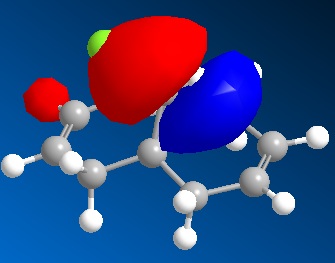
MOPAC provides information of molecular orbitals, the four important MOs that have influence on chemical reactivity are shown below:
Two double bonds sitting on opposite end of the ring are denoted as endo and exo to C-Cl bond. The exo C=C is in HOMO-1 while endo C=C is in HOMO. If C=C is acting as eletron rich species in the reaction, higher energy of π orbital enhance the reacitivity of electrophilic reaction. Therefore endo C=C is more reactive towards electrophilic reagent such as dichlorocarbene or peracid.
In experiment, the endo double bond is more reactive towards electrophile than exo double bond. The steric effect barely determine the selectivity as the steric induced by this conformation is almost indistinguishable. By examining the frontier orbitals, the C-Cl σ* orbital appeared in HOMO+1 MO is low in energy and largely on C atom due to relatively electronegative Cl atom. These property enables σ* orbital to interact with filled π orbital of exo double bond in anti-periplanar fasion. Therefore, the electron density of π bond is reduced and become less nucleophilic compared to endo double bond. We can conclude that the orbital interaction is the main contribution to the selectivity in the reaction.
Not only the reactivity changes, the geometry is also distorted for stablizing the total energy. The energy of π orbital is lowered thus less susceptible to be attack by electrophile.
| C=C Bond length(Å) | C4-CH2-(C=C)bond angle | |
|---|---|---|
| Exo C=C | 1.3355 | 114.6854 |
| Endo C=C | 1.3319 | 115.8481 |
part 2
Compound 12
Energy minimisation:
Gaussian Interface ------------
Model: MOPAC
1) Gaussian Job: # RB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) Opt Test Finished @ Energy = -556696.69 Kcal/Mol (-887.153374 Hartrees)
| C=C (1) | C=C (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| reduced mass(a.u) | 6.3540 | 6.3838 |
| frc constats | 11.4076 | 11.6240 |
| IR intensity | 4.3021 | 2.7203 |
| frequency(cm-1) | 1745.6180 | 1757.9704 |
exo Hydrogenated compound 12
Pentahelicene |
Gaussian Interface ------------
Model: MOPAC
1) Gaussian Job: # RB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) Opt Test Finished @ Energy = -888.3001 Hartrees
| endo C=C | |
|---|---|
| reduced mass(a.u) | 6.4062 |
| frc constats | 11.6557 |
| IR intensity | 3.3191 |
| frequency(cm-1) | 1757.2908 |
The optimized energy and related frequency for original and hydrogenated versions are shown above. In the table of original version, one C=C has lower frequency than the other C=C. By comparing these frequencies with hyrogenated data, the concidence of higher frequency 1757cm-1 indicate that endo C=C has higher vib freq than exo C=C. The decrease in reduced mass and force constant for exo implies the lengthening of C=C bond and decrease in electron density. As mentioned above, this is attributed to weak overlap and donation of electron density from C=C π orbital to C-Cl σ* orbital. However, this overlap is not observed in hydrogenated version because of absence of π bond and correct symmetry. The energy of hydrogenated molecules is 1 Hartree more stable than original one which the energy difference is smaller than I expected. If my expectation is reasonable, the stablizing of original molecule is due to the same effect mentioned above thus the total energy get stablized.
Improvement can be made to this question if we analyse the molecule which C-Cl is replaced by C-H. This can tell the effect made by Chlorine atom more explicitly whether Cl stablise the exo C=C or destablise the endo C=C.
Structure based Mini project using DFT-based Molecular orbital methods
Programs: ChemBio3D, Gauss View
methods: MM2, MOPAC, Gaussian interface(Optimisation of energy and 13C and 1H NMR)
Reaction Title:
- ↑ A. G. Shultz, L. Flood and J. P. Springer, J. Org. Chemistry, 1986, 51, 838DOI:10.1021/jo00356a016
- ↑ S. Leleu, C.; Papamicael, F. Marsais, G. Dupas, V.; Levacher, Vincent. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2004, 15, 3919-3928DOI:j.tetasy.2004.11.004