User:Hg3117
NH3 molecule
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy (E(RB3LYP)): -56.55776873 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Ammonia Molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
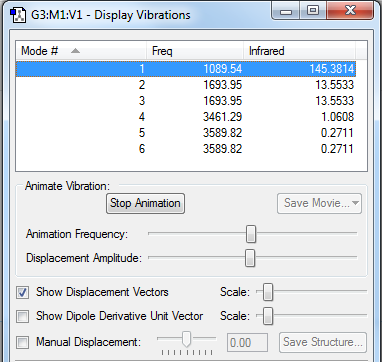
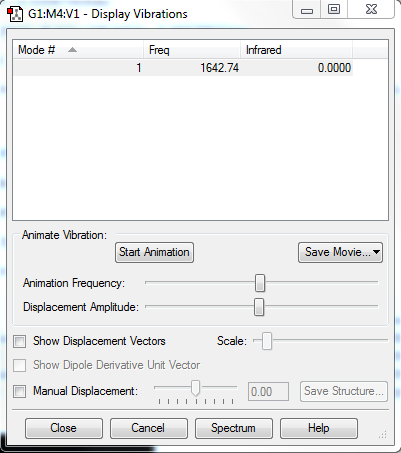
Vibrational Modes
Expect 6 modes from the 3N-6 rule
Nodes number 2 and 3 are degenerate, and modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
Bending vibrations:1, 2, 3 Stretching Vibrations: 4,5,6
Mode 4 is highly symmetric and there is an umbrella mode which is mode 1
In the IR spectrum you should expect to see 2 bands. 2 of the degenerate stretches and one other bend modes cause no overall change in dipole moment so wont show on the spectrum.
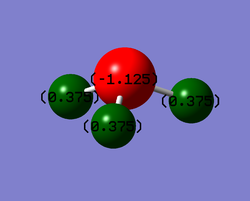
Charges
You would expect Nitrogen to have the negative charge as it is the more electronegative atom so draws electron density towards itself.
H2
Optimisation
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936au
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Hydrogen Molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
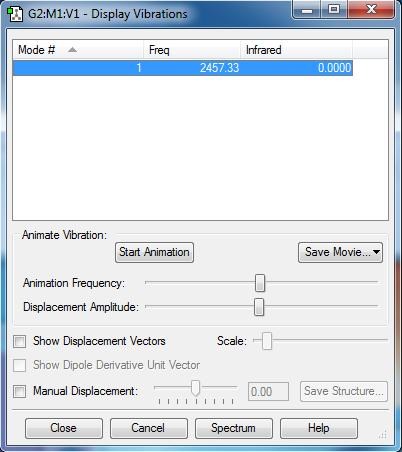
Vibrational Modes
It's a linear molecule so the 3N-5 rule is used, Expext 1 vibrational mode.
The mode is a stretch, and there's no dipole moment so no peaks will show up on the IR spectrum.
Charges
N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 au
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Nitrogen Molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibrational Modes
Only 1 vibrational mode, the mode is a stretch. Linear so use the 3N-5 Rule, therefore only one mode expected.
No dipole moment so no bands would be visible on spectrum.
Charges
Energy
E(NH3)= -56.55776873au
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375au
E(N2)= -109.52412868au
E(H2)= -1.17853936au
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808au
dE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074au
in kj/mol: -146.479KJ/mol
The more stable side of the reaction is the ammonia product as there is a decreases in energy so NH3 molecule has less E.
Literature Energy Change Value -45.8 KJ/mol
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haber_process
O2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Energy E(RB3LYP): -150.25742434au
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Oxygen Molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibrational Modes
Will see no bands in the IR spectrum as there is only one vibrational mode which is a stretch and it causes no change in dipole moment.
Charges
Molecular Orbitals
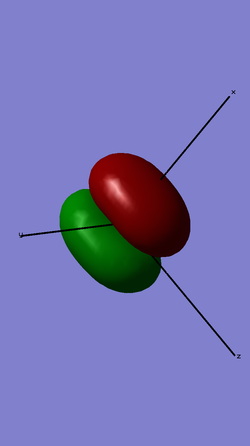 This shows the bonding molecular orbital made up of 2 pi 2px orbitals overlapping.
This shows the bonding molecular orbital made up of 2 pi 2px orbitals overlapping.
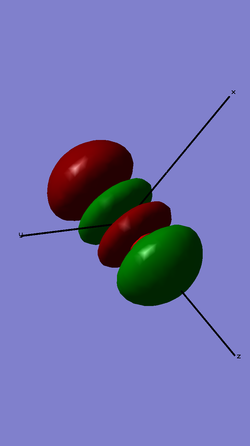 This is an anti-bonding molecular orbital, made up of the 2 pi2pz atomic orbitals out of phase.
This is an anti-bonding molecular orbital, made up of the 2 pi2pz atomic orbitals out of phase.
 This is the HOMO as all the molecular orbitals with higher energy contain no electrons. It is made up of anti-bonding pi 2px atomic orbitals.
This is the HOMO as all the molecular orbitals with higher energy contain no electrons. It is made up of anti-bonding pi 2px atomic orbitals.
 This is the LUMO, the lowest energy molecular orbital which contains no electrons. It's the anti-bonding molecular orbital made up of pi 2py atomic orbitals on the 2 O atoms.
This is the LUMO, the lowest energy molecular orbital which contains no electrons. It's the anti-bonding molecular orbital made up of pi 2py atomic orbitals on the 2 O atoms.
 This is the sigma 2pz MO made of the oxygen atoms bonding pi 2pz atomic orbitals.
This is the sigma 2pz MO made of the oxygen atoms bonding pi 2pz atomic orbitals.