Rep:Mod:mh2710tata
Computational lab module 2
Computational chemistry is widely used to predict structure ,energy and electronic charge distributions etc. to help running the real experiment and to solve problems for situations that impossible or too expensive to do experimentally.
In this computational lab, GaussView 5.0 was used to determine the structure, vibrational frequency and molecular orbitals of several similar molecules.
Week 1:Optimisation and Analysis of BH3, TlBr3, BBr3, NH3 and NH3BH3
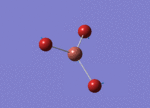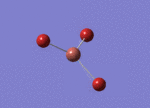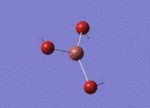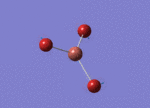
Create and optimise Molecule BH3 using basis set 3-21G
Create a BH3 molecule and change its bond length to 1.5 angstrom
The BH3 molecule created was then optimised with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 3-21G
BH3 Optimisation Summary Table
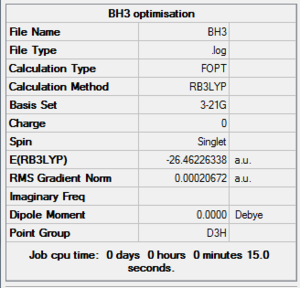
| File Name | BH3 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 3-21G |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.46226338 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00020672 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 15.0 seconds |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for BH3
Optimised B-H bond distance 1.19349 angstrom.
Optimised H-B-H bond angle 120.00002 degree.
Item Table for BH3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000413 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000271 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001581 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.001054 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.071764D-06
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimisation Log File of BH3
The optimisation file is linked to here.
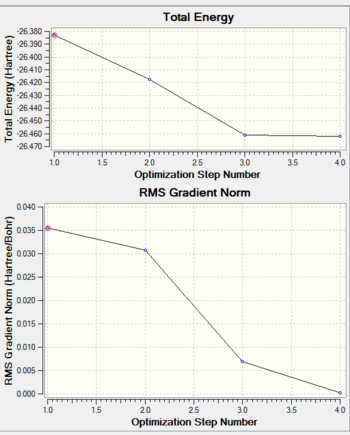
Optimistion Total Energy and RMS Gradient of BH3
Discussion
The RMS Gradient Norm is less than 0.001,which shows the optimisation is complete.
From the item table, all forces and displacements converged; optimisation goes to complete.
From the graph (total energy vs optimising step number),the total energy became stable between step 3 and 4, indicating reaching its minimum value.
From the graph (RMS Gradient Norm vs optimising step number), the force became 0 when the optimisation finished. From (where is the interatomic distance), changing of bond length should be 0 as force is 0.
Both bond length and minimum energy indicate the molecule has been optimised.
3-21G basis set was used here to provide a quick calculation with low accuracy.
Further optimisation of Molecule BH3 using basis set 6-31G
Open the log file for optimised BH3 from last step. The BH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
BH3 Optimisation Summary Table
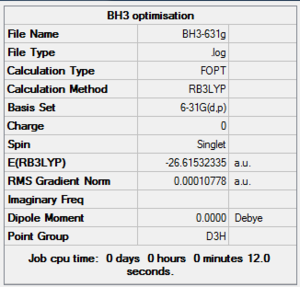
| File Name | BH3-631g |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.61532335 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00010778 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 12.0 seconds |
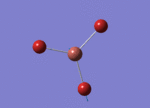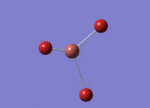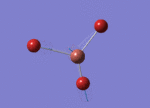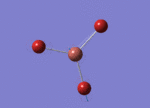
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for BH3
Optimised B-H bond distance 1.19189 angstrom.
Optimised H-B-H bond angle 119.99997 degree.
Item Table for BH3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000216 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000141 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000847 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000555 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.944350D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1919 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1919 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1919 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimisation Log File of BH3
The optimisation file is linked to here.
Discussion
The RMS Gradient Norm is less than 0.001,which shows the optimisation is complete.
From the item table, all forces and displacements converged; optimisation goes to complete.
From the graph (total energy vs optimising step number),the total energy became stable between step 3 and 4, indicating reaching its minimum value.
From the graph (RMS Gradient Norm vs optimising step number), the force went to 0 when the optimisation finished. From (where is the interatomic distance), changing of bond length should be 0 as force is 0.
Both bond length and minimum energy indicate the molecule has been optimised.
