Rep:Title=Mod:pbd15 complab2
NH3 Optimisation
Data
Molecule: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Energy: -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Bond Length: 1.01798 Angstroms
Bond Angle: 105.741 Degrees
Log file: File:PDAVIS NH3 OPTF POP.LOG
Item Table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 Molecule |
Vibrations
From the 3N-6 rule, we would expect 6 modes.
Modes 2 and 3 and modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
Modes 1,2,3 are bending vibrations and modes 4,5,6 are bond stretch vibrations.
Mode 1 is an 'umbrella' vibration.
Mode 4 is highly symmetric
We would expect to see 4 bands in an IR spectrum of gaseous ammonia
Charge Distribution
Optimised charge on H atoms: 0.375
Optimised charge on N atom: -1.125
We would expect a slight positive charge on each hydrogen atom, and a negative charge on the nitrogen atom equal to -3 times the charge on each hydrogen, which is what we have here.
N2 Optimisation
Data
Molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Energy: -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group: D∞H
Bond Length: 1.10550 Angstroms
Log File: File:PDAVIS N2 OPTF POP.LOG
Item Table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
Frequency: 2457.33 Hz
H2 Optimisation
Data
Molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Energy: -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000068 a.u.
Point Group: D∞H
Bond Length: 0.74279 Angstroms
Log File: File:PDAVIS H2 OPTF POP.LOG
Item Table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000002 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
Frequency: 4465.70 Hz
Haber-Bosch Process
Energy Calculations
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.478494 kJ mol-1
From this we can deduce that the ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants in this reaction:
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
H2CO Optimisation
Data
Molecule: H2CO
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Energy: -114.50319933 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00007386 a.u.
Point Group: CS
C-H Bond Length: 1.11057 Angstroms
C=O Bond Length: 1.20676 Angstroms
H-C-H Bond Angle: 115.219 Degrees
H-C=O Bond Angle: 122.395 Degrees
Log file: File:PDAVIS H2CO OPTF POP.LOG
Item Table:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000197 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000085 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000232 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000149 0.001200 YES
H2CO Molecule |
Vibrations
6 modes, none degenerate:
"Umbrella" bend: 1200.65 Hz
Asymmetric C-H bend: 1274.54 Hz
Symmetric C-H bend: 1554.64 Hz
C=O stretch: 1845.74 Hz
Symmetric C-H stretch: 2897.28 Hz
Asymmetric C-H stretch: 2954.03 Hz
Charge Distribution
Optimised charge on C atom: 0.221
Optimised charge on H atoms: 0.137
Optimised charge on O atom -0.494
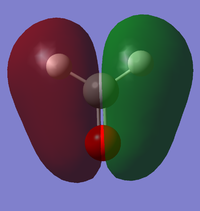
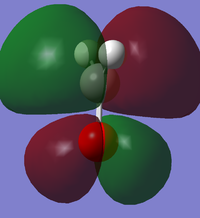
Molecular Orbitals
A mixture of the C-H sigma bonding orbitals with the non-bonding sp2 orbitals on the oxygen, with an energy of -0.49430 a.u. Occupied.
The antibonding equivalent of the above (a mixture of the C-H sigma* orbitals and the non-bonding sp2 orbitals on the oxygen), with an energy of -0.26816 a.u. Occupied (HOMO).
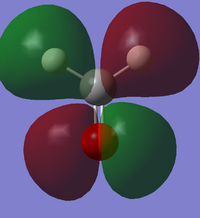
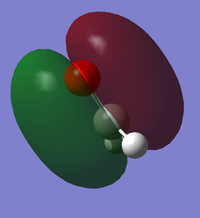
Sigma bonding orbital between C and O, with an energy of -0.44941 a.u. Occupied.
Pi* antibonding orbital between C and O, the antibonding equivalent of the below orbital with an energy of -0.04309 a.u. Unoccupied (LUMO).
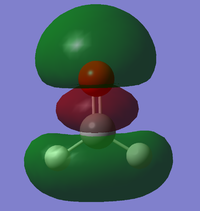
Pi bonding orbital between C and O, with an energy of -0.39919 a.u. (The next highest occupied molecular orbital after the HOMO).