Rep:Mod:yts15
NH3
NH3 is optimized and gives the following results.
Summary
| Name of Molecule | NH3 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 a.u. |
| Point group | C3V |
Optimized bond distance and bond angle
The optimized bond distance N-H is 1.01798 Å. The optimized bond angle of H-N-H is 105.741 degrees.
Final set of forces and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Optimization File
NH3 |
The optimization file is linked to here
Vibration and Charge
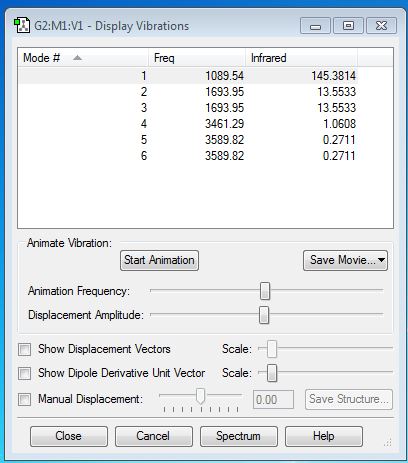
From the 3N-6 rule, I expect there are 6 modes. Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate. Also, mode 5 and 6 are degenerate. Mode 1,2 and 3 are "bending" vibrations and mode 4,5 and 6 are "bond stretch" vibrations. Mode 4 is highly symmetric because the point group doesn't change. Mode 1 is known as the "umbrella" mode.
I would expect to see only 2 bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia. This is because the intensity of mode 4, 5 and 6 are too small which is unlikely to be recognizable in an experimental spectrum. Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate which give the same band. Mode 5 and 6 are degenerate which give the same band.
I would expect the charge for N is negative and the charge for H is positive. This is because N is more electronegative than H. Therefore, the charge on the N-atom and H-atoms is -1.125 and +0.375 respectively.
N2
N2 is optimized and gives the following results.
Summary
| Name of Molecule | N2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Point group | DinfH |
Optimized bond distance and bond angle
The optimized N≡N bond distance is 1.10550Å. N2 is diatomic which is a linear molecule.
Final set of forces and displacements
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Optimization file
N2 |
The optimization file is linked to here
Vibration and Charge
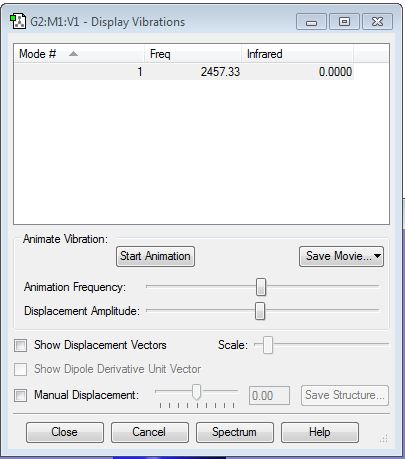
It is confirmed that there is no negative frequency. Since N2 is a linear molecule, from the 3N-5 rule, I expect there is 1 mode. Mode 1 is bond stretch vibration. I expect to see no bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous nitrogen as there is no change of dipole moment.
I would expect the charge is neutral since there is no change in electronegativity.
H2
H2 is optimized and gives the following results.
Summary
| Name of Molecule | H2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 a.u. |
| Point group | DinfH |
Optimized bond distance and bond angle
The optimized H-H bond distance is 0.74279Å. H2 is diatomic which gives a linear molecule.
Final Set of Forces and Displacements
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Optimization file
H2 |
The optimization file is linked to here
Vibration and charge
It is confirmed that there is no negative frequency. Since H2 is a linear molecule, from the 3N-5 rule, I expect there is 1 mode. I expect to see no bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous hydrogen as there is no change of dipole moment.
I would expect the charge is neutral since there is no change in electronegativity.
Haber-Bosch reaction energy calculation
The calculation of the Haber-Bosch reaction energy is as followings.
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.4784829 kJ/ mol
Since the enthalpy of the reaction is negative, this reaction is exothermic. Therefore, the ammonia product is more stable than reactant as energy is released during the reaction.
My choice of molecule: Cl2
Cl2 is optimized and gives the following results.
Summary
| Name of Molecule | Cl2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -920.34987886 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00002511 a.u. |
| Point group | DinfH |
Optimized bond distance and bond angle
The optimized Cl-Cl bond distance is 2.04174Å. Cl2 is diatomic which gives a linear molecule.
Final set of Forces and Displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Optimization file
Cl2 |
The optimization file is linked to here
Vibration and Charge
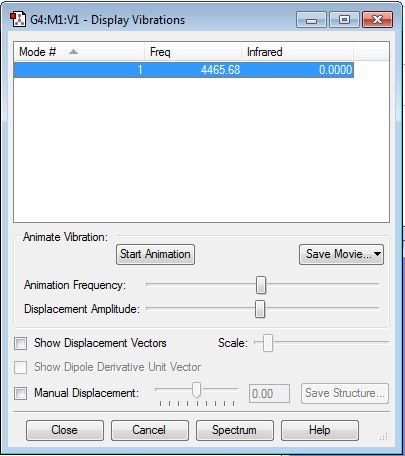
It is confirmed that there is no negative frequency. Since Cl2 is a linear molecule, from the 3N-5 rule, I expect there is 1 mode. I expect to see no bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous Chlorine as there is no change of dipole moment.
I would expect the charge is neutral since there is no change in electronegativity.
Molecular Orbitals
HCl
HCl is optimized and gives the following results.
Summary
| Name of Molecule | HCl |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-311G(d.p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -460.83346909 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00002859 a.u. |
| Point group | CinfV |
Optimized bond distance and bond angle
The optimised H-Cl bond distance is 1.28687 Å. It is a linear molecule.
Final set of forces and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000050 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000050 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000077 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000110 0.001200 YES
Optimization File
HCl |
The optimization file is linked to here
Vibration and Charge
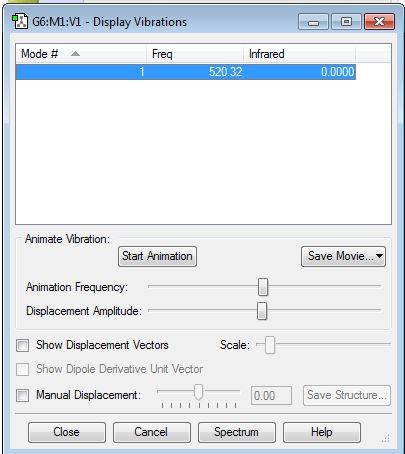
It is confirmed that there is no negative frequency. Since HCl is a linear molecule, from the 3N-5 rule, I expect there is only 1 mode.
I would expect to see only 1 bands in an experimental spectrum.
I would expect the charge for Cl is negative and the charge for H is positive. This is because Cl is more electronegative than H. Therefore, the charge on Cl and H are -0.258 and +0.258 respectively.