User:Mw4015
Introduction
The program Gassview is used to build and analysis the information of NH3 molecules and ClF molecules. It gives all the information of molecular orbitals and vibrations which is helpful when analyzing the reactions.
NH3 molecule
general information
N-H bond distance=1.01798 H-N-H bond angle=109.47122 Calculation type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set:6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP):-56.55776873 RMS gradient Norm:0.00000485 Dipole moment:1.8466 Point group:C3V
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
optimized file link File:MENGYUANWANG-NH3 OPTF POP.LOG
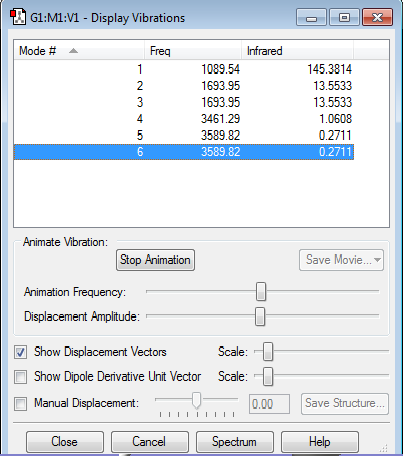
Vibrations
Questions
1.how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 3*4-6=6 modes from 3N-6 rule. 2.which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Modes 2 and 3 with frequency of 1693.95, modes 5 and 6 with frequency of 3589.82 are degenerate. 3.which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 123 are bending, 456 are stretching. 4.which mode is highly symmetric? 4 and 1 are highly symmetric. 5.one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1 is umbrella mode. 6.how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 bands would see in an experimental-spectrum although there should be 4 peaks show on the spectrum however other 456 are symmetric and show weak signals on spectrum so only two vibrational modes change dipole moments which give high peaks.
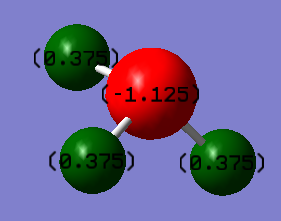
Charge Distribution
Hydrogen:+0.375 Nitrogen:-1.125 positive charge is expected on hydrogen due to its low electronegativity, Nitrogen has high electronegativity and attract electron pairs away from hydrogen, so its negative.
N2 and H2
N2 General information
Bond length:1.092 Bond angle: 180 Calculation type:FREQ Calculation method :RB3LYP BasisSet:6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP):-109.52359111 RMS Gradient Norm:0.02473091 Point Group: D*H
N2 |
optimized file link File:MENGYUANWANG N2.LOG
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
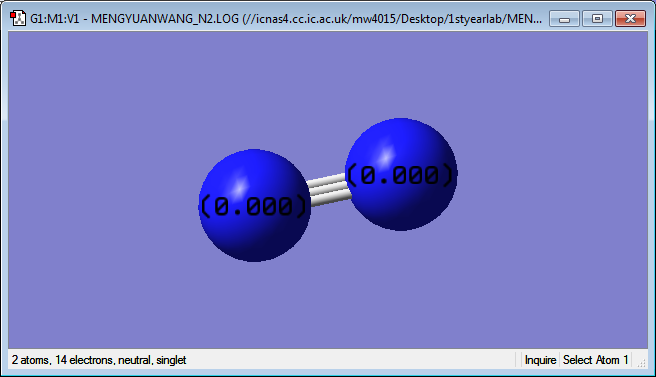
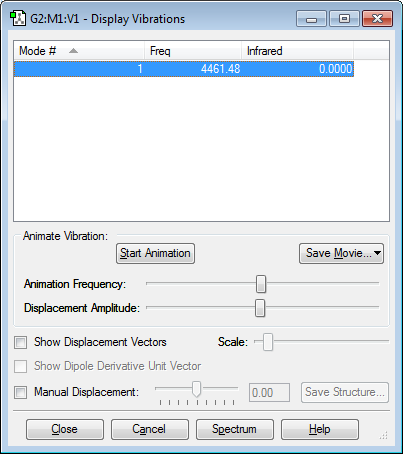
Vibrations
Only one mode shown on picture because there is no change in dipole moment.
Charge Distribution
Charge of Ns are 0 because they have same electronegativity.
H2 general information
H2 Bond length: 0.743 Bond angle:180 Calculation Type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set:6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP)=-1.17853930 RMS Gradient Norm=0.00012170 Point Group: D*H
H2 |
File link is File:MENGYUANWANG H2.LOG
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
There is no dipole moment shown on the molecule so only one value shown on picture.
