Rep:Mod:sl5811
Contents [hide]
Inorganic Computational Chemistry Lab
Day 1
Optimising a Molecule of BH3
Method
A BH3 molecule was created by GaussView 5.0. The three bond lengths of the three B-H bonds were set to 1.53 angstrom, 1.54 angstrom, 1.55 angstrom separately. The BH3 molecule was optimized using the method: B3LYP and the basis set: 3-21G.
Results
The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 1.
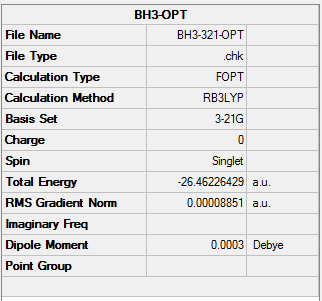
BH3 Bond length and Bond angle
| BH3 | ||
| Data | Bond Angle(°) | Bond length(Å) |
| 3-21G | 120.0 | 1.19 |
| 120.0 | 1.19 | |
| 120.0 | 1.19 | |
| Average | 120.0 | 1.19 |
From the table above, which presented the three sets of BH3 molecule data in bond lengths and band angles. Proved the experiment data that highly matched to the theoretical expectation of trigonal planar molecular geometry. The point group of the optimized BH3 molecule is C3v rather than D3h.


The "Item" table that indicated converged forces and distances was displayed below. And It showed that the calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000220 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000106 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000709 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000447 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.672479D-07
Optimization completed.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1944 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1947 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1948 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 119.9983 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 119.986 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0157 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The original output Log. file could be check through the link BH3-321-OPT
Day 2
Better Basic Set of Opt BH3
Method
A a higher level basis set: 6-31G(d,p)was chose for optimization.
Results
The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 4.
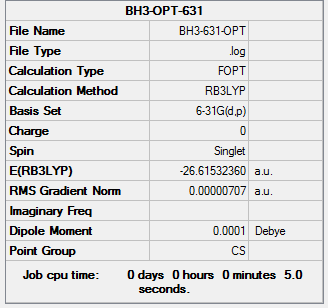
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000061 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000038 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.069288D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 119.9938 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The original output Log. file could be check through the link BH3-631-OPT
BH3 Bond length and angle
| Data | Angle(°) | Bond length(Å) |
| 6-31G | 120.0 | 1.19 |
| 120.0 | 1.19 | |
| 120.0 | 1.19 | |
| Average | 120.0 | 1.19 |
| Literature[1] | 120.0 | 1.19 |
The experiemental value above proved highly agreement with literature values, which suggested that used basic data 6-31G also provides a optimised structure of BH3.
 |
 |
For high level basis set 6-31G(d,p),the molecules pictures showed in Picture. 5 and Picture. 6, the B-H bond length after optimize is 1.19 Å and H-B-H bond angel is 120 degree.
The total energy BH3 of 3-21G optimised structure was -26.46226429 au. The total energy BH3 of 6-31G(d,p) optimised structure was -26.61532360 au. There were not too much different between the total energy for these two optimised models.
Opt GaBr3
Method
Created the GaBr3 molecule by Gaussview then first then the symmetry was restricted to D3h point group, run the calculation by HPC system.The GaBr3 molecule was optimized by this method: B3LYP and the basis set: LanL2DZ. Pseudo-potentials and larger basis sets are used to study the property of heavy atom in trigonal planar structure.
Results
The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 7.

Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000003 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000002 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.282688D-12
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.3502 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 2.3502 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 2.3502 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The HPC output Log. file could be check through the link DOI:10042/26920


In Picture.8 and Picture 9, the Br-Ga-Br angle was 120.0 degree and the Ga-Br bond length was is 2.35 Å after optimized, compared to the literature value the Ga-Br bond length of Gabr3 is 2.249 Å [2]. The optimized Ga-Br bond length is a bit longer than the literature Ga-Br bond length . Due to the bond length calculated by Guass view was from gaseous state Gabr3, the literature data was got from crystal solid Gabr3 by experiment. Gabr3 molecules are more condensed in solid phase that is the reason why Ga-Br bond length in solid phase is a bit shorter. As well as the optimized bond length deviates from literature might due to the basis set chose for the calculation. The basis set was not accurate enough for the calculation.Finally,the different in bond length is just 1%, so the optimization is still accurate.
Using a mixture of basis-sets and psuedo-potentials
Method
A BBr3 molecule was build up. The BBr3 molecule was optimized using 6-31G(d,p) , the basis set: GEN, and the additional keywords section was "pseudo=read gfinput". At the end, the basis sets for all atoms were specified. The file was uploaded to HPC to run the analysis.
Results
The result of calculation is summarized in the picture. 10.