6-31G basis set was used here, which is more accurate as RMS Gradient Norm is closer to 0 when compared to 3-21G basis set.
Comparison of Energies of BH3
| Basis Set | Energy (a.u.) |
| 3-21G | -26.46226338 |
| 6-21G(d,p) | -26.61532335 |
| Difference in Energy | 0.15305997 |
By using 6-31G(d,p) basis set, the optimised system was 0.15305997 a.u.(401.8589512 kJ/mol) lower in energy.
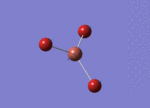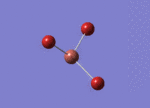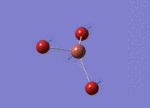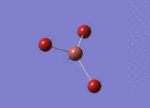
Create and optimise Molecule TlBr3 using basis set LanL2DZ
Draw out the TlBr3 trigonal planar and restrict its symmetry to point group D3h and increase the tolerance to 'Very tight (0.0001)'.
The TlBr3 molecule was optimised with calculation:
Job type: optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: LanL2DZ
Run calculation using HPC service.
TlBr3 Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23517
TlBr3 Optimisation Summary Table
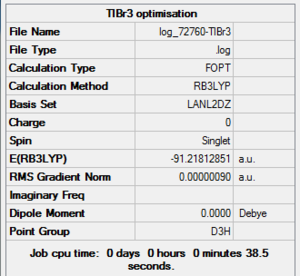
| File Name | log_72760-TlBr3 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -91.21812851 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000090 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 38.5 seconds |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for TlBr3
Optimised Tl-Br bond distance 2.65095 angstrom.
Optimisd Br-Tl-Br bond angle 120.00000 degree.
Literature[1] bond length: 2.512 angstroms.(percentage difference 5.5%)
- ↑ [1] J. Glaser, G. Johansson. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1982, 36a, Pp. 125-135. .
Optimisation Log File of TlBr3
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for TlBr3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.084086D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Create and optimise Molecule: BBr3
Open 6-31G(d,p) optimised log file for BH3 and change 'H' to 'Br'.
The BBr3 molecule was optimised with calculation:
Job type: optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: GEN
Additional keywords:pseudo=read gfinput
Save and open the saved copy. Go to the results tab and select view file, insert:
B 0 6-31G(d,p) **** Br 0 LanL2DZ **** Br 0 LanL2DZ
to the bottom section.
Run calculation using HPC service.
BBr3 Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked toDOI:10042/23554 .
BBr3 Optimisation Summary Table
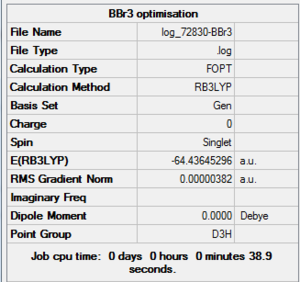
| File Name | log_72830-BBr3 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | GEN |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -64.43645296 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000382 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 38.9 seconds |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for BBr3
Optimised B-Br bond distance 1.93396 angstrom.
Optimised Br-B-Br bond angle 120.00001 degree.
Optimisation Log File of BBr3
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for BBr3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000023 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.028006D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Discussion
Analysis: BH3, BBr3, and TlBr3 Bond Distance and Bond Angle
| Molecule | Bond Distances | Bond Angle |
| BH3 | 1.19189 angstrom | 119.99997 degree |
| BBr3 | 1.93396 angstrom | 120.00001 degree |
| TlBr3 | 2.65095 angstrom | 120.00000 degree |
change ligand
BBr3 has larger bond length than BH3. This is because ligand Br is in row 4 and H is in row 1. Br is larger in size as it has more electron shells than H, therefore Br has more diffused electron orbital and has weaker overlap with the electron orbital of B. The bond strength of B-Br bond is weaker than B-H bond. what's more, Br is more electronegative than H, which polarises the B-Br covalent bond and weaken the bond strength.
change central atom TlBr3 has larger bond length than BBr3. This is because ligand Br is in row 2 and Tl is in row 6. The reasons are same as above.
Questions
In some structures GaussView does not draw in the bonds where we expect, does this mean there is no bond? Why?
Answer: No. They are there but not shown as the bond distance exceed the pre-defined GaussView distance value.
(2) What is a bond?
Answer:A bond is the attraction between atoms.
