Rep:Mod:wikidont
What is the molecule?
NH3
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-56.55776873
What is the RMS gradient (au)?
0.00000485
What is the point group of your molecule?
C3V
Optimised Bond Length (Å):
1.01798
Optimised Bond Angle:
105.741
Optimisation Data:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Jmol Image:
NH3 |
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
2,3;5,6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bending Modes = 1,2,3
Stretching = 4,5,6
Which mode is highly symmetric?
4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
4
Charge for N = -1.125
Charge for H = 0.375
This is expected because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, hence I expect nitrogen to be negative and hydrogen to be positive.
N2 Molecule
The summary information
What is the molecule?
N2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-109.52412868
What is the RMS gradient (au)?
0.00000060
What is the point group of your molecule?
D*H
Optimised Bond Length (Å):
1.10550
Optimised Bond Angle:
180
Optimisation Data:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
List the frequencies and confirm that there are no negative frequencies:
2457.33 cm-1, hence there are no negative frequencies.
Jmol Image:
H2 Molecule
The summary information
What is the molecule?
H2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-1.17853936
What is the RMS gradient (au)?
0.00000017
What is the point group of your molecule?
D*H
Optimised Bond Length (Å):
0.74279
Optimised Bond Angle:
180
Optimisation Data:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
List the frequencies and confirm that there are no negative frequencies:
4465.68 cm-1, hence there are no negative frequencies.
Jmol Image:
Energy Calculations of Reaction
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE = 2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746-[-109.52412868 + -3.53561808] = -0.0557907 au = -146.47848285 KJ mol-1
As the energy is negative, the reaction must be exothermic which suggests the product NH3 is more stable than the reactants H2 and N2.
O2 Molecule
Data
What is the molecule?
O2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-150.25742434
What is the RMS gradient (au)?
0.00007502
What is the point group of your molecule?
D*H
Optimised Bond Length (Å):
1.21602
Optimised Bond Angle:
180°
Optimisation Data:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Jmol Image:
O2 |
Vibrational modes of O2
There is one mode at 1642.74 cm-1 which would be expected according to 3N-5 rule.
There are no charges because the molecule only contains one element, its a diatomic.
Molecular Orbitals of O2
1πu
Energy: - 0.50754
Contributing AOs: two 2px or two 2pz
Contributes to Oxygen bond
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied: Occupied with a pair of electrons
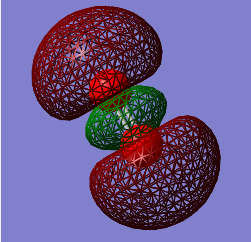
3σg
Energy: - 0.53151
Contributing AOs: two 2pz
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied: Occupied with a pair of electrons
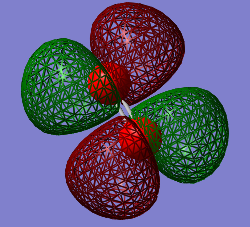
1πg*
Energy: - 0.17928
Contributing AOs: 2px and 2py
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied: Unoccupied
This is the LUMO
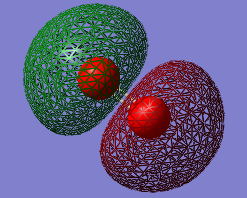
3σu*
Energy: - 0.79821
Contributing AOs: Two 2pz
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied: Occupied with a pair of electrons electrons
2σg
Energy: - 1.27663
Contributing AOs: Two 2s
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied: Occupied with a pair of electrons