Charge Distribution
Charge on both hydrogen atoms are zero due to the same electronegativity.
energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873au 2*E(NH3)=-113.115537au E(N2)=-109.52359111au E(H2)=-1.17853930au 3*E(H2)=-3.5356179au ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0563281au=-147.89kJmol^-1 This reaction is exothermic and the energy level of NH3 is lower than the engery level of N2 and H2. Literature value=-92.4 kJ/mol[1]The value calculated by the computer is not same as the literature value which shows that the computer is biased.
Literature value: [1]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haber_process
Project molecule: ClF
general information
bond legth:1.66434 Bond angle:180 Calculation type:FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP):-559.94269578 RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00014211 Dipole Moment: 0.9787 Point Group: C*V
ClF |
optimised file link:File:MENGYUANWANG CLF.LOG
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
One vibration mode is shown on picture due to linear structure and only two atoms on it, the dipole moment changes with vibration because of the difference in electronegativity.
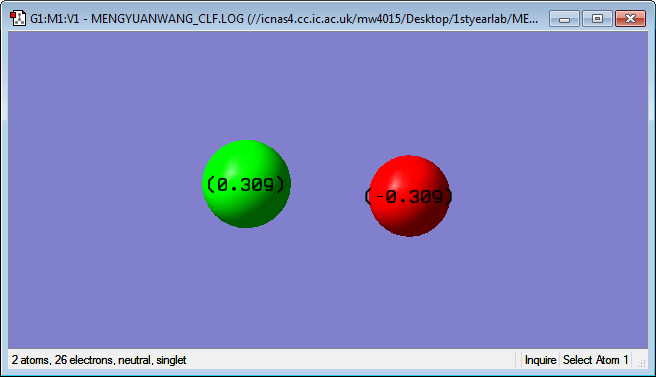
Charge distribution
Cl has a charge of o.309 F has a charge of -0.309 F has a strong electronegativity and It is a small atom so it attract bonded pair of electrons more than Cl. This makes F more negative and Cl becomes more positive.
MO Analysis
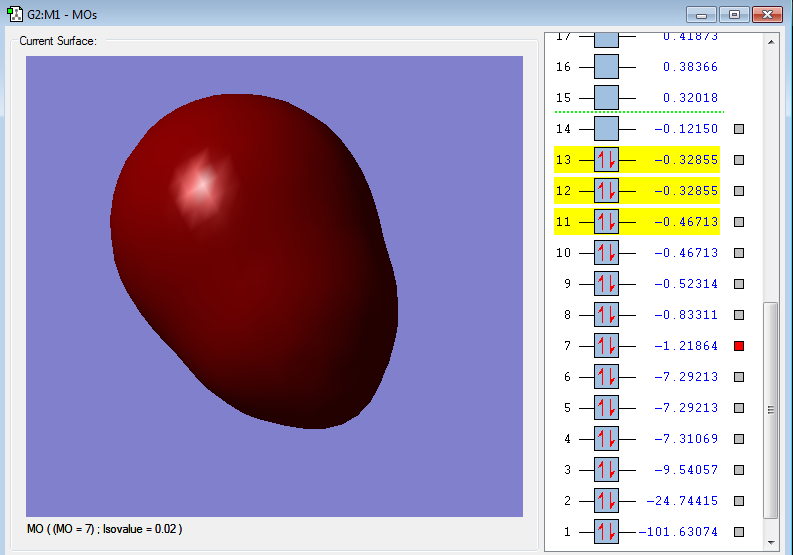
2s-3s σg bonding orbital
2s orbital in F and 3s orbital in Cl
Energy: -1.21864au
when 2s orbital in F forms bond with 3s in Cl the bonding energy is lower than both 2s and 3s.
2s orbital in F has a lower energy so the 2s energy in F is closer to bonding energy which contribute more with bonding.