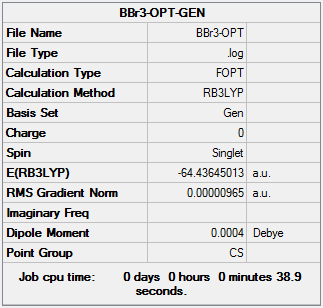
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000015 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000009 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000069 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000041 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.505648D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,4) 1.9339 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(2,4) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(3,4) 1.9339 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(1,4,2) 120.0018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(1,4,3) 120.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,4,3) 119.9974 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(1,4,3,2) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The HPC output Log. file could be check through the link DOI:10042/26921
 |
 |
The optimized OPT-BBr3 molecule pactures presented in Picture.11 and Picture 12. The Br-B-Br angel became 120 degree and B-Br bond length became 1.93 Å. Compared to the literature value,the B-Br bond length was 1.892 Å[2].
Comparison of bond distances
The bond distances of BH3, BBr 3, GaBr3 are showed in the table 2.
Table 2
| ' | Bond Length in literature[2]./ Å | Bond Length/ Å |
| B-H of BH3 | 1.19 | 1.19 |
| B-Br of BBr3 | 1.892 | 1.93 |
| Ga-Br of GaBr3 | 2.249 | 2.35 |
The table 2 presents that bond length of the BBr3 was longer than BH3 which indicated the bromide ligand is the main reason for increasing the bond length. The difference between BH3 and BBr3 is that the hydride ligands are replaced by bromide ligands.The bond length increases form 1.19 Å (B-H) to 1.93 Å (B-Br). The above table shows that the bond length of BH3 is shorter than that of BBr3. This indicates that bromide ligand increases bond length rather than hydride ligand with the same central atom.The reason is that bromide has larger radius and is more electronegative than hydride. The comparison is based on the assumption that both hydride and bromide are x-type donor for 2c-2e bonds with boron center.Besides, Br is sp2 and B([1s22p22p1, the mismatch of the orbital size causes the orbital overelap poorer.in contrast H has the electronic configuration: 1s1, hydride has a better overlap with B, because the 1s orbital of H has similar size with the sp2 hybridized B orbital. In conclusion, B-Br bond is more polar and weaker than B-H bond. In conclusion, B-Br bond is longer, more polar and weaker than B-H bond.
For the comparison of the bond length of GaBr3 and BBr3,The bond length increases form 1.93 Å (B-Br) to 2.35 Å (Ga-Br. Gallium's radius is the major reason for increasing the bond length. Gallium and boron are in the same group, group 3 with three valance electrons but Gallium is in the lower row and less electronegative than boron causes the Ga-Br more polar than B-Br.The orbital overlap between Ga([Ar]3d104s24p1) and Br is 4p-4p which is weaker than 2p-4p orbital overlap (B-Br)since Ga(4s,4p) occupies larger and more diffuse orbital than boron (2s,2p). Finally, it concludes that bond length GaBr3 is longer than BBr3 because the larger atomic radius, more polarized bond and poor 4p-4p orbital overlap.
Due to the bond length was not in the pre-defined range so Gaussview could not present the bond in the same struture.[3] There is still bonding interation between atoms. The definition of the chemical bond is that the attraction between atoms which forms new substance between atoms with opposite charge. It exists four different types of chemical bonds, covalent bond (by sharing electrons), ionic bond (exchange electrons),van der waals' force and metallic bond (attraction between ions and electrons). In this experiment, it only consider the covalent bond between atoms.[4].
Day 3
Frequency analysis for BH3
Method
The frequency analysis was carried out for the optimized BH3 molecule to analysis the structure of BH3 molecule. The symmetry of the BH3 molecule was restricted to D 3h.
Summary
The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 14. The summary shows that the " Imaginary frequency" is 0. It means that the molecule was in the stable state.

The original Log. output could be check through the link BH3-Freq
Low frequencies --- -24.9563 -13.1428 0.0005 0.0007 0.0007 15.1819 Low frequencies --- 1162.9975 1213.0240 1213.1458
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000014 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000088 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000045 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.482703D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
There are six types of vibration of BH3 while there are only three shows on the spectrum. This is because mode two and three are degenerate so as mode five and six. Therefore, there are two peaks (1213 cm-1,2715 cm-1) presented in the IR spectrum. Besides, the selection rule of IR spectroscopy suggest that only dipole moment equals to non-zero can present peaks. Mode four as total symmetric vibration turns a zero value in dipole moment due to all the dipole moments are cancelled with equivalent bond angles of 120°. Therefore, there is not peaks for mode 4 in the spectrum.
IR
The calculated IR spectrum presents in Picture. 14

Frequency Analysis of GaBr3
Method
The frequency analysis was run for the optimized GaBr3 to analysis the structure of GaBr3 molecule. The symmetry of the GaBr3 molecule was restricted to D3h. And the file was analysed by HPC system.
Summary
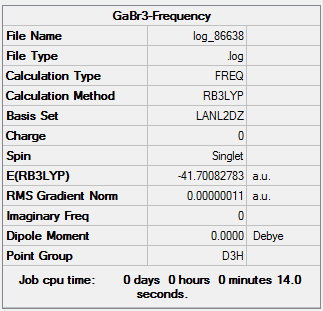
The "Item" table which includes converged forces and distances is displayed below. And It shows that the calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-6.142862D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are displayed below. It shows that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1.
