Rep:Mod:zw4415
NH3
Calculation method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP)
-56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm
0.00000485 a.u.
Point group of your molecule
C3v
Optimised N-H bond distance
1.01798 Å
Optimised H-N-H bond angle
105.74115 °
Converged?
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986495D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol
NH3 |
File
Display Vibrations
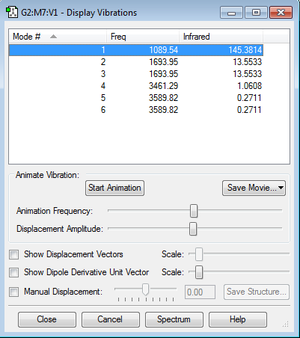
Questions
•how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
3N-6=3*4-6=6
•which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Mode 2 and Mode 3, Mode 5 and Mode 6
•which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bending:1,2,3 Stretching:4,5,6
•which mode is highly symmetric?
4,5,6
•one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
1
•how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2
Charge Distribution
N:-1.125 H:0.375 Due to the higher electronegativity of N, we would expect positive charge on H and negative charge on N.
N2
Calculation method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP)
-109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm
0.00000060 a.u.
Point group of your molecule
D*H
Bond length
1.10550 Å
Converged?
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401058D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol
N2 |
File
Display Vibrations

H2
Calculation method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP)
-1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm
0.00000017 a.u.
Point group of your molecule
D*H
Bond length
0.74279 Å
Converged?
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol
H2 |
File
Display Vibrations
Haber-Bosch reaction energy
E(NH3)=
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)=
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u.= -146.478494 kJ/mol
NH3 is more stable as the enthalpy of the forwarding reaction is exothermic
compare to literature value on wikipedia= −92.4 kJ·mol
this could be due to that the entropy of the reaction was not considered.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haber_process
ClF
Calculation method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP)
-559.94269578 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm
0.00014211 a.u.
Point group of your molecule
C*V
Optimised Cl-F bond distance
1.66434 Å
Charge Distribution
Cl = +0.309 F = -0.309 F is more electronegative than Cl.
Converged?
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.066054D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol
CLF |
File
Display Vibrations
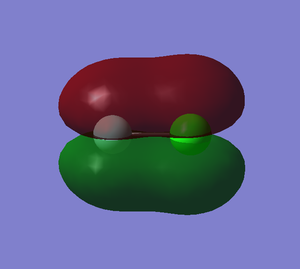
Molecular orbitals

This is a bonding orbital, relatively high in energy. Form by overlapping two 2px orbitals.
This is a bonding orbital, relatively high in energy. Form by overlapping two 2py orbitals.

This is a bonding orbital, relatively high in energy. Form by overlapping two 2pz orbitals.
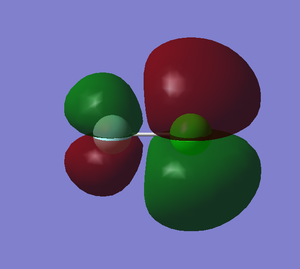
This is a anti-bonding orbital, relatively high in energy. This is the highest occupied molecular orbital.
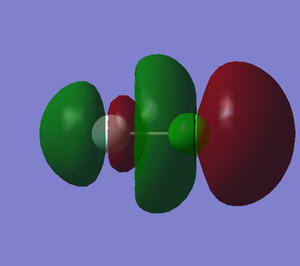
This is a anti-bonding orbital, relatively high in energy. This is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital.