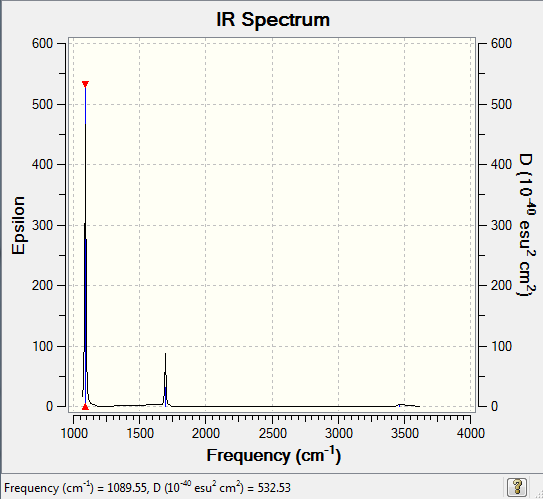
Frequency analysis for BH3
Open the log file for optimised BH3 (6-31G) from previous steps and save a copy. The BH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
BH3 Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23678
BH3 Frequency Summary Table
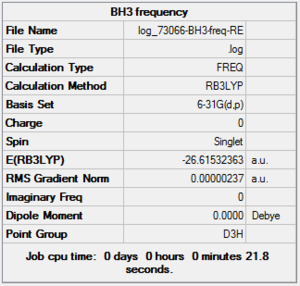
| File Name | log_73066_BH3-freq-RE |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000237 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 21.8 seconds |
Frequency Analysis Log File of BH3
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for BH3 Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -0.9033 -0.7343 -0.0055 6.7375 12.2491 12.2824
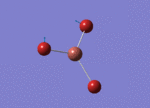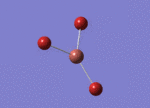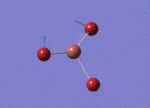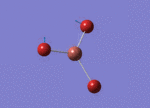
Low frequencies --- 1163.0003 1213.1853 1213.1880
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A2" E' E'
Frequencies -- 1163.0003 1213.1853 1213.1880
Red. masses -- 1.2531 1.1072 1.1072
Frc consts -- 0.9986 0.9601 0.9601
IR Inten -- 92.5478 14.0553 14.0589
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 5 0.00 0.00 0.16 0.00 0.10 0.00 -0.10 0.00 0.00
2 1 0.00 0.00 -0.57 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.81 0.00 0.00
3 1 0.00 0.00 -0.57 -0.39 -0.59 0.00 0.14 0.39 0.00
4 1 0.00 0.00 -0.57 0.39 -0.59 0.00 0.14 -0.39 0.00
Vibration Modes of BH3
IR Spectrum of BH3
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
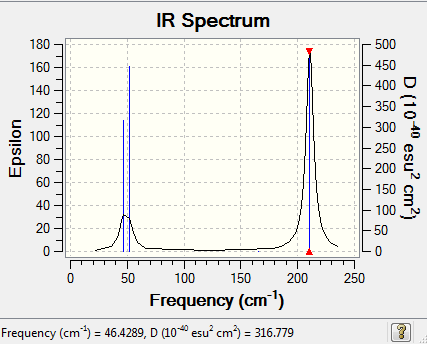
Frequency analysis for TlBr3
Open the log file for optimised TlBr3 from previous steps and save a copy. The TlBr3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: LanL2DZ
Run calculation using HPC service.
