Rep:Mod:rum123
NH3 molecule
The molecule is a nitrogen molecule bonded covalently to three hydrogen atoms, forming and NH3 molecule knows as ammonia.
The optimised structure of ammonia can be caluculated using the programme Gaussview. Calculations made can be seen below.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986266D-10
Optimisation completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Optimised values can be seen below
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Final energy | -56.557au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 |
| Point group | C3v |
NH3 molecule |
Vibrations of NH3
From the 3N-6 rule we expect to have 6 vibration modes. Here we expect the stretching vibrations seen in modes 5 and 6 to have degenerate energies, as well as bending vibrations from modes 2 and 3. Modes 1 and 4 can be seen to be highly symmetric. Mode 1, is also known as the umbrella mode.
Due to degenerate energies, 4 bands can be observed in the infrared spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
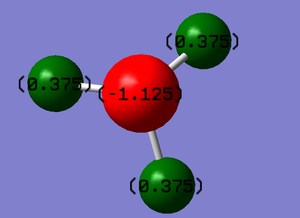
The charges on the atoms of an ammonia can be seen to be -1.125au and +0.375au for nitrogen and hydrogen respectively. This is due to the high electronegativity of nitrogen, this allows the nitrogen atom to attract the electrons in the bonds towards itself, resulting in the fomentation of a polarized bond. A image of this can be seen below.
N2 and H2
Furthermore both N2 and H2 have the point groups D∞h due to them being linear molecules.
N2 molecule |
The bond length of N2 was found to be 1.09Å,the optimization of N2 can be seen below.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.400973D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Final energy | -109.52412868au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000060au |
For H2 the optimized bond length was found to be 0.743Å, the optimization can be seen below.
H2 molecule |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Final energy | -1.17853936au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000017au |
The balanced symbol equation of the formation of NH3, with their corresponding energies, can be sen below.
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
| Molecule | energy value |
|---|---|
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 au |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553746 au |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 au |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 au |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 au |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -146 kJ/mol |
Due a negative difference of energy, the products are more stable than the reactants.
F2 molecule
As fluorine is the most electrnegative atom, it is also the most reactive. The atom has 7 valence electrons and can form strong covelant bonds with other atoms. A structure for the F2 molecule was optimised, the calculation for this and the optimised values can be seen here.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.995025D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4028 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Bond energy | -199.49825218 KJ/mol |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00007365 |
The high bond energy reflects the strength of the bond formed by the molecule. As the molecule is linear, only a single stretch vibration can be seen. This is estimated to occur at a frequency of 1065.09Hz. Furthermore literature values of the bond energy can be found to be -154.39 [1], this is comparable to our calculated value of -199KJ/mol.
F2 molecule |
Molecular orbitals for F2 consist of 2s and 2p orbitals, combining in and out of phase to form σ and π orbitals.
<references> [1]