Low frequencies --- -0.5252 -0.5247 -0.0024 -0.0010 0.0235 1.2010 Low frequencies --- 76.3744 76.3753 99.6982
The original Log. output could be check through the linkDOI:10042/27121 The lowest "real" normal mode is 76 cm-1. The optimised structure of GaBr3 is a minimum. Due to the imaginary frequency of the structure is zero which presented in the summary and the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1.
The calculated IR spectrum is showed in Picture. 15

Comparison of IR
Comparison of BBH3 and GaBr3
| no. BH3 | frequency/ cm-1 | Intensity | symmetry D3h point group | no. GaBr3 | frequency/ cm-1 | Intensity | |
| 1 | 1163 | 93 | A2" | 1 | 100 | 9 | |
| 2 | 1213 | 14 | E' | 2 | 76 | 3 | |
| 3 | 1213 | 14 | E' | 3 | 76 | 3 | |
| 4 | 2582 | 0 | A1' | 4 | 197 | 0 | |
| 5 | 2716 | 126 | E' | 5 | 316 | 57 | |
| 6 | 2716 | 126 | E' | 6 | 316 | 57 |
The analysis is consider successfully as the low frequencies for both BH3 and GaBr4. The frequency is proportional to the force constant of the bond which is reversely proportional to the reduced mass for IR spectrum. GaBr3 vibrational modes have higher frequency than BH3 due to BH3 owns small reduced mass and the reduce mass of GaBr3 is large. It shows Ga-Br bond is weaker than B-H bond. The reason is that the orbital overlap between the 4p orbital of Ga and 4p orbital of Br is poor compare to the overlap between 1s orbital of H and 2p orbital of B is much better. BH3 and GaBr4 have same point group D3h so they have similar vibrational environments. As a result, the IR spectrum of BH3 and GaBr4 shows similar pattern and three peaks are recorded.The above table illustrate that the vibrational frequencies of BBH3 is much higher than GaBr4.
In both IR spectra, A2" and E' modes are close in energy. A1' and E' modes are close in energy. In A2" and E' modes, no bond stretch could be observed. So the bond length keeps constant during the vibrations. However, in A1' and E' modes, bond stretch could be observed. Vibrational frequency is higher for the modes with bond stretch. As a result, A1' and E' modes are higher in frequency. For BH3, A2" mode is lower in frequency than E' mode. For GaBr3, A2" mode is higher in frequency than E'mode. It is because than the bond length of Ga-Br is longer and more polar than B-H.
The purpose of frequency analysis is to ensure that the molecule is maximum optimized. The method and basis set must be same to make sure the consistency and accuracy. If different methods and basis sets are used, the result of frequency is no significance. What do the "Low frequencies" represent? For non-linear molecules,the number of vibration modes equals to 3N-6 where N is the total number of atoms and -6 present as low frequencies. Due to low frequencies are the motions of the center of mass which is much lower than real frequencies. The real frequency is the lowest visible peak shown in the IR spectrum. Here, the real frequency of GaBr3 is 76 cm-1.
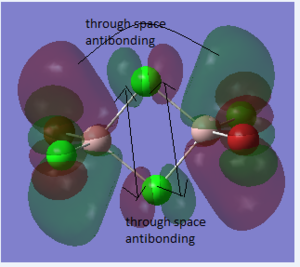
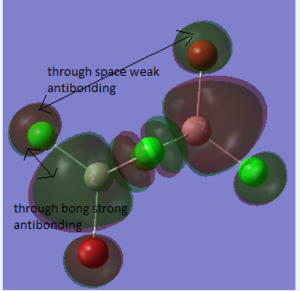
Molecular Orbitals of BH3
Method
The molecular orbitals of BH3 was obtained by calculating of the electronic structure. Before the calculation, the method was set to energy. "pop=full" was used to the "additional keywords" section. And "Full NBO" was selected. The file was sent to HPC system to run the analysis.
