User:Gd1118
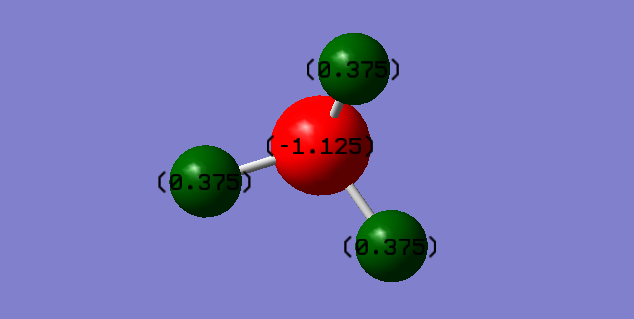
NH3
Basic information
| Molecule name | Ammonia |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) | -56.557769 |
| the point group of NH3 | C3V |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000014 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000009 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
| Mode | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 1089 | 1694 | 1694 | 3461 | 3590 | 3590 |
| Symmetry | A1 | E | E | A1 | E | E |
| Intensity | 145.4 | 14.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
According to 3N-6 rule, there are 6 modes, and 4 of them are degenerate. Mode 1,2,3 are "bending" vibrations and mode 4,5,6 are "bond stretch" vibrations. Mode 1 and 4 are highly symmetric, with mode 1 being the "umbrella" mode. Four bands are expected to be seen in the experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
Charge Distribution
The charge fits what is expected to see as nitrogen is the most electronegative atom so its sign should be negative and largest, and the overall charge is zero which agrees with the fact that the molecule is neutral.
N2
Basic information
| Molecule name | Nitrogen |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) | -109.524129 |
| the point group of N2 | D∞H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 2457 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity | 0 |
Charge Distribution
Comparison with N2 in crystal
In DEFHAA, NN bond length is 1.096Å, which is slightly smaller than the computational value of 1.106Å. This means in crystal NN triple bond is slightly compressed. This indicates that the interaction is weaker between the crystal and nitrogen in comparison with the Van der Waal's interaction between two nitrogen molecules because in computer, there are only nitrogen molecules, while it is the crystal and nitrogen in experiment. [[1]]
H2
Basic information
| Molecule name | Hydrogen |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) | -1.178539 |
| the point group of H2 | D∞H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
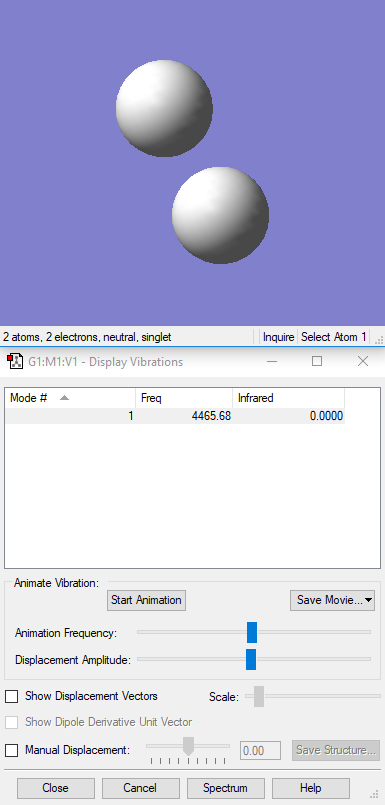
Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 4466 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity | 0 |
Charge Distribution
Reaction energy of formation of NH3
| E(NH3)= -56.557769 au |
| 2*E(NH3)= -113.115538 au |
| E(N2)= -109.524129 au |
| E(H2)= -1.178539 au |
| 3*E(H2)= -3.535617 au |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.055792 au |
| ΔE=-146.48190716 kJ/mol |
NF3
Basic information
| Molecule name | Nitrogen trifluoride |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Bond length | 1.38Å |
| Bond angle | 102° |
| final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) | -354.071311 |
| the point group of NH3 | C3V |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000164 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000108 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000612 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000296 0.001200 YES
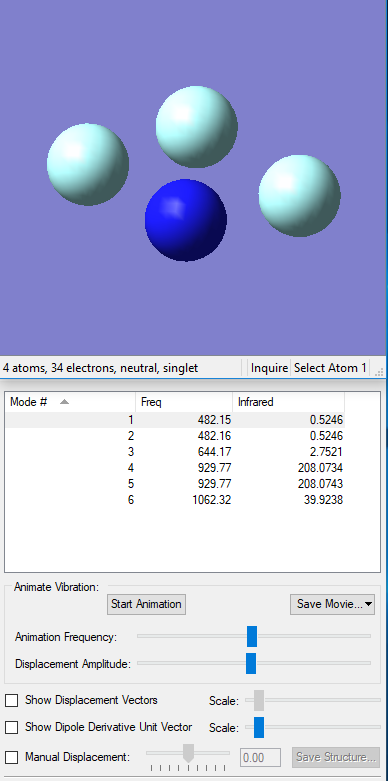
Vibrations
| Mode | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 482 | 482 | 644 | 930 | 930 | 1062 |
| Symmetry | E | A1 | A1 | E | A1 | A1 |
| Intensity | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 208.0 | 208.0 | 39.9 |
According to 3N-6 rule, there are 6 modes, and 4 of them are degenerate. Mode 1,2,3 are "bending" vibrations and mode 4,5,6 are "bond stretch" vibrations. Mode 3 and 6 are highly symmetric, with mode 3 being the "umbrella" mode. Four bands are expected to be seen in the experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
