Rep:Mod:sammacer
Introduction
The aim of this wiki page is to provide a documentation of using Gaussian to run quantum mechanical calculation on some simple molecules to learn the software. Firstly, an energy change estimation will be made for the Haber-Bosch reaction by examining the energy levels of electrons around the molecules involved. Secondly, Diphosphorus and it's molecular orbitals will be examined to make an argument for it's bonding.
The Haber-Bosch reaction
NH3
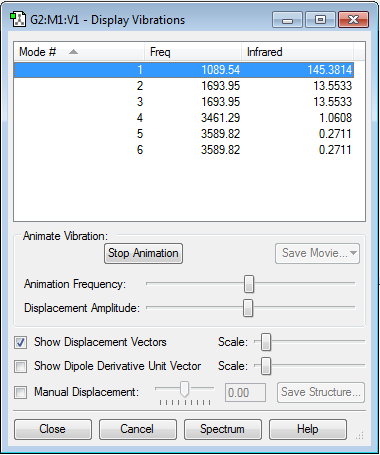
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -56.55776873 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000485 a.u. Point Group C3V
Optimised NH Bond Length: 1.018 Å
Optimised HNH Angle: 105.741 °
Structure: Trigonal Pyramidal
Item table: Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986271D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
NH3 |
6 modes of vibration are present, as expected from the 3N-6 rule (3*4-6=6). Modes 2 and 3, and modes 5 and 6 are degenerate. Modes 1-3 are bending, while modes 4-6 are stretching. Modes 1 and 4 are highly symmetric. Mode 1 is known as the umbrella mode. Gaseous ammonia should have 4 absorption bands due to vibrations occurring at 4 different frequencies (as 2,3 and 5,6 are degenerate). Only 2 of these are likely to be seen however, due to background noise; the absorbances for modes 4 and 5+6 are significantly lower that the maximum of 145, so are unlikely to be seen on a spectrum.
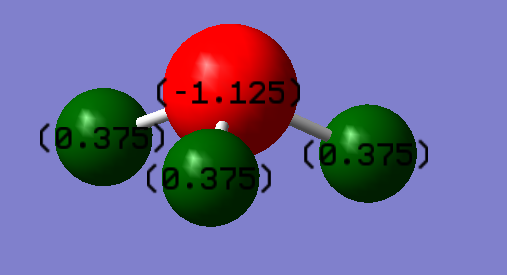
Nitrogen is more electronegative than Hydrogen, and so the N atom has a greater negative charge as expected due to greater electronic contribution from each of the NH bonds.
N2
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -109.52412868 RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000060 Point Group D*H
Optimised NN Bond Length: 1.106 Å
Structure: Linear
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401004D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Vibrational modes:
- 1 freq.=2457.33
This absorbance will not be present on a spectrum due to the lack of a net magnetic dipole moment. There is no net charge across the homo-nuclear diatomic molecule.
N2 |
H2
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -1.17853936 RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000017 Point Group D*H
Optimised HH Bond Length: 0.743 Å
Structure: Linear
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Vibrational modes:
- 1 freq.=4465.68
This absorbance will not be present on a spectrum due to the lack of a net magnetic dipole moment. There is no net charge across the homo-nuclear diatomic molecule.
H2 |
Haber Bosch Reaction Energy Calculation
E(NH3)=-56.55776873
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746
E(N2)=-109.52412868
E(H2)=-1.17853936
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557907
=-146.48 kJ/mol
The exothermic reaction shows the products exist at a lower energy than the reactants, so ammonia is more thermodynamically stable than it's elemental constituents.
P2
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -682.68894541 RMS Gradient Norm 0.00001744 Point Group D*H
Optimised PP Bond Length: 1.904 Å
This bond length is much greater than for the other diatomic molecules studied. This can be justified by noticing the principal quantum number, and so covalent radius is greater than for N2 and H2.
Structure: Linear
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000030 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000030 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000041 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000057 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.223542D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Vibrational modes:
- 1 freq.=797.67
This absorbance will not be present on a spectrum due to the lack of a net magnetic dipole moment. There is no net charge across the homo-nuclear diatomic molecule;

P2 |
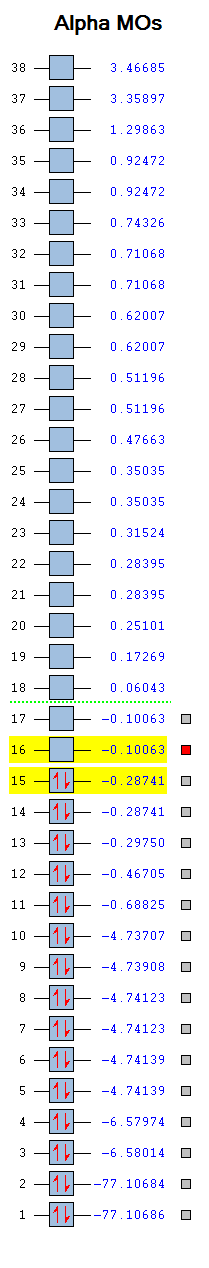
Below I have shown the molecular orbitals for P2 constructed with the valence atomic orbitals (3S, 3P). MO 11 can be seen as a linear combination of two in phase 3S orbitals (sigma g). MO 12 is the corresponding anti-bonding orbital arising from an out of phase combination of the same orbitals. MO 13 is a bonding sigma g orbital resulting from the head on overlap of two p orbitals where the overlap is in phase. MOs 14 and 15 are pi u bonding orbitals resulting from the in phase sideways overlap of two 3P orbitals. MOs 16 and 17 Are the corresponding anti-bonding orbitals (pi g) due to destructive interference between the wave functions. The HOMO is MO 15 and the LUMO is MO 16, so overall is can be seen that the bond order is three, making the structure of P2 similar to that of N2.

MO 11
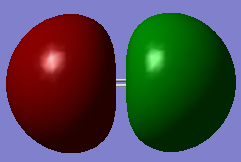
MO12
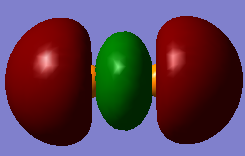
MO13

Degenerate MOs 14 and 15
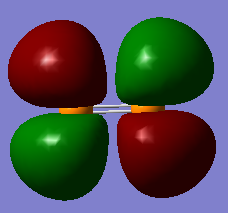
Degenerate MOs 16 and 17
Comparison with P4
Phosphorus does not exist at RTP as P2 [1], but instead is P4. To attempt to justify this, I modeled P4;
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -1365.44183011 RMS Gradient Norm 0.00005228 Point Group C1
Optimised PP Bond Length: 2.218 Å
Bond angle: 60.0 °
Structure: Tetrahedral
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000061 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000505 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000383 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-8.897922D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
P4 |
The energy of the P2 molecule was calculated to be -682.68894541 a.u. and that of P4 was calculated to be -1365.44183011 a.u. Per phosphorus atom, the energy is therefore -341.344472705 a.u. for P2 and -341.3604575275 for P4, making P4 0.0159848225 a.u. lower in energy, equivalent to 41.96815147375 Kj/mol. This shows that P2 exists only at a local energy minimum which is not deeper than the minimum for P4. This accounts for why P4 is the standard state for Phosphorus, not P2.
References
- ↑ Shriver and Atkins' Inorganic Chemistry Author Peter Atkins Edition illustrated Publisher OUP Oxford, 2010 ISBN 0199236178, 9780199236176