Summary
The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 15. The summary shows that the " Imaginary frequency" is 0. It means that the molecule was in the stable state. DOI:10042/27124
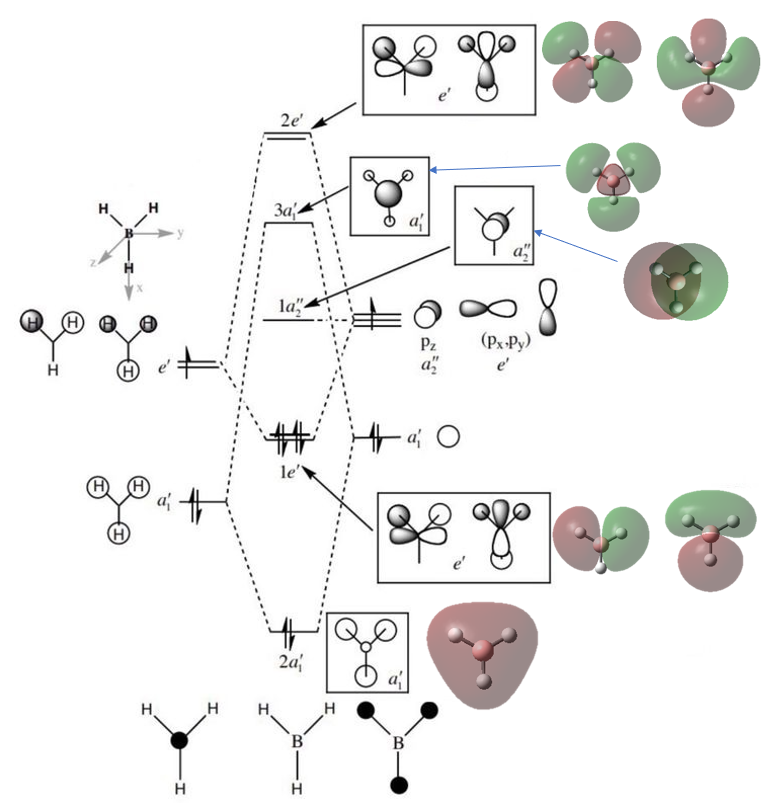
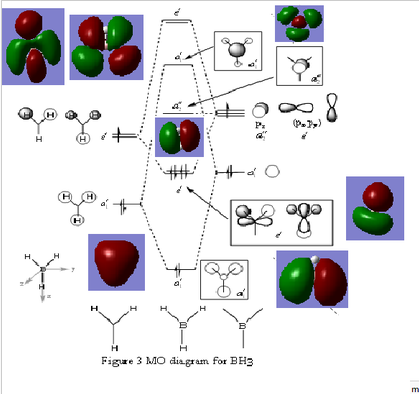
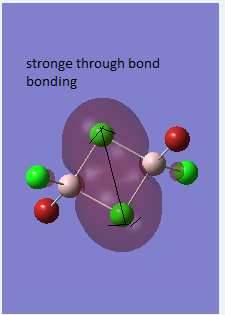
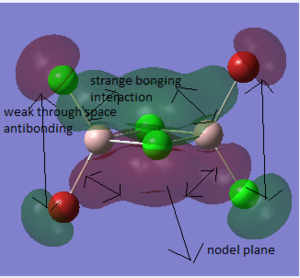
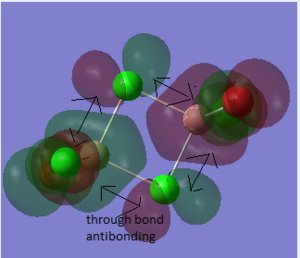
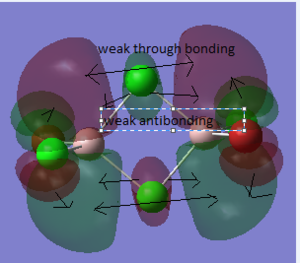
The difference between the LMAO MO and real MOs is obvious. Sicne LMAO MOs is the result of combination each atomic orbital directly, ignoring the electron diffusion. LMAO MO presents normal orbital combination that is useful to solve problems involve orbital interactions and nodal planes. However real MO show shape and location of the electron density clearly. Qualitative MO theory could be use to predict the position of orbitals and the their combination. And the nodal planes of the combined orbitals could be predicted but qualitative MO theory cannot predict the delocalized electron distribution and the shape of electron density.The result is high accuracy and usefulness of qualitative MO theory.
NBO Analysis
The original Log. output could be check through the link nh3-Opt NH3-FreqNH3-MO
Optimization:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-9.844311D-11 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Frequnecy:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000013 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000007 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.131315D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -0.0128 -0.0016 0.0014 7.0747 8.1044 8.1047 Low frequencies --- 1089.3849 1693.9369 1693.9369
Optimization: The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 17.
Frequency: The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 18.
MO :The information of calculation is summarized in the picture. 19


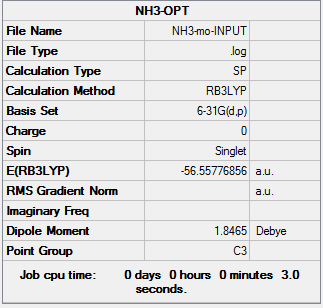
Method
Picture. 20 presents the charge distribution. And the charge range is (-1.0 to +1.0).
Picture. 21 presents the specific NBO chargeS for nitrogen and hydrogen. The charge of nitrogen atom is -1.125. The charge of each hydrogen atom is +0.375.


Day 4
Association energies: Ammonia-Borane
Method
A NH3BH3 molecule was built and it was optimized at the b3lyp/6-31G(d,p) level. The structure of NH3BH3 molecule was confirmed by frequency analysis.