Charge Distribution
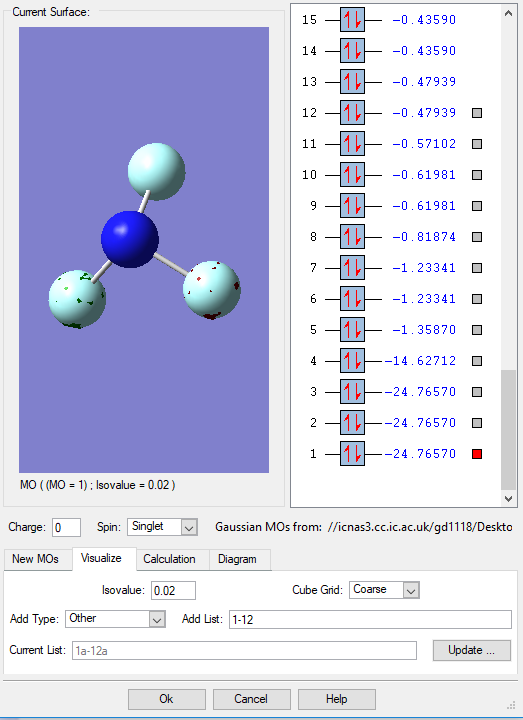
Molecular Orbital
F2
Basic information
| Molecule name | Fluorine | ||
| Calculation method | B3LYP | ||
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) | ||
| final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au) | -199.498252 | the point group of H2 | D∞H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 1065 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity | 0 |
Reaction energy of formation of NF3
| E(NF3)= -354.071311 au |
| 2*E(NF3)= -708.142622 au |
| E(N2)= -109.524129 au |
| E(F2)= -199.498252 au |
| 3*E(F2)= -598.494756 au |
| ΔE=2*E(NF3)-[E(N2)+3*E(F2)]= -0.123737 au |
ΔE= -324.8715182kJ/mol
MarkingNote: All grades and comments are provisional and subject to change until your grades are officially returned via blackboard. Please do not contact anyone about anything to do with the marking of this lab until you have received your grade from blackboard. Wiki structure and presentation 1/1Is your wiki page clear and easy to follow, with consistent formatting? YES Do you effectively use tables, figures and subheadings to communicate your work? YES - Good subheadings, well done! NH3 0/1Have you completed the calculation and given a link to the file? No - you have not linked directly to the .log file as required. Have you included summary and item tables in your wiki? YES Have you included a 3d jmol file or an image of the finished structure? YES Have you included the bond lengths and angles asked for? YES Have you included the “display vibrations” table? YES Have you added a table to your wiki listing the wavenumber and intensity of each vibration? YES Did you do the optional extra of adding images of the vibrations? No Have you included answers to the questions about vibrations and charges in the lab script? YES - most answers are correct however the are only 2 visible peaks in the spectra of NH3, due to the low intensity of the other 2 peaks. (See infrared column oin vibrations table.) N2 and H2 0/0.5Have you completed the calculations and included all relevant information? (summary, item table, structural information, jmol image, vibrations and charges) No - you have not linked directly to the .log file as required. Crystal structure comparison 0.5/0.5Have you included a link to a structure from the CCDC that includes a coordinated N2 or H2 molecule? YES Have you compared your optimised bond distance to the crystal structure bond distance? YES Haber-Bosch reaction energy calculation 0.5/1Have you correctly calculated the energies asked for? ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] YES Have you reported your answers to the correct number of decimal places? No - you should report to a maximum of 1 d.p for kj mol-1 Do your energies have the correct +/- sign? YES Have you answered the question, Identify which is more stable the gaseous reactants or the ammonia product? No Your choice of small molecule 1/5Have you completed the calculation and included all relevant information? YES But you didn't link directly to the log file. Have you added information about MOs and charges on atoms? You have included two basic images with no analysis in words of the MOs or charges. Independence 0.5/1If you have finished everything else and have spare time in the lab you could: Check one of your results against the literature, or Do an extra calculation on another small molecule, or Do some deeper analysis on your results so far YES - you did an extra energy calculation, and calculated an extra small molecule well done! You would have got the extra 0.5 for including links to the log files and giveing the energy value to the correct number of d.p. |