Rep:Mod:mm2wp216
NH3 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP), FINAL ENERGY | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000485 a.u. |
| Point Group | C3V |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
N-H bond length = 1.01798 angstroms
H-N-H bond angle = 105.741 degrees
NH3 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis
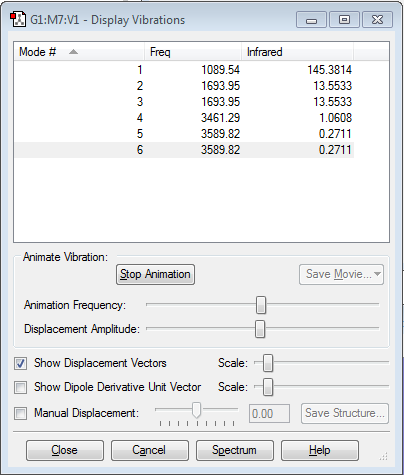
1. How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
2. Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
2 and 3, 5 and 6.
3. Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
1,2,3 are bending vibrations, 4,5,6 are bond stretching vibrations.
4. Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4
5. One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1
6. How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
4 bands
Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen and is therefore expected to be negatively charged (hydrogen = positive)
Nitrogen charge: -1.125 Hydrogen charge: +0.375
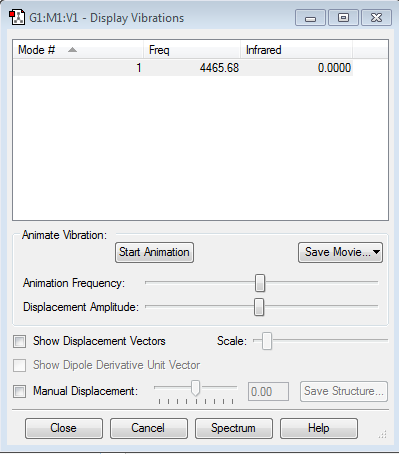
N2 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP), FINAL ENERGY | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis
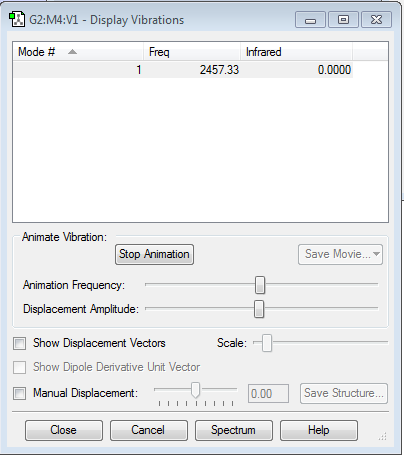
H2 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP), FINAL ENERGY | -1.15928020 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient | 0.09719500 a.u. |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis
Reactivity (Haber-Bosch Process)
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.15928020 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.4778406 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -20.11356922 a.u.=-52808.18 kJ/mol
F2 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP), FINAL ENERGY | -199.49825218 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00007365 a.u. |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
F-F bond length = 1.40 angstrom
F2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis
There is no change in dipole moment in F2 (not charged); the molecule is not IR active. No peak in IR spectrum.
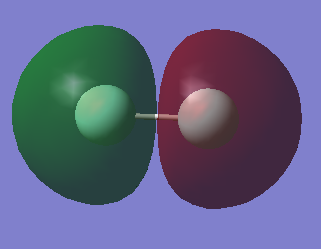
| MO | AOs | Bonding/Antibonding | Filled? | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2s | Bonding | Yes | |
 |
2s | Antibonding | Yes | |
 |
2p | Antibonding | Yes | |
 |
2p | Bonding | Yes | |
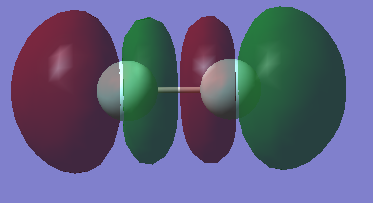 |
2p | Antibonding | No | LUMO |