OPT:
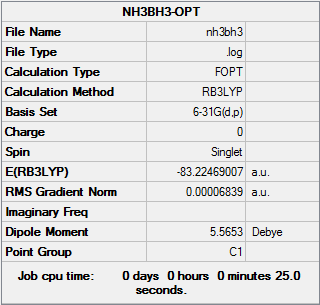
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000139 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000063 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000771 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000338 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-2.028054D-07 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The original Log. output could be check through the linkNH3BH3.LOG
Freq:
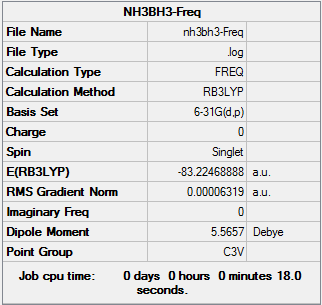
Low frequencies --- -0.0246 -0.0032 -0.0011 17.6808 17.6833 37.1786 Low frequencies --- 265.6718 632.2168 639.3347
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000139 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000063 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000771 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000338 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-2.028054D-07 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The original Log. output could be check through the linkNH3BH3.LOG
Summary
Optimization
Dissociation Energy
The energy of optimized NH3BH3, NH3,BH3 are listed in the Table. 3.
Table. 3.
| Molecule | Energy/au |
| BH3 | -26.61532360 |
| NH3 | -56.55776873 |
| NH3BH3 | -83.22468888 |
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]= -0.05159655 au. The association energy in kJ/mol is -135.7803947 kJ/mol. The dissociation energy is -135.7803947 kJ/mol. Therefore the dissociate process is endothermic and it is not a spontaneous process. Due to the NH3BH3 is a very stable molecule. The reason is that a lone pair on N donates to the empty p orbital on B to form a N-B bond.
Project: Lewis acids and bases
Optimization
Four Al2Cl4Br2 isomers were built up by Gaussview. The four isomers were optimized using the method: B3LYP and the basis set: Gen. Full basis set 6-31G(d,p) was selected for Al and Cl. A PP LANL2DZdp was used for Br.
The structure of each isomer and information of calculation are listed in the Table. 1. In the pictures, the green atoms, red atoms and pink atoms are chlorine, bromine and aluminum separately. The calculated point group and real point group are not restrict to be the same. So the real point groups of isomer are showed below of Table. 1.
| Table. 1 | Isomer 1 | Isomer 2 | Isomer 3 | Isomer 4 | ||||||||||||
| Sturucture |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
| File Name | js-isomer1-clean-opt | js-isomer2-clean-opt | js-isomer3-clean-opt | js-isomer4-clean-opt | ||||||||||||
| File Type | .log | .log | .log | .log | ||||||||||||
| Calculation Type | FOPT | FOPT | FOPT | FOPT | ||||||||||||
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | ||||||||||||
| Basis Set | Gen | Gen | Gen | Gen | ||||||||||||
| Charge | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Spin | Singlet | Singlet | Singlet | Singlet | ||||||||||||
| E(RB3LYP) | -2352.40630798 a.u | -2352.41109946 a.u | -2352.41631610 a.u | -2352.41626680 a.u | ||||||||||||
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000182 a.u | 0.00000701 a.u | 0.00001373 a.u | 0.00001283 a.u | ||||||||||||
| Imaginary Frequency | ||||||||||||||||
| Dipole Moment | 0.0002 Debye | 0.1393 Debye | 0.0013 Debye | 0.1661 Debye | ||||||||||||
| Point Group | C1 | C1 | CS | C2v | ||||||||||||
| Link to D-Space | DOI:10042/27241 | DOI:10042/27239 | DOI:10042/27244 | DOI:10042/27242 | ||||||||||||
| Real point Group | D2h | C1 | C2h | C2v |
Isomer 1
File:2br in the middle3 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000003 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000038 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-2.660925D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Isomer 2
File:1_br_in_the_middle.mol |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000014 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000098 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000033 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.771795D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Isomer 3
File:Trans_br.mol |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000022 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001322 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000482 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.142035D-08 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
isomer 4
File:CIS_br.mol |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000362 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000112 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-7.122660D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Symmetry
| Isomer | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Point Group | D2h | C1 | C2h | C2v |
| Symmetry |  |
 |
 |

|
Comparison of Energy
| Energy (au) | Energy (kJ/mol) | Relative Energy(kJ/mol) | ||
| A | -2352.4063 | -6190543 | -26.34 | the highest Energy isomer |
| B | -2352.4111 | -6190556 | -13.73 | |
| D | -2352.4163 | -6190569 | -0.13 | |
| C | -2352.4163 | -6190569 | 0.00 | the lowest Energy isomer |
The table above confirmed that the isomer with lowest energy is isomer 3, which has two bromide in terminal position and trans respect to each other. In the case of isomer 4 which also two bromide with position of terminal but cis to each other.The total energy of isomer 4 is slightly higher than isomer 3. Since bromide atoms owns larger atomic radius than chlorine, isomer 4 is more steric hindrance than isomer 3 cause in higher energy.Besides, isomer 1 is the most unstable isomer with two bromide on the bridging position. The overlap between Br-Al (4p-3p) is weaker that Cl-Al (3p-3p) which lead to weaker covalent bond. Moreover, two bromide on the bridging condition cause steric repulsion. Comparing with isomer 1, isomer 2 has one bromide in the bridging while the other on the terminal position. Therefore, the energy of isomer 2 is slightly lower than isomer 1.The energies of isomer 3 and 4 are lower than isomer 1 and 2 which suggests that the bromide in terminal position gives lower energy than bridging position.
