Rep:Mod:mz5717
NH3
Molecule Name
Ammonia
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis Set
6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in Atomic Units (au)
-56.55776873
Point Group
C3v
'Item' Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986273D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol Dynamic Image
NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
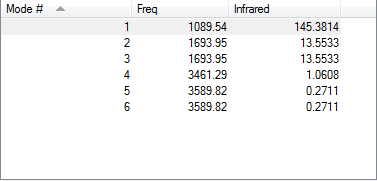
Vibrations
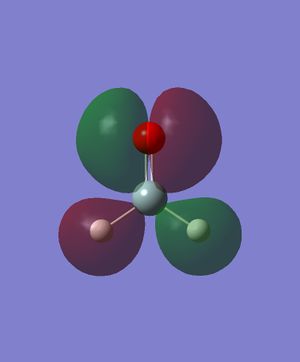
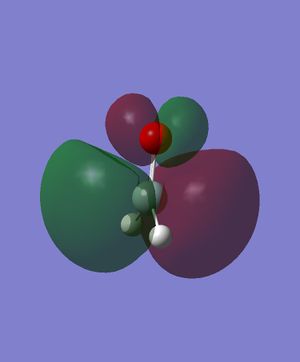
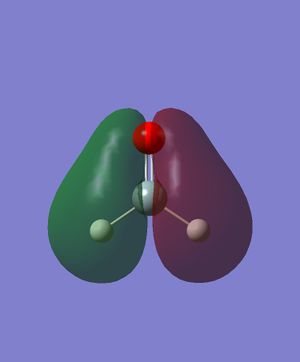
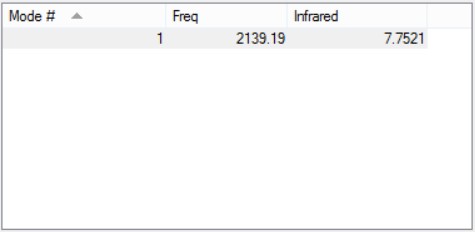
- One would expect 6 vibration modes from the 3N-6 rule.
- Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate; Modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
- Modes 1, 2 and 3 are 'bending' vibrations; Modes 4, 5 and 6 are 'bond stretch' vibrations.
- Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
- Mode 1 is the 'umbrella' mode.
- I would expect to see 2 bands in an experimental spectrum. Mode 1,2 and 3 have relatively strong permanent dipole, but Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate so we would only see 2 bands instead of 3. The change in dipole of Modes 4, 5 and 6 are negligible and we would likely not see them in the spectrum.
Charges
Charge on the N atom: -1.125
Charge on an H atom: 0.375
The result meets our expectation because N is much more electronegative than H. Thus the N atom is expected to carry a negative charge, and the H atoms are expected to carry positive charges.
H2
Molecule Name
Hydrogen
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis Set
6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in Atomic Units (au)
-1.17853935
Point Group
D∞h
'Item' Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000066 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000066 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000087 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000123 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.726834D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol Dynamic Image
H2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
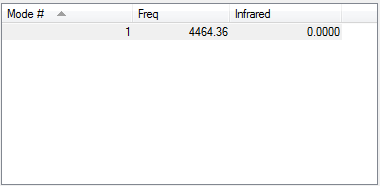
Vibrations
Charges
No charge on either atom.
N2
Molecule Name
Nitrogen
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis Set
6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in Atomic Units (au)
-109.52412868
Point Group
D∞h
'Item' Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401127D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol Dynamic Image
N2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
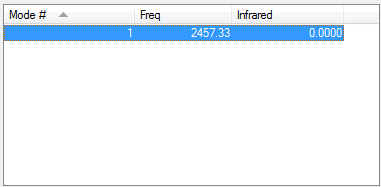
Vibrations
Charges
No charge on either atom.
Energy of the Haber Process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
Calculation
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)=2*(-56.55776873)=-113.11553746 au
E(N2)=-109.52412868 au
E(H2)=-1.17853935 au
3*E(H2)=3*(-1.17853935)=-3.53561805 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579073 au ≈-0.055791 au =-146.48 kJ/mol
The reaction is exothermic, which means that the product (NH3) is more stable.
H2SiO
Molecule Name
Silanone
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis Set
6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in Atomic Units (au)
-365.90001403
Point Group
C2v
'Item' Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000009 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000023 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000017 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.110523D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol Dynamic Image
H2SiO |
The optimisation file is linked to here
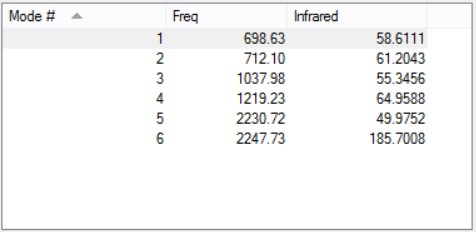
Vibrations
Charge Distribution
On the Si atom: 0.681
On the O atom: -0.502
On each of the H atom: -0.090
Molecular Orbitals
Energy: -0.2849747610. There is the constructive combination of two p orbitals in the same direction (one on Si and one on O respectively). There is also the destructive combination of 1s orbitals on the Hs with them. This is the HOMO, which is occupied by 2 electrons.
Energy: -0.0772801286. There is the destructive combination of two p orbitals in the same direction (one on Si and one on O respectively). There is also the constructive combination of the p orbital on Si with the two 1s orbitals on the Hs. This is the LUMO, but still in relatively lower energy than all the anti-bonding orbitals.
Energy: -0.3969718010. This is likely to be the constructive combination of two p orbitals in the same direction (one on Si and one on O respectively) and two 1s orbitals on the Hs. The two 1s orbitals have opposite signs. This MO is relatively deep in energy, and is a bonding orbital occupied by two electrons.
Energy: -3.6817834300. This is likely to be a p orbital of Si, not participating in bonding and occupied by two electrons. Relatively deep in energy.
Energy: -19.1231964000. This is likely to be the non-bonding 2s orbital on Si. Deepest in energy of all five orbitals shown here.
CN-
Molecule Name
Cyanide
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis Set
6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in Atomic Units (au)
-92.82453153
Point Group
D∞h
'Item' Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000005 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.650241D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol Dynamic Image
CN- |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Vibrations
Charge Distribution
Charge on the C atom: -0.416
Charge on the N atom: -0.584
HOMO and LUMO
Energy: 0.0185679972. This is the constructive combination of two 2p orbitals on C and N. This is the bonding HOMO which is occupied by 2 electrons.
Energy: 0.3543507530. This is the anti-bonding LUMO, resulting from the destructive combination of the 2p orbitals on C and N.