Sbs17
NH3, N2, H2 and the Haber-Bosch Process
NH3
Summary of results
| NH3 | |
|---|---|
| Bond Length | 1.01798 Å |
| Bond Angle | 37.129° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Set Symmetry | C3V |
| Energy | -56.55776873 au |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
Vibration Modes
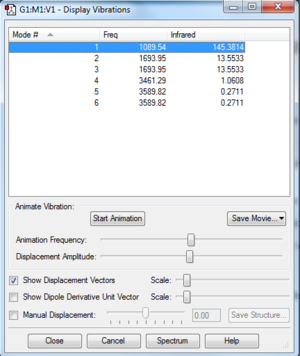
Ammonia should have 3 vibrational modes, according to the 3N-6 rule: 3(3)-6=3. The fact that 6 are shown here for the Gaussview optimised molecule of ammonia is due to the fact that some of these vibrational modes are degenerate. These degenerate modes are modes 2 and 3, which along with 1 represent a "bending" mode, and modes 5 and 6 which, along with mode 4 represent a "bond stretch". Mode 4 is highly symmetric as all three stretches are in the same direction. Mode 1 represents the "umbrella mode", as the bending here resembles the opening and closing of an umbrella. As 4 of these modes are degenerate, four different bands would be seen in the IR spectrum of NH3.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Charge Distribution
The N-atom on ammonia has a partial charge of -1.125, while the H-atoms on the molecule have a partial charge of 0.375. The negative charge on the N-atom and the postive charge on the H-atom is expected, as Nitrogen is electronegative than Hydrogen, and would therefore pull electron density towards itself in a bond, thus creating the partial negative charge on Nitrogen and the partial positive charge on Hydrogen.

N2 and H2
| N2 | H2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Set Symmetry | D∞H | D∞H |
| Energy | -109.52112868 au | -1.17853936 au |
N2
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 |
Vibrational Modes

The optimised file for N2 can be found here
H2
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 |
Vibrational Modes
The optimised file for H2 can be found here
Energy of the Haber-Bosch Process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au
E(N2)= -109.52112868 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05879074 au = -154.36 kJ/mol
As such, the energy to convert nitrogen and hydrogen gas into ammonia is -154.3550879 kJ/mol, where the negative sign suggests that energy is released in the process of the reaction. As such, NH3 is more stable.
HCl
Results of calculation
Summary of results
| HCl | |
|---|---|
| Bond Length | 1.28599 Å |
| Bond Angle | 180° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Set Symmetry | C∞v |
| Energy | -460.80077875 au |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
HCl |
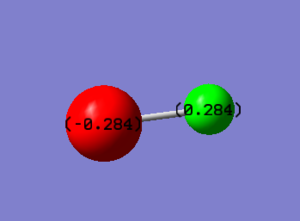
Charge Distribution
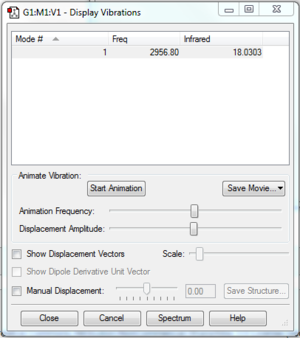
Vibrational Modes
Molecular Orbitals
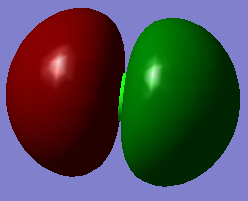
This particular molecular orbital of HCl is the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) and is therefore, occupied. The AO's (atomic orbitals) which contribute to this particular MO (molecular orbital) is the 3pz orbital of the Cl atom, resulting in this particular MO to be a π non-bonding orbital, as the 3pz AO of Cl does not have the correct symmetry to overlap with the H 1s orbital.
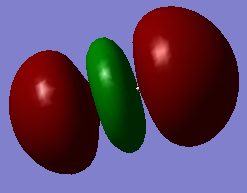
This particular MO is the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) of HCl. As such, it is unoccupied. It is an antibonding orbital, and the AO's which contribute to this orbital is the 3px orbital of the Cl atom and the 1s orbital of hydrogen, resulting in this being the 3σ* molecular orbital. This orbital can participate in bonding.
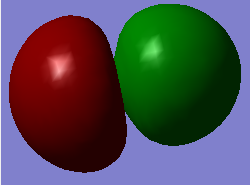
This particular molecular orbital of HCl is the 3σ bonding orbital. The AO's which contribute to this is the 3px orbital of Cl and the 1s orbital of the H atom, and is the result of the constructive overlap between these two. This orbital is occupied.

This low-energy molecular orbital of HCl is non-bonding, occupied orbital. The AO's contributing to this orbital is the 3s orbital of the Cl atom.
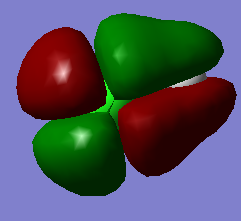
This high-energy molecular orbital of HCl and is an unoccupied antibonding π orbital. The AO's contributing to this orbital is the 4py orbital of Cl.
The optimisation file is linked to here
NaCl
Results of calculation
Summary of results
| HCl | |
|---|---|
| Bond Length | 2.37565 Å |
| Bond Angle | 180° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Set Symmetry | C∞v |
| Energy | -622.56029785 au |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
NaCl |
Charge Distribution

Vibrational Modes
The optimisation file is linked to here