Monomer analysis
The structure of the monomer AlBrCl2 presents below. In the pictures, the green atoms, red atoms and pink atoms are chlorine, bromine and aluminum respectly.
|

|
D-Space:DOI:10042/27291
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000136 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000073 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000760 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000497 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-7.984419D-08 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Dissociation Energy
Dissociation Energy = 2E(AlBrCl2) - E(Isomer 3)
| ' | Energy (au) | Energy (kJ/mol) |
| Al2Cl2Br | -1176.1901 | -3095237 |
| Isomer 3 | -2352.4163 | -6190569 |
| Dissociation Energy | 0.0360 | 95 |
The above table suggests that the dissociation energy of Al2Cl4Br2 (95kJ/mol)is positive that shows that the reaction is endothermic.Therefore, isomer 3 is more stable than two isolate AlBrCl2.
Frequency
Isomer 1
The "Item" table which consists of converged forces and distances is displayed below. And It presents that the frequency calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000293 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000143 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-4.006395D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are displayed below. It presents that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1. The calculated imaginary frequency is 0. It shows that the structure was fully optimized
Low frequencies --- -5.1277 -4.9552 -3.1726 -0.0055 -0.0055 -0.0053 Low frequencies --- 14.8534 63.2885 86.0886
The simulated IR spectrum of isomer 1 is presented in Picture. 1.

Isomer 2
The "Item" table which includes converged forces and distances is showed below. And It indicates that the frequency calculation was finished. Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000020 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000937 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000453 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-4.164422D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are displayed below. It shows that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1. The calculated imaginary frequency is 0. It shows that the structure was fully optimized.
Low frequencies --- -2.5287 0.0029 0.0031 0.0034 0.6261 3.0980 Low frequencies --- 17.1094 55.9276 80.0590
The simulated IR spectrum of isomer 2 is presented in Picture. 2.
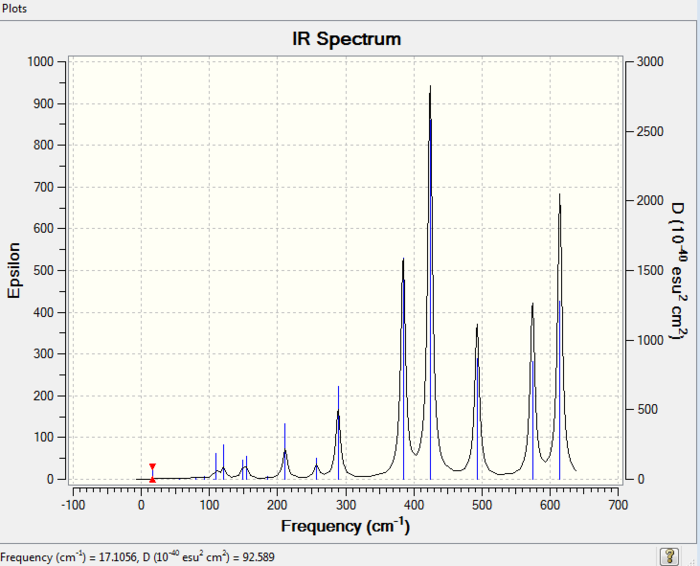
Isomer 3
The "Item" table which includes converged forces and distances is showed below. And It indicates that the frequency calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000040 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000014 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001356 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000593 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.806994D-08 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are showed below. It indicates that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1. The calculated imaginary frequency is 0. It shows that the structure was fully optimized.
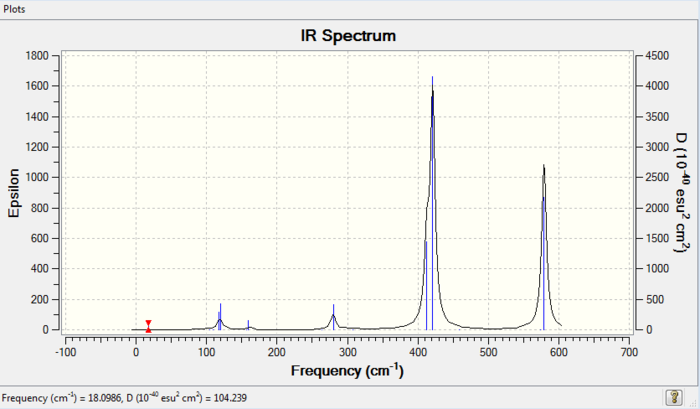
Low frequencies --- -0.0037 -0.0035 -0.0031 1.8914 1.9699 3.9618 Low frequencies --- 18.0987 49.0857 72.9223
The simulated IR spectrum of isomer 3 is presented in Picture. 3.
