Rep:Mod:pp4717
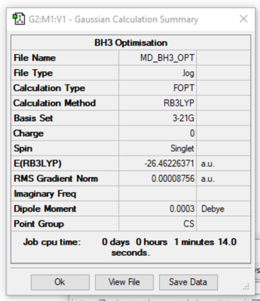
BH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 3-21G
Final energy in atomic units (a.u): -26.46226
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000220 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000106 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000940 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000447 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.672478D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
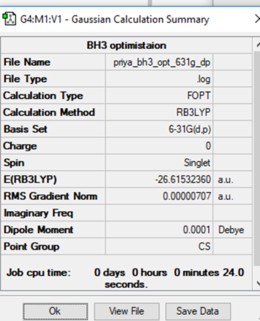
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G (d,p)
Final energy in atomic units (a.u): -26.61532
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000061 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000038 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.069047D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
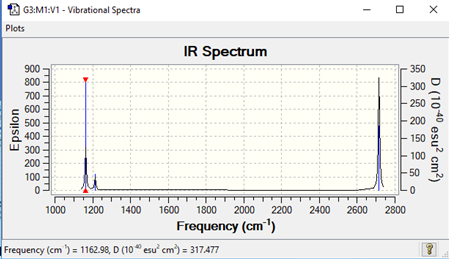
Low frequencies --- -0.2263 -0.1037 -0.0054 47.9770 49.0378 49.0383 Low frequencies --- 1163.7209 1213.6704 1213.6731
| Vibration | Intensity | Symmetry | IR active | Type of vibration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1164 | 92 | symmetric | yes | stretch |
| 2 | 1214 | 14 | asymmetric | yes | bend |
| 3 | 1214 | 14 | asymmetric | yes | bend |
| 4 | 2580 | 0 | symmetric | no | n/a |
| 5 | 2713 | 126 | symmetric | yes | bend |
| 6 | 2713 | 126 | asymmetric | yes | stretch |
IR Spectrum
There are less than 6 peaks seen in the IR spectrum because 1 peak is not IR active and there are are 2 sets of degenerate frequencies which thus show up as the same peak in the spectrum.
Good identification of both reasons for the number of visible peaks although you could have been clearer about which modes you were referring to. To improve you also needed to include the symmetries of the modes in your table and even the IR inactive mode has a type for its vibrational motion (not N/A)! Smf115 (talk) 12:22, 18 May 2019 (BST)
test molecule |
MO diagram of BH3
There are no significant differences in the LCAOs and the computed MOs; this shows the usefulness of the qualititative MO diagram.
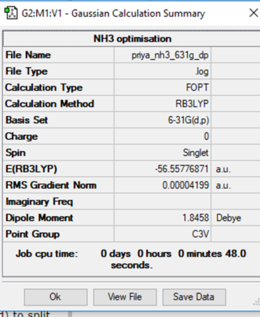
NH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G (d,p)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000060 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000040 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000369 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000162 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.259212D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
Low frequencies --- -32.4128 -32.3999 -11.4544 -0.0032 0.0078 0.0521 Low frequencies --- 1088.7642 1694.0248 1694.0252
test molecule |
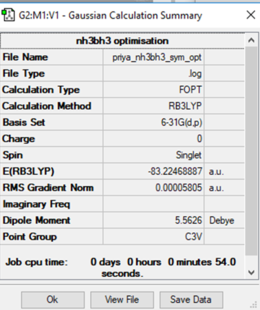
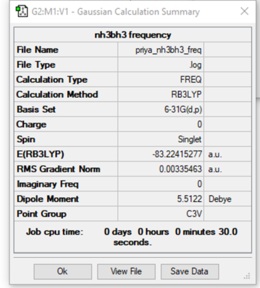
NH3BH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G (d,p)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000137 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000038 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001017 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000224 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.131227D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
Low frequencies --- -0.0172 -0.0141 -0.0074 100.7930 100.7958 165.6168 Low frequencies --- 421.7202 601.9051 685.5876
test molecule |
Energy Calculation
E(NH3) = -56.55777 a.u
E(BH3) = -26.61532 a.u
E(NH3BH3) = -83.22415 a.u
N-B bond strength = -83.22145 -(-56.55777+ -26.61532) = -0.05106 a.u = -134 kjmol-1
The N-B bond is a dative covalent bond. It is a relatively weak bond compared to the bond strength of C-N which is 305 kJ/mol
Correct calculation, the final reported value has the correct accuracy and good presentation of the energies of the three molecules. Nice comparison used to evaluate the bond strength, just make sure that any literature value used is referenced! Smf115 (talk) 12:22, 18 May 2019 (BST)
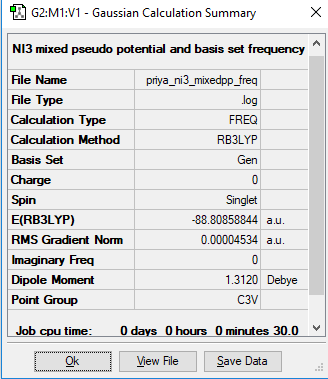
NI3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: GEN
