Rep:Mod:mywiki
NH3
Optimization
The optimization file is liked to here
NH3 |
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basic Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
N-H bond distance: 1.01798
H-N-H bond angle: 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986289D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
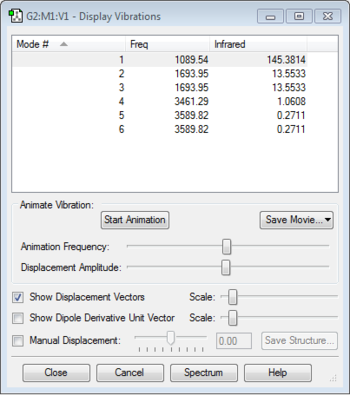
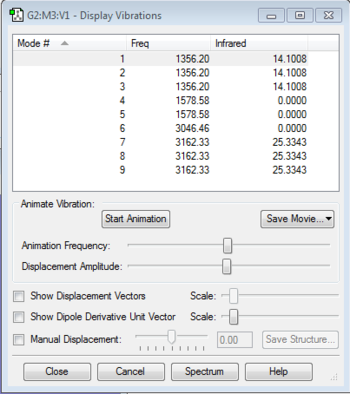
Vibration Analysis
6 modes are expected from the 3N-6 rule. Mode 5 and mode 6 are degenerate as they have the same frequency of 3589.86. Modes 1, 2 and 3 are "bending" vibrations while modes 4, 5 and 6 are "bond stretch" vibrations. Mode 4 is highly symmetric and mode 1 is known as the "umbrella" mode. 4 Bands would be seen in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
Charge Analysis
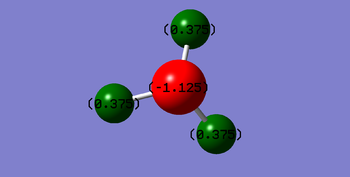
N is expected to be negatively charged while H is expected to be positively charged as N is more electronegative than H and therefore pulls electrons towards N, making it more negatively charged.
N2
Optimization
The optimisation file is liked to here
N2 |
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Bsaic set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Bond distance: 1.10550
Bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.400991D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
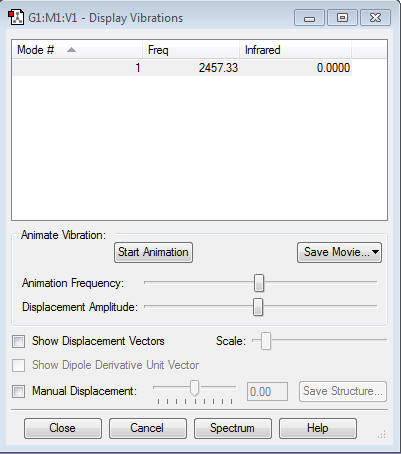
Vibration Analysis
H2
Optimization
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2 |
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point group: D*H
Bond length: 0.60000
Bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
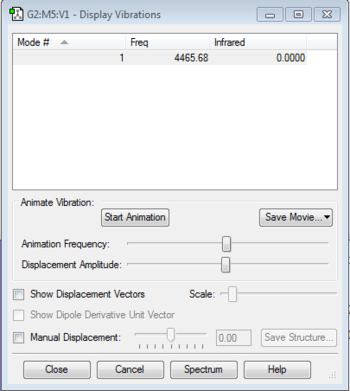
Vibration Analysis
Haber-Bosch Process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53591808 a.u.
Change in energy= 2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05549074 a.u.= -145.6909379 kJ/mol
Since energy is given off, it is an exothermic process. Thus the ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
CH4
Optimization
The optimisation file is liked to here
CH4 |
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy: -40.52401404 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00003263 a.u.
Point group: TD
Bond distance (C-H): 1.09197
Bond angle (H-C-H): 109.471
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.255986D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Vibration Analysis
9 modes are expected from the 3N-6 rule. Modes 1, 2 and 3 are degenerates. In addition, modes 4 and 5 are degenerates. Modes 7, 8 and 9 are also degenerates. Modes 1 to 5 are "bending" vibrations while modes 6-9 are "bond stretch" vibrations. Mode 6 is highly symmetric. Mode 2 is known as the "umbrella" mode. 6 bands are expected to been seen in an experimental spectrum.
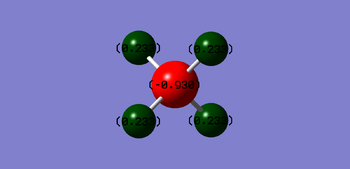
Charge Analysis
Carbon is expected to be negatively charged while hydrogen is expected to be positively charged as carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen. Therefore, carbon pulls electrons towards itself, making it negatively charged.
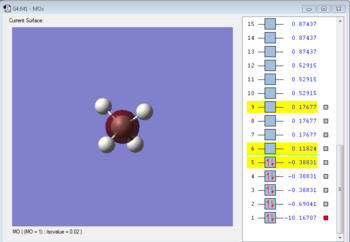
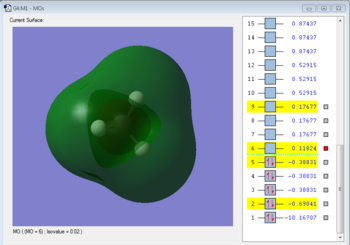
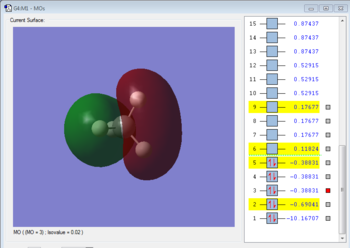
Molecular Orbitals Analysis
Bonding molecular orbital formed with 1s orbital of carbon. The MO is occupied. It is a HOMO and it forms bond by donating electrons.
Bonding molecular orbital formed by overlapping 2s orbital of carbon and 1s orbital of hydrogen. The MO is occupied. It is a HOMO and it forms bond by donating electrons.
Antibonding molecualr orbital formed by overlapping 2s orbital of carbon and 1s orbital of hydrogen. The MO is unoccupied. It is a LUMO and it forms bond by accepting electrons.
Bonding molecular orbital formed by overlapping 2p orbital of carbon and 1s orbital of hydrogen. The MO is occupied. It is a HOMO and it forms bond by donating electrons.
Antibonding molecular orbital formed by overlapping 2p orbital of carbon and 1s orbital of hydrogen. The MO is unoccupied. It is a LUMO and it forms bond by accepting electrons.