Isomer 4
The "Item" table which includes converged forces and distances is showed below. And It indicates that the frequency calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000032 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000013 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000421 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000153 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.221637D-08 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are showed below. It indicated that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1. The calculated imaginary frequency is 0. It shows that the structure was fully optimized.
Low frequencies --- -4.0768 -2.0661 -0.0022 -0.0015 -0.0012 1.4891 Low frequencies --- 17.1900 50.9075 78.5442
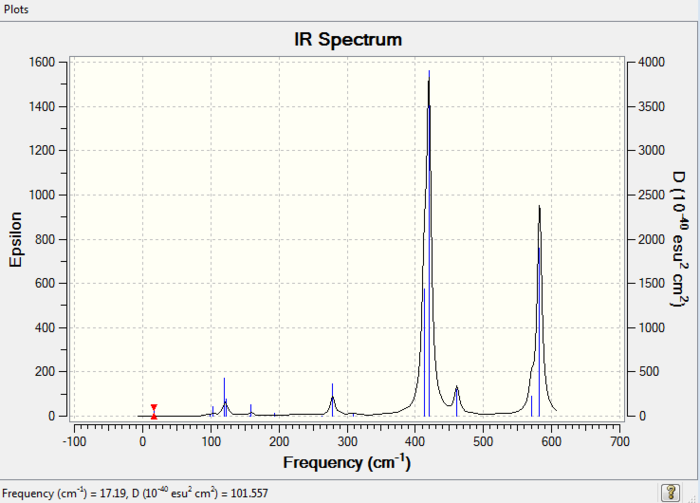
The result of frequency is shown in the below table.
| 1(D2h) | 2(C1) | 3(C2h) | 4(C2v) | |||||
| Mode | Frequency(cm-1) | Infrared | Frequency(cm-1) | Infrared | Frequency(cm-1) | Infrared | Frequency(cm-1) | Infrared |
| 1 | 15 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 17 | 0 |
| 2 | 63 | 0 | 56 | 0 | 49 | 0 | 51 | 0 |
| 3 | 86 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 73 | 0 | 79 | 0 |
| 4 | 87 | 0 | 92 | 1 | 105 | 0 | 99 | 0 |
| 5 | 108 | 5 | 107 | 0 | 110 | 0 | 103 | 3 |
| 6 | 111 | 0 | 110 | 5 | 117 | 9 | 121 | 13 |
| 7 | 126 | 8 | 121 | 8 | 120 | 13 | 123 | 6 |
| 8 | 135 | 0 | 149 | 5 | 157 | 0 | 157 | 0 |
| 9 | 138 | 7 | 154 | 6 | 160 | 6 | 158 | 5 |
| 10 | 163 | 0 | 186 | 1 | 192 | 0 | 194 | 2 |
| 11 | 197 | 0 | 211 | 21 | 263 | 0 | 264 | 0 |
| 12 | 241 | 100 | 257 | 10 | 280 | 29 | 279 | 25 |
| 13 | 247 | 0 | 289 | 48 | 308 | 0 | 309 | 2 |
| 14 | 341 | 161 | 384 | 154 | 413 | 149 | 413 | 149 |
| 15 | 467 | 347 | 424 | 274 | 421 | 438 | 420 | 411 |
| 16 | 494 | 0 | 493 | 107 | 459 | 0 | 461 | 35 |
| 17 | 608 | 0 | 574 | 122 | 574 | 0 | 570 | 32 |
| 18 | 616 | 332 | 614 | 197 | 579 | 316 | 582 | 278 |
| Total Number of Inactive Mode: | 11 | 4 | 11 | 6 | ||||
The number of vibration mode of four isomer are all 18 due to the rule of 3N-6 where N is the number of atoms.However, not all the modes are active in IR. Only those vibrations that change the dipole moment of the isomer are active in IR spectrum. The high symmetric of the molecule structure, the easy of dipole moment be cancelled out while vibrating. As the dipole moment of the molecule vibration equals to zero, the mode are treated as IR inactive that shows there is no peaks be presented on the spectrum. The above table indicates that isomer 1 and isomer 3 are the molecules own most number of inactive mode. This suggests that isomer 1 and isomer 3 present less bands than the others because of the highly symmetric structures.
| Mode | Isomer 1 | Isomer 2 |
| 11 |  |

|
| Frequency | 197 | 263 |
| Intensity | 0 | 0 |
These two pictures are mode 11 for isomer 1 and isomer 2 respectively. In these two modes, the bridging bonds stretch and the bridging atoms move in opposite direction. The difference of these two modes which one bridging Br is replaced by Cl in isomer 2. The frequency of mode 11 for the isomer 1 is 197 cm-1. The frequency of mode 11 for the isomer 2 is 263 cm-1. Isomer 1 owns lower frequency than isomer 2. Frequency is directly proportional to the bond strength. Therefore Br-Al bond is longer and weaker than Cl-AL bond, as the poor orbital overlap between Br and Al. Br-Al bond is more weaker in the bridging position than in the terminal position.