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000114 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000079 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000735 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000543 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.081659D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
Low frequencies --- -12.7242 -12.7182 -6.3942 -0.0039 0.0189 0.0623 Low frequencies --- 101.0680 101.0688 147.4487
File:PRIYA NI3 MIXEDPP FREQ.LOG
test molecule |
Optimised N-I bond length: 2.18368
While your structure information is thorough and well done for including all the correct information, not all the calculations (e.g. BH3 3-21G(d,p) calcualtion) needed to be included, in the future consider the information you're presenting and if it is relevant. Additional presentation considerations are the lack of clear sections in the report and here the basis set presented is GEN which is just the Gaussian keyword, you actually used a mix of 6-31G(d,p) on N and the Lanl2dz pseudopotential and basis on the I. Smf115 (talk) 12:22, 18 May 2019 (BST)
Ionic Liquids: Designer Solvents
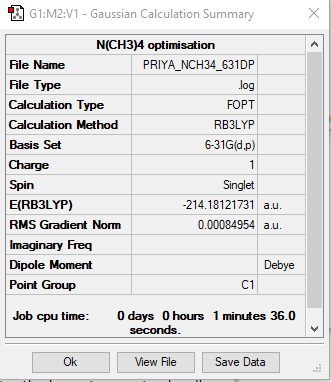
N(CH3)4 optimisation:
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31 (d,p)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000132 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000049 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001021 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000301 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.883750D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
Low frequencies --- -0.0013 -0.0013 -0.0009 32.7135 32.7135 32.7135 Low frequencies --- 213.0784 313.6512 313.6512
test molecule |
P(CH3)4 optimisation:
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31 (d,p)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000058 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000016 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000663 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000249 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.209118D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency analysis:
Low frequencies --- 0.0010 0.0012 0.0015 50.3813 50.3813 50.3813 Low frequencies --- 185.7545 210.8019 210.8019
test molecule |
Good inclusion of the charges on both molecules and attention has been given to the symmetry of the molecule in the final frequency calculations. Smf115 (talk) 20:31, 20 May 2019 (BST)
NBO Charge distribution:
The NBO charge analysis of N(CH3)4 and P(CH3)4 are differemt because they show a postive charge subsided on the phosphorus atom but a negative charge on the nitrogen atom.
The magnitude of the charges are also different; the magnitude of charge on the phosphorus atom is 1.667 which is much larger than the magnitude on the nitrogen atom (0.295). This shows that the phosphorus atom is more charged.
You've calculated the charges correctly which is good, however, presentation wise the resulting charges aren't clearly presented. Your analysis of the charge distribution is too brief and you needed to consider why these charges arise in the molecules (for example, think about the electronegativities or symmetry). Smf115 (talk) 20:39, 20 May 2019 (BST)
The traditional description of the positive charge on the nitrogen centre in the molecule N(CH3)4 is flawed by the NBO analysis. The NBO analysis shows a negative charge on the nitrogen atom and positive charges on the hydrogen atoms. In reality however the charges are not localised; they are distributed around the whole molecule.
You haven't really answered the question here of how does the +1 charge on the N arise in the traditional picture? Smf115 (talk) 20:39, 20 May 2019 (BST)
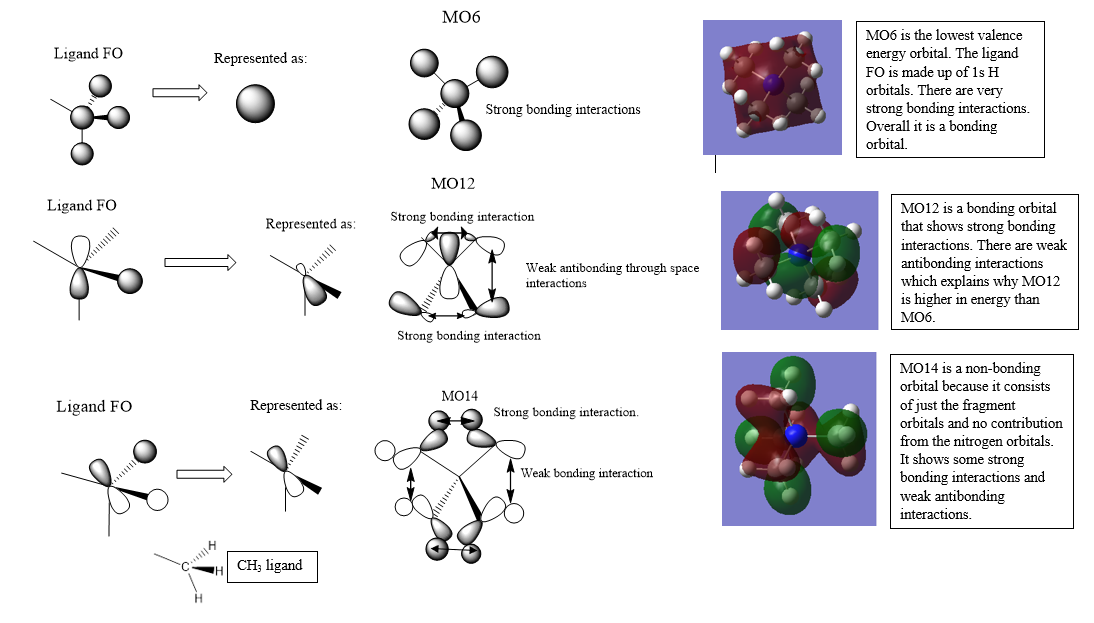
MOs from N(CH3)4
Clearly presented FOs and LCAOs and good analysis of the overall character of the MOs. You've made a good attempt at constructing the FOs but MO 12 isn't correct and considering the BH3 MO diagram may have helped. You have the right FO for MO14 but have then not used the representation in the LCAO, it would have also been nice to maybe see a more complex/antibonding MO chosen. Smf115 (talk) 22:15, 21 May 2019 (BST)
Overall, nice report with a good first section in particular. Smf115 (talk) 22:15, 21 May 2019 (BST)