Sum inorg comp jp
Day 1 excercise
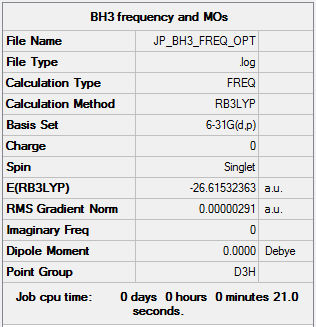
BH3
RB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000023 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file JERZYP_BH3_FREQ_OPT.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.9432 -0.8611 -0.0054 5.7455 11.7246 11.7625 Low frequencies --- 1162.9963 1213.1826 1213.1853
BH |
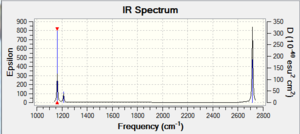
Vibrational spectrum for BH3
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1162 | 93 | A2 | yes | out-of-plane bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | symmetric bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | asymmetric bend |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2715 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
| 2715 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
For a peak to show on an IR spectrum the vibration responsible for it must change the dipole moment of the molecule. This criterion eliminates the A1' mode at 2582. Furthermore, there are two pairs of degenerate modes; ones that would appear at the same frequency. These peaks simply overlap and cannon be distinguished between on the spectrum. These factors reduce the amount of visible peaks on the spectrum to three.
Smf115 (talk) 22:26, 22 May 2018 (BST)Correct assignment of the symmetries and vibrational modes and nice mention of both the degeneracy and the inactive peak.
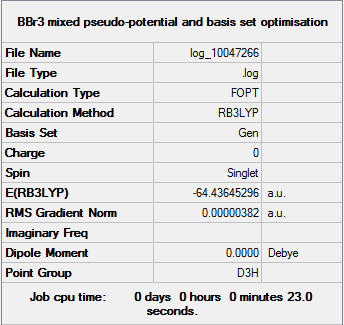
BBr3
B3LYP/6-31G(d,p)LANL2DZ level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000023 0.001200 YES
Optimization log file JERZYP_BBR3_OPT_GEN.log
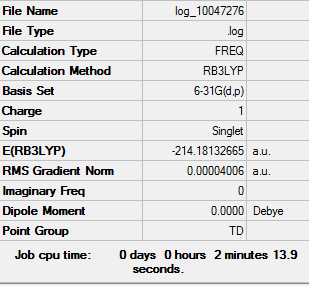
Low frequencies --- -0.9432 -0.8611 -0.0054 5.7455 11.7246 11.7625 Low frequencies --- 1162.9963 1213.1826 1213.1853
BBr3 |
Vibrational spectrum for BH3
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1162 | 93 | A2 | yes | out-of-plane bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | symmetric bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | very slight | asymmetric bend |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2715 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
| 2715 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
Ionic Liquids: Designer Solvents
[N(CH3)44]+
RB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000078 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000040 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000763 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000433 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file JERZYP_[NCH34]_FREQ_OPT.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0005 -0.0002 0.0003 34.6141 34.6141 34.6141 Low frequencies --- 216.7663 316.0912 316.0912
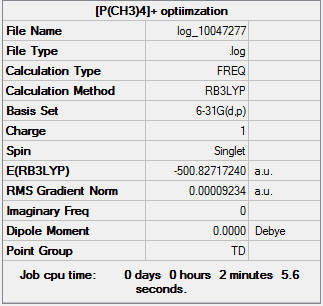
[P(CH3)44]+
RB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000153 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000092 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001384 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000828 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file JERZYP_[PCH34]_FREQ_OPT.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0021 -0.0015 0.0019 50.8156 50.8156 50.8157 Low frequencies --- 186.5407 211.4597 211.4597
Smf115 (talk) 22:25, 22 May 2018 (BST)Good structure information for the two cations with everything included. However, the low frequencies are a little high, in the future make sure these are considered and a demonstrator should have been consulted.
Comparing Charges
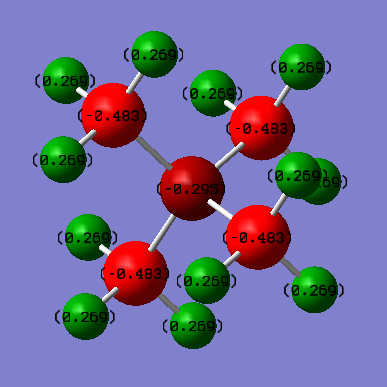
The overall positive charge can be seen to reside in different positions of the two molecules. The central nitrogen has a charge of -0.295 and is surrounded by carbon atoms of charge -0.483. In this complex the positive charge is therefore located entirely on the hydrogen atoms. Despite the greater electronegativity of nitrogen, it has a less negative charge than the surrounding carbon atoms suggesting electron density is removed from the nitrogen to give the molecule an overall positive charge. However, the formal representation of this molecule shows that an electron is removed from the nitrogen atom. In fact the charge analysis shows that electron density is shared over the entirety of the molecule.
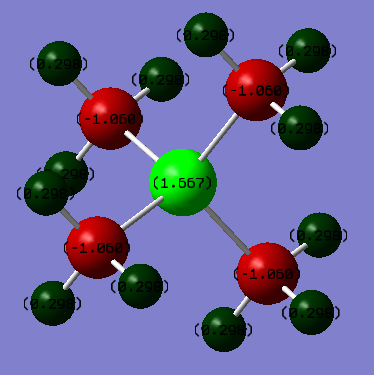
In the phosphorous complex the central atom is far more positive than the surrounding carbons with charges of 1.667 and -1.060 respectively. Here the charge resides mostly on the central atom. The more diffuse orbitals of phosphorous along with a much larger electronegativity difference between it and the ligands makes the molecule far more polarized.
Smf115 (talk) 22:22, 22 May 2018 (BST)Nice mention of electronegativity to try to explain the charges within the compounds. To improve, the location of the positive charge on the central N in the traditional description of the cation should have been discussed further and the comparison between the two molecules could have been developed further.
MOs of [N(CH3)44]+
Smf115 (talk) 22:30, 22 May 2018 (BST)Overall a disapointing report with both sections left incomplete. Where you have completed sections they have been attempted well but mistakes, such as missing files, have been made throughout.