TlBr3 Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23631
TlBr3 Frequency Summary Table
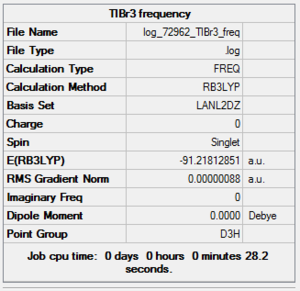
| File Name | log_72962_TlBr3_freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -91.21812851 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000088 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 28.2 seconds |
Frequency Analysis Log File of TlBr3
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for TlBr3 Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -3.4213 -0.0026 -0.0004 0.0015 3.9367 3.9367
Low frequencies --- 46.4289 46.4292 52.1449
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
E' E' A2"
Frequencies -- 46.4289 46.4292 52.1449
Red. masses -- 88.4613 88.4613 117.7209
Frc consts -- 0.1124 0.1124 0.1886
IR Inten -- 3.6867 3.6867 5.8466
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 81 0.00 0.28 0.00 -0.28 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.55
2 35 0.00 0.26 0.00 0.74 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.48
3 35 0.43 -0.49 0.00 -0.01 -0.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.48
4 35 -0.43 -0.49 0.00 -0.01 0.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.48
Vibration Modes of TlBr3
IR Spectrum of TlBr3
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
IR analysis: BH3 and TlBr3
Molecular Orbitals of BH3
Open the chk file for optimised BH3 from previous steps and save a copy. The BH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
BH3 Population Analysis "D-space" File
The population analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23694
BH3 MO Analysis Summary Table
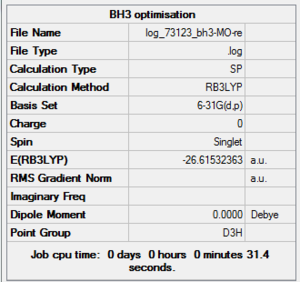
| File Name | log_73123_bh3_MO-re |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3h |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 31.4 seconds |
MO Analysis Log File of BH3
The MO analysis file is linked to here
MOs of BH3
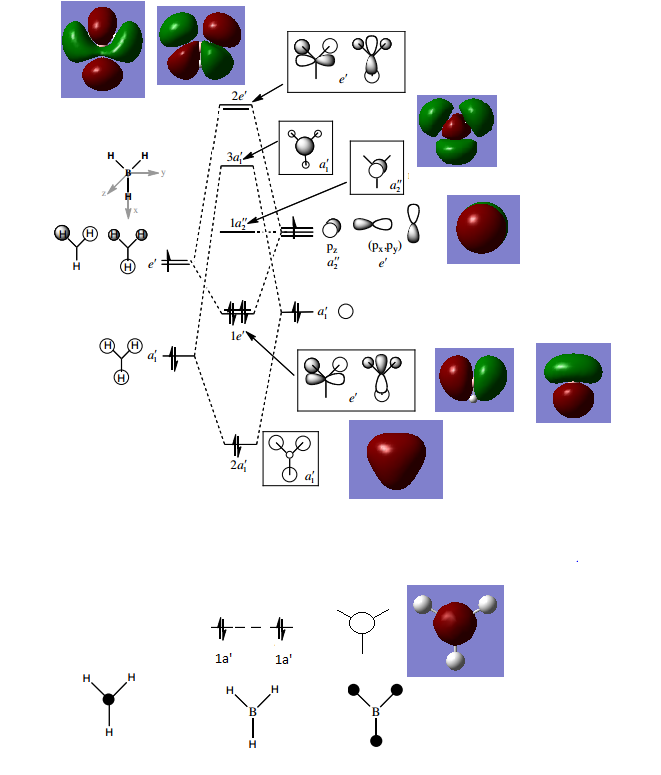
Discussion
Create and optimise NH3
Create a NH3 molecule. The NH3 molecule was then optimised with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
keywords:nosymm
Run calculation on HPC.
NH3 Optimisation Summary Table
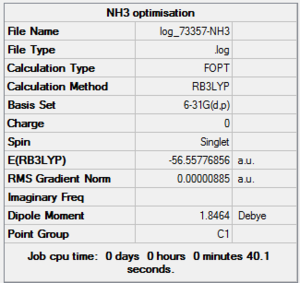
| File Name | log_73357-NH3 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776856 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000885 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8464 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 40.1 seconds |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for NH3
Optimised N-H bond distance 1.01797 angstrom.
Optimisd H-N-H bond angle 105.74139 degree.
Optimisation Log File of NH3
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for NH3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000024 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000079 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000053 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.629731D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7413 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7486 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7479 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Frequency analysis for NH3
Open the log file for optimised NH3 (6-31G) from previous steps and save a copy. The NH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
NH3 Frequency Summary Table
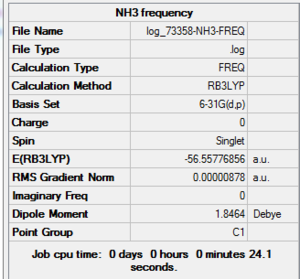
| File Name | log_73358-NH3-FREQ |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776856 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000878 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8464 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 24.1 seconds |
Frequency Analysis Log File of NH3
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for NH3 Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -30.8045 0.0011 0.0018 0.0021 20.2188 28.2150
Low frequencies --- 1089.5530 1694.1235 1694.1861
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 1089.5530 1694.1235 1694.1861
Red. masses -- 1.1800 1.0644 1.0644
Frc consts -- 0.8253 1.8000 1.8001
IR Inten -- 145.4405