| Mode | Isomer 3 | Isomer 4 |
| 15 |  |

|
| Frequency | 421 | 438 |
| Intensity | 420 | 411 |
These two pictures are mode 15 for isomer 3 and isomer 4 respectively. In these two modes, The bridging bonds stretch and the bridging atoms move in the identical direction. The two Br sits in tran terminal position in isomer 3. The two Br sits in cis terminal position in isomer 3. The frequency of isomer 3 of mode 15 is 421 cm-1. The frequency of isomer 4 of mode 15 is 420 cm-1. Frequency is directly proportional to the bond strength. It indicates the Br-Al bond strength an length of isomer 3 and isomer 4 are quite similar. Finally, the two Br are in the cis or trans terminal position do not effect the nature of Br-Al bond.
MO
The molecular orbitals of isomer 3 was got by calculating of the electronic structure. For the calculation, the method was set to energy. "pop=full" was used to the "additional keywords" section. And "Full NBO" was selected. The file was sent to HPC system to run the analysis. The information of calculation is summarized below:
The original output could be check through the link DOI:10042/27308
Further study
The monomer AlICl2 was optimized and analysed below:
 |
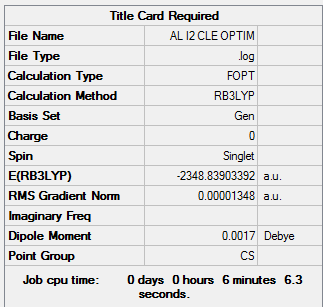
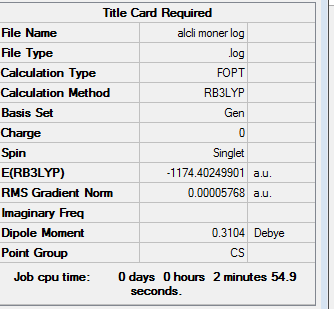 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000159 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001771 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.001069 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.253229D-07 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The original output could be check through the link DOI:10042/27309
The energy of the monomer is -1174.402499 a.u (-3083393.76 KJ/mol)
The association energy ΔE=E(Al2Cl4I2)-2*E(AlICl2)= -51.55 kJ/mol. The dissociation energy is 51.55 kJ/mol. Therefore the dissociate process is endothermic and it is not a spontaneous process. It shows that trans Al2Cl4I2 form is more stable than the isolated monomer. Due to the monomer, it only exists 6 electrons in the valence orbital of Al. Therefore Al prefer to get two electrons to get the octet structure. While becoming the dimer, the electron deficiency has been released. Compare to isomer 3, the Al2Cl4I2 chosen is less stable. The monomers are still prefer to couple to each others then form the dimer.
The same method and basis set as previous were set to run optimization and frequency analysis for Al2I2Cl4. I is a bigger atom than Br. In theory, Al2I2Cl4 should be less stable than isomer 1 because of the poor overlap. The purple atoms are I. The calculation information is listed below:
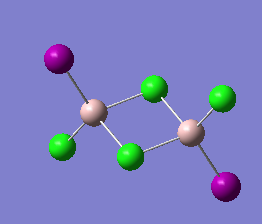 |
 |
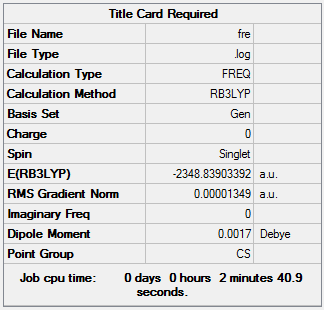 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000027 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000333 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000097 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-9.599815D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The original output could be check through the link DOI:10042/27320
The "Item" table of frequency analysis which includes converged forces and distances is showed below. And It indicates that the calculation was finished.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000042 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000013 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000388 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000169 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.243404D-08 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
The low frequencies lines are displayed below. It presents that the low frequencies are in the range of plus/minus 15cm-1. The calculated imaginary frequency is 0. It shows that the monomer was fully optimized
Low frequencies --- -0.0041 -0.0038 -0.0037 1.9739 3.9188 5.0416 Low frequencies --- 16.3883 41.7199 60.4395
The original output could be check through the link DOI:10042/27329
References
- ↑ "Physical Constants of Organic Compounds", in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2005, David R. Lide, ed., <http://www.hbcpnetbase.com>, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2005.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 W. M. Haynes, D. R. Lide and T. J. Bruno, CRC handbook of chemistry and physics : a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data, 2012, 93, 9–23.
- ↑ Hunt Research Group, Understanding optimisation part a., http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/teaching_comp_lab_year3/3a_understand_opt.html
- ↑ Carl R. Nave (2005). HyperPhysics http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/chemical/bond.html Retrieved May 18, 2005.