SXY19970601
Ammonia Molecule
Summary of NH3
After optimisation of structure of ammonia, we can measure the N-H bond length and H-N-H bond angle:
N-H bond length=1.01798 Å
H-N-H bond angle=105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
It's easy to find that the structure of NH3 is optimized because the force is nearly zero which means it's the lowest energy form of ammonia.
calculation method:RB3LYP basis set:6-31G(d,p) final energy E(RB3LYP):-56.55776873au point group:C3V
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibration display of NH3
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
Answer:6
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Answer:mode2and3, mode5and6
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Answer:"bending" vibrations:mode1,2,3/"bond stretch" vibrations:mode4,5,6
which mode is highly symmetric?
Answer:mode4
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Answer:mode 1
It has the highest intensity because of largest change in dipole moment.
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
Answer:2
Since there are four different vibration frequency, four bands are expected to to be seen in the spectrum. However, only two peaks are observed because the change in dipole moment of mode 4, mode 5 and mode 6 is very small and the intensity is too low.
charge distribution of NH3
 N is expected to be negatively charged, and H is expected to possess positive charges because N has larger electronegativity than H.
N is expected to be negatively charged, and H is expected to possess positive charges because N has larger electronegativity than H.
H2 molecule
summary of H2
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13 Optimization completed.
Structure is optimised when force equals zero.
calculation method:RB3LYP basis set:6-31G(d,p) final energy E(RB3LYP):-1.17853936au point group: D∞h
Vibration display of H2
 Intensity is zero because there is no change in dipole moment.
Intensity is zero because there is no change in dipole moment.
charge distribution of H2
 No charge was expected on H because no difference between electronegativity
No charge was expected on H because no difference between electronegativity
N2 molecule
summary of N2
calculation method:RB3LYP basis set:6-31G(d,p) final energy E(RB3LYP):-109.52412868au point group: D∞h
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401002D-13
Vibration display of N2
 Intensity is zero because there is no change in dipole moment.
Intensity is zero because there is no change in dipole moment.
charge distribution of N2
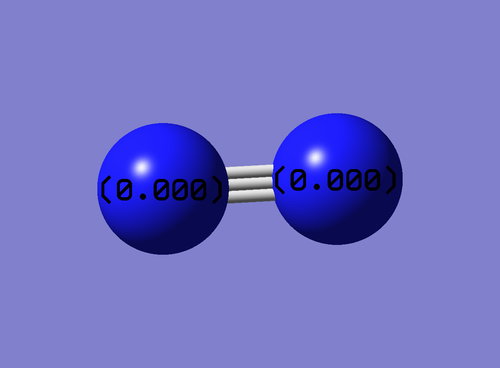 No charge was expected on N because no difference between electronegativity
No charge was expected on N because no difference between electronegativity
Enthalpy change of formation of NH3
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873au
2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375au
E(N2)=-109.52412868au
E(H2)=-1.17853936au
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579074au=-146.478599028 KJ/mol
The enthalpy change is negative, therefore exothermic reaction and the ammonia product is favoured.
HCL Molecule
Vibration display of HCL
 Intensity is not zero because there is change in dipole moment.
Intensity is not zero because there is change in dipole moment.
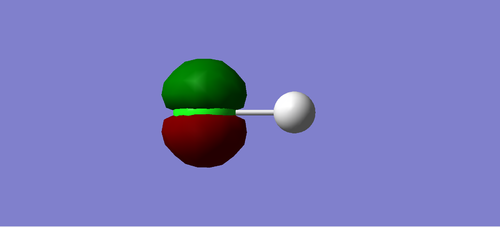
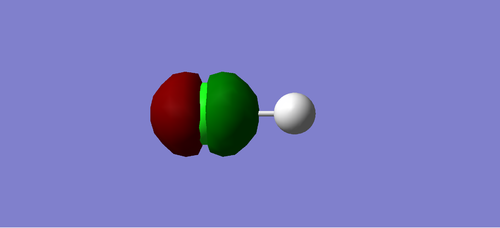
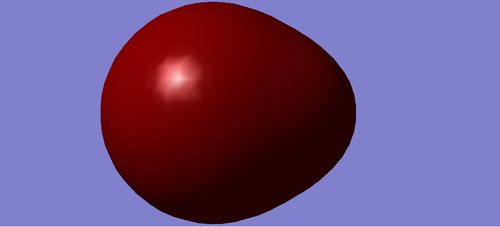
Charge Distribution of HCL
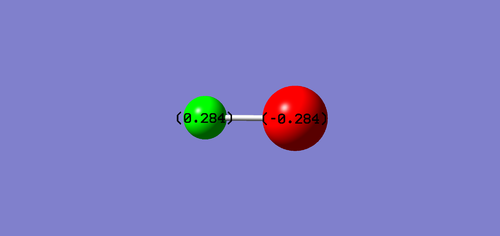 Cl atom is negatively charged due to higher electronegativity than H, and H atom is positively charged.
Cl atom is negatively charged due to higher electronegativity than H, and H atom is positively charged.
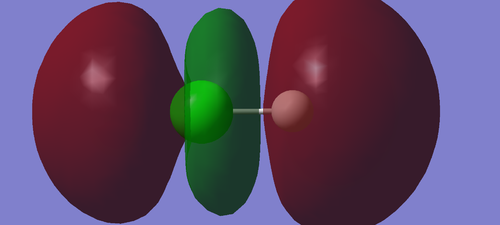
Molecular Orbital of HCl
This is the 1π molecular orbital of HCl which is occupied by 2 electrons and deep in energy(-7.22836au). It is contributed by 2py atomic orbital of Cl. It is a non-bonding orbital.
This is the 3σ molecular orbital of HCl which is occupied by 2 electrons and deep in energy(-7.23847au). It is contributed by 2pz atomic orbital of Cl. It has lower energy than 1pi as a result of mixing with 1s orbital of H because of same symmetry. It is a non-bonding orbital.
This is the 4σ molecular orbital of HCl which is occupied by 2 electrons and deep in energy(-0.84773au). It is formed by mixing 3s atomic orbital of Cl and 1s orbital of H. It is a bonding orbital.
This is the 5σ molecular orbital of HCl which is occupied by 2 electrons and deep in energy(-0.47433au). It is formed by mixing 3sp atomic orbital of Cl and 1s orbital of H . It is a bonding orbital.
This is the 6σ* molecular orbital of HCl which is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (0.01366au). It is formed by mixing 3sp atomic orbital of Cl and 1s orbital of H . It is an anti-bonding orbital.