Rep:Mod:myfirstwikipage
NH3
Summary Information
Molecule: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy: -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.000000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
H-N-H Bond Angle: 105.74115o
N-H Bond Length: 1.01798 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986292D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NH3 molecule |
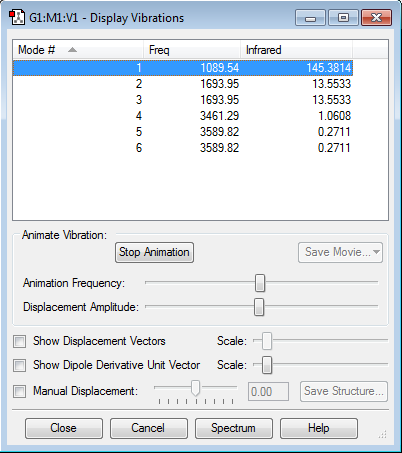
Vibrations
1) N = 4 , so the number of modes = 3 x 4 - 6 = 6. One would expect 6 vibrational modes.
2) Modes 2 and 3 and modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
3) Bending vibrations: modes 1,2 and 3 Bond stretches: modes 4,5 and 6
4) Mode 4
5) Mode 1
6) 5 bands. Mode 4 would not produce a band as it is a symmetric stretch and there is no change in dipole.
Charge Distribution
Charge on N-atom: -1.125
Charge on each H-atom: +0.375
We would expect the partial charge on the N-atom to be negative, as nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. Hence, the expected partial charge on the H-atoms of ammonia are expected to be positive. This agrees with the partial charges computed by Gaussview.
N2
Summary Information
Molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy: - 109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
N-N Bond Angle: 180o
N-N Bond Length: 1.10550 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401146D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
N2 molecule |
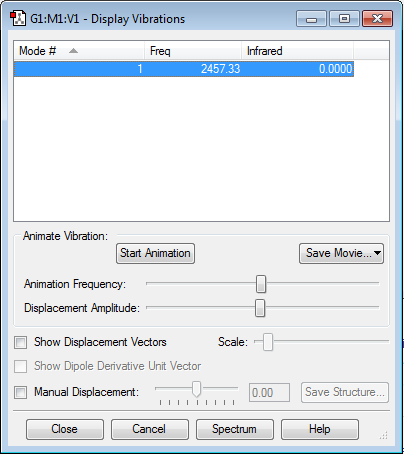
Vibrations
No negative frequencies
H2
Summary Information
Molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy: -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
H-H Bond Angle: 180o
H-H Bond Length: 0.74279 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
H2 molecule |
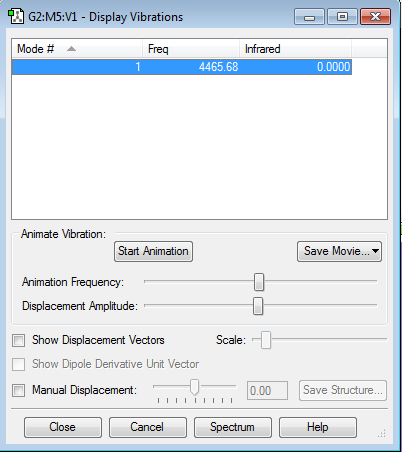
Vibrations
No negative frequencies
Haber-Bosch Reaction
N2 + H2 -> NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= - 109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE= 2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.1155375 - ( - 109.52412868 + -3.53561808) = -0.05579074 a.u.
ΔE= -0.05579074 a.u. = -0.05579074*2625.5 kJ/mol = -146.48 kJ/mol
HCl
Summary Information
Molecule: HCl
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy: -460.80077875 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00005211 a.u.
Point Group: C*V
H-Cl Bond Angle: 180o
H-Cl Bond Length: 1.28599 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.256951D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.286 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HCl molecule |
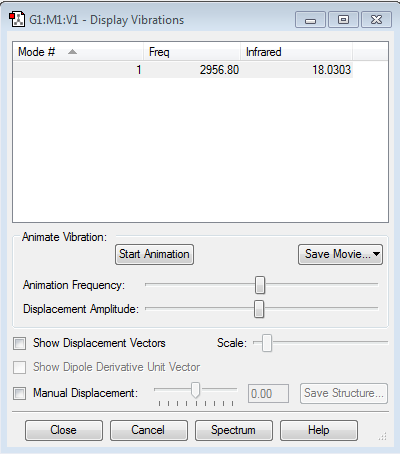
Vibrations
Number of vibrational modes: 1. This the number of modes one would anticipate, as 3*(2)-5 = 1 (according to the 3N-5 rule for linear molecules).
Charge Distribution
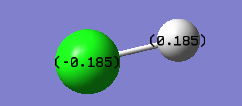
Charge on H-atom: +0.185
Charge on Cl-atom: -0.185
Charge distribution is equal and opposite, as expected, as the molecule is neutral overall. As anticipated, the more electronegative carries the negative partial charge.
Molecular Bonding
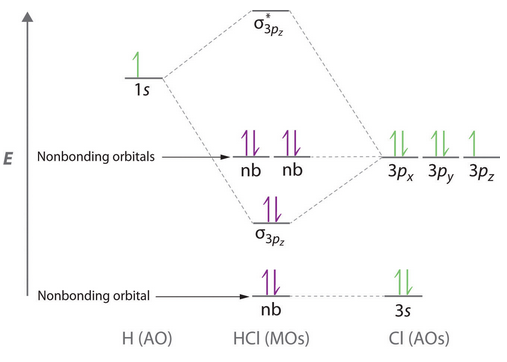
MO energy diagram of HCl (for n=3)
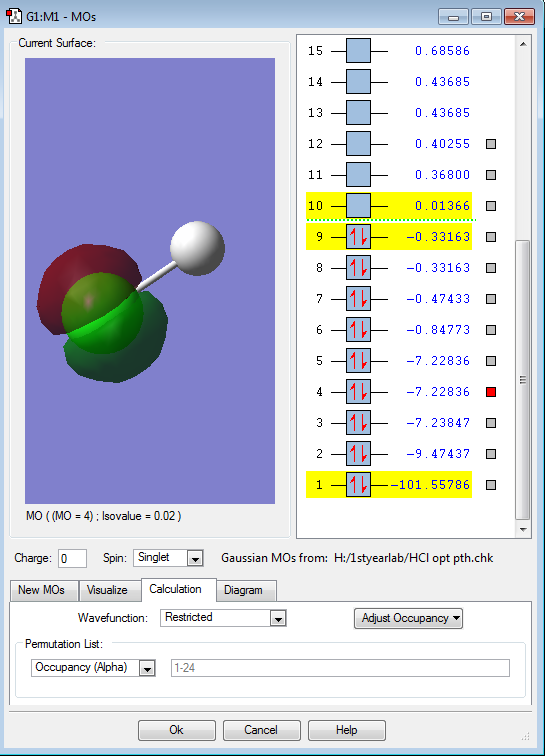
The image shows one the two non-bonding 2p-orbitals (from the Cl-atom). The energy of this orbital is -7.22836 a.u. . These two orbitals do not contribute to the bonding at all.
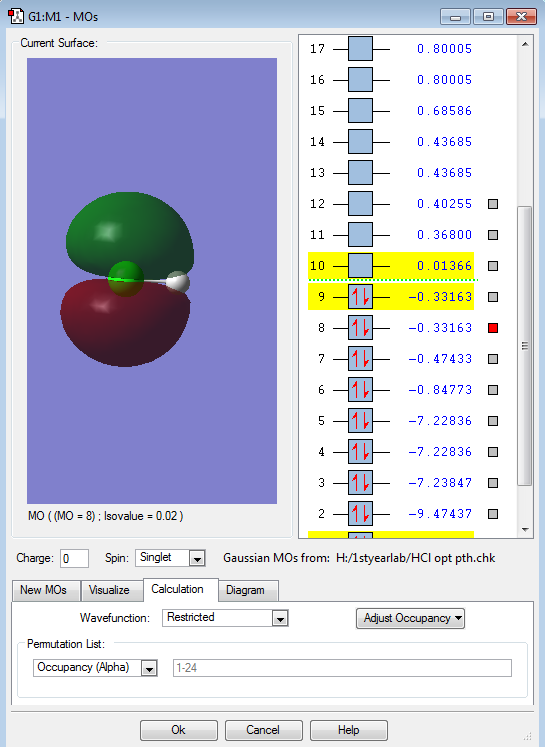
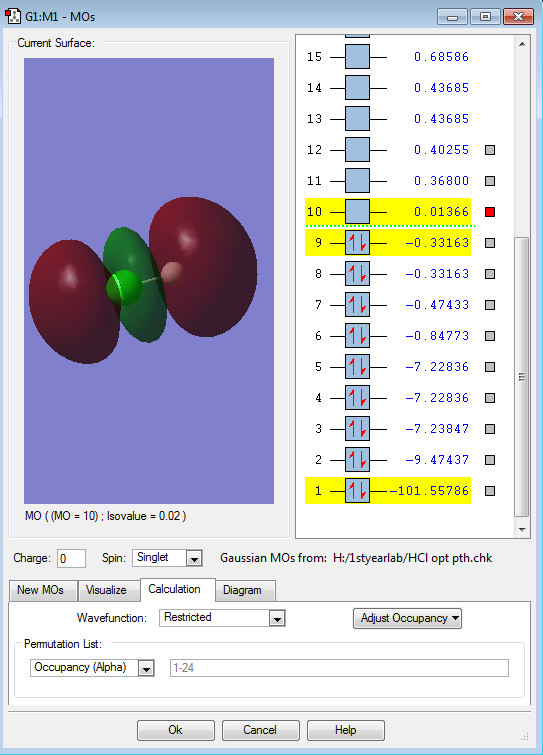
The image illustrates the σ3pz bonding orbital. This bonding σ-orbital is formed by the overlap of the H-atom's 1s-orbital and the Cl-atom's 3pz-orbital. The energy of the orbital is -0.47433 a.u. . It is evident, that the Cl-atom contributes more to the bonding than the H-atom, as the overall shape of the bonding orbital resembles a slightly rounded dumbbell. The dumbbell shape is similar to the 3pz-orbital form the Cl-atom involved in the bonding.
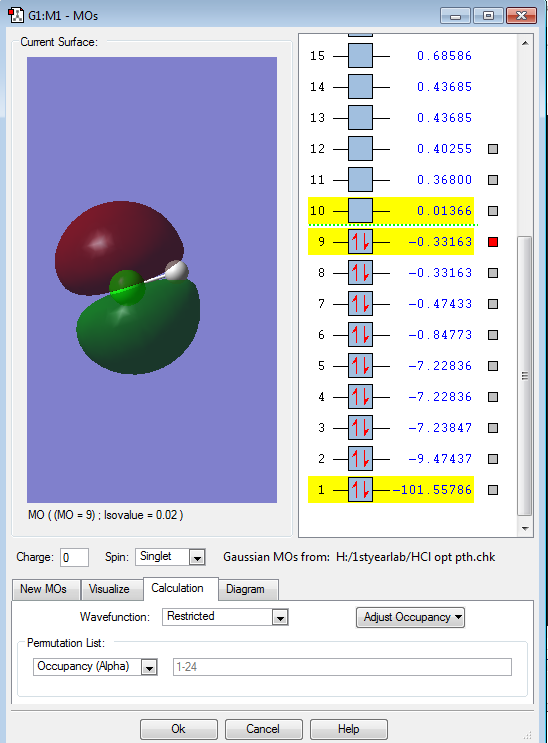
Each image shows one of the two non-bonding 3p-orbitals (3px and 3py)from the Cl-atom. Both orbitals are degenerate at an energy of -0.33163 a.u. . Each 3p-MO is occupied with two lone pair electrons. Both of these filled 3p-orbitals are degenerate HOMOs (highest occupied molecular orbitals). These two non-bonding orbitals do not contribute to the bonding at all.
The picture displays the anitbonding σ*pz orbital. This orbital is the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital), which is unfilled, containing no electrons. The energy of this antibonding orbital is 0.01366 a.u. .
Independent Work: Cl2
Summary Information
Molecule: Cl2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy: -920.34987886 a.u.
RMS Gradient: 0.00002510 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Cl-Cl Bond Angle: 180o
Cl-Cl Bond Length: 2.04174 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.277179D-09 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Vibrations
No negative frequencies
Charge Distribution
There is no charge on any of the two Cl-atoms, as expected. Each Cl-atom has an equal attraction for the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond.