Tty115
Tty115
NH3
Summary
Molecule: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient: 0.05399560 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to NH3 Molecule
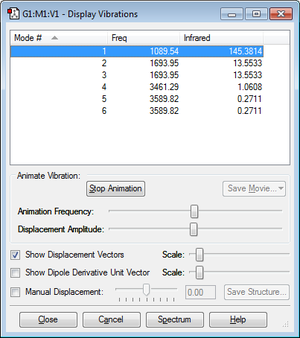
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2,3 and 5,6
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Vibration modes 1,2,3 are "bending" vibrations and modes 4,5,6 are "bond stretch" vibrations
which mode is highly symmetric? Vibration modes 1 and 4.
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? Vibration mode 1
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 Bands. There are 4 degenerate modes giving four different peaks. But modes 4,5,6 have intensities too low therefore two of the peaks would not appear on the spectrum, hence only 2 bands would be seen.
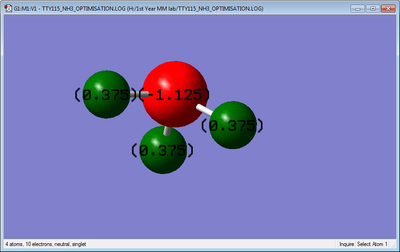
Charge Distribution
N-Atom: -1.125C
H-Atom: 0.375C
We'd expect the N atom to be negative as it is more electronegative than H, and therefore H should be positive.
N2 optimisation
Summary
Molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient:0.02473091 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to N2 Molecule
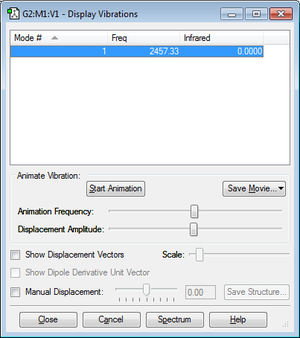
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? N=2, therefore 1 mode
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Only one mode therefore no degenerate modes
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?Mode 1 is a stretching mode.
Which mode is highly symmetric? Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum? 0 due to no change in dipole moment.
Charge Distribution
N-Atom: 0.000C
N-Atom: 0.000C
Neutral charge expected on both atoms as there is no difference in electronegativity.
H2 optimisation
Summary
Molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient:0.09719500
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to H2 Molecule

How many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? N=2, therefore 1 mode
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Only one mode therefore no degenerate modes
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?Mode 1 is a stretching mode.
Which mode is highly symmetric? Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum? 0 due to no change in dipole moment.
Charge distribution
H-Atom: 0.000C
H-Atom: 0.000C
Neutral charge expected on both atoms as there is no difference in electronegativity.
Haber-Bosch Reaction Energy Calculation
Energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3 can be determined:
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.47784060 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u.
ΔE = -146.48 kJ/mol
Therefore the energy for converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia gas is -146.48 kJ/mol. Reaction is exothermic meaning the product is more stable as it is lower in energy therefore the ammonia product is more stable.
Literature value of the Haber-Bosch Reaction is -92.44 kJ/mol. [1]
- ↑ Max Appl "Ammonia" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_143.pub2
ClF
Summary
Molecule: ClF
Calculation Method: RB3lYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
RMS Gradient: 0.03767912
Point Group: C*V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES
ClF molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to ClF Molecule
Vibration Modes
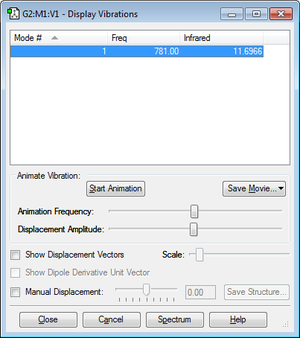
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? N=2, therefore 1 mode.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Only 1 mode therefore no degenerate modes.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Mode 1 is stretching.
Which mode is highly symmetric? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ClF? 1
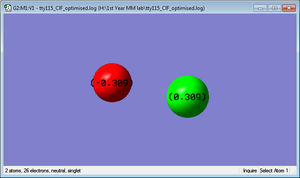
Charge Distribution
Cl-Atom : 0.309C
F-Atom : -0.309C
We would expect too see a negative charge on F as it is more electronegative than Cl
Energy for the reaction of Cl2 + F2 → 2ClF
E(Cl2) = -920.34853296 a.u.
E(F2) = -199.42620785 a.u.
E(ClF) = -559.94269578 a.u.
2×E(ClF) = -1119.885392 a.u.
ΔE = [2×E(ClF)]-[E(Cl2) + E(F2)]
ΔE = -0.11065119 a.u.
ΔE = -290.51 kJ/mol
The reaction is exothermic meaning the product ClF is more stable as it is lower in energy, therefore the equation favours the ClF product.
Molecule Orbitals
Electronic configuration of Cl: 1s22s22p63s23p5
Electronic configuration of F: 1s22s22p5
The first six occupied orbitals are all Atomic orbitals(AO), Orbitals 4,5 and 6 all have energies of around -7.30 a.u., relatively deep in energy.

and therefore they must be 2p orbitals in Cl, as there are three of them and they don't contribute to Molecular orbitals, as shown on the right.
The diagrams below shows the 7th and 8th MO that are occupied; these represent the 3s-2s sigma occupied MO(-1.21864 a.u.) and 3s-2s sigma antibonding occupied MO(-0.83311 a.u.) respectively.The occupied antibonding orbital is higher in energy

The diagrams below show the 3p-2p MOs in ClF that are all occupied. There are two different energies, showing that there are two different types of interaction, sigma and pi. 3p-2p sigma MO has energy of -0.52314 a.u. while the two degenerate 3p-2p pi MOs have energies of -0.46713 a.u.



The diagram on the right shows the 3p-2p sigma antibonding unoccupied MO in ClF. It has an energy value(-0.12150a.u. )higher than both 2p-3p sigma bonding(-0.52314 a.u.) and 3p-2p pi antibonding(-0.32855 a.u.). It is also the LUMO of ClF.