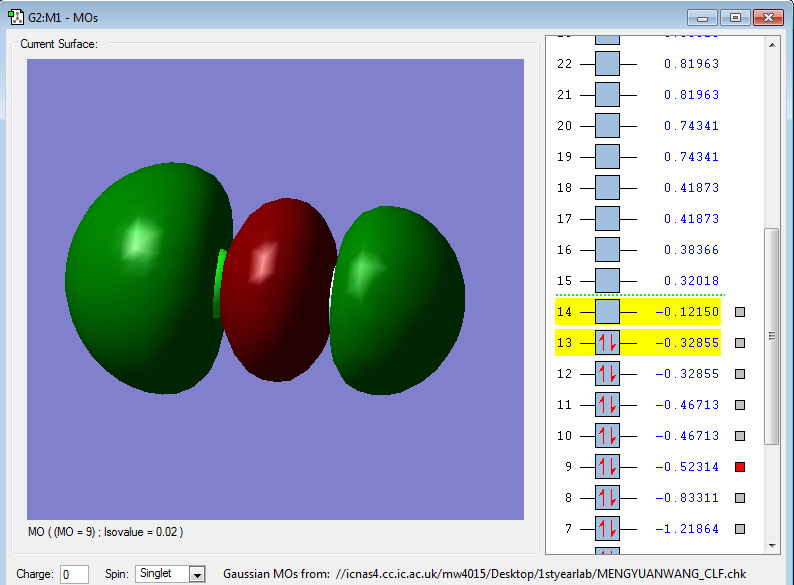
2pz-3pz σg bonding orbital
2pz orbital in F and 3pz orbital in Cl
Energy: -0.52326 a.u.
2pz in F forms bond with 3pz in Cl the bonding energy is lower than both 2pz and 3pz.
2pz orbital in F has a lower energy so the 2pz energy in F is closer to bonding energy which contribute more with bonding.
2p-3p πu bonding orbital
2py orbital in F and 3py orbital in Cl
Energy: -0.46728 a.u.
2py in F forms bond with 3py in Cl the bonding energy is lower than both 2p7 and 3p7.
2py orbital in F has a lower energy so the 2py energy in F is closer to bonding energy which contribute more with bonding.
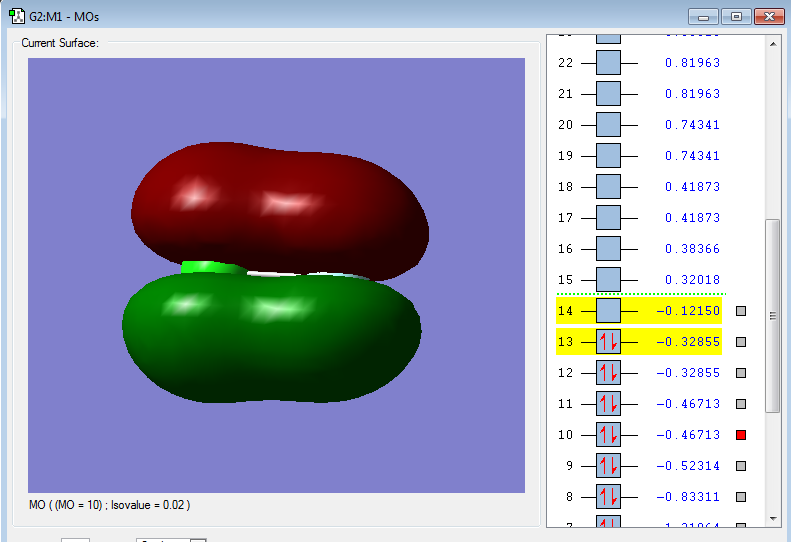
2p-3p σu anti-bonding orbital
2px orbital in F and 3px of Cl
Energy: -0.12121 a.u.
This molecular orbital is the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital)
The 3p orbital of Cl has higher energy level and it is much closer to the energy level of anti-bonding orbital so Cl will have more contribution to the anti- bonding orbital.
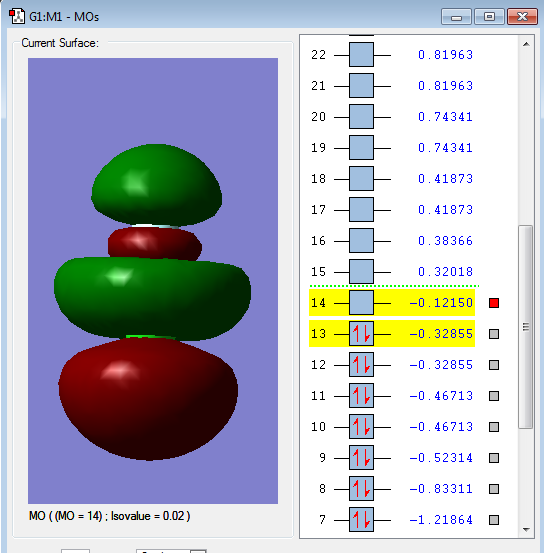
2p-3p πg antibonding orbital
2py orbital in F and 3py orbital in Cl
Energy: -0.32847 a.u.
This molecular orbital is the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital)
The 3p orbital of Cl has higher energy level and it is much closer to the energy level of anti-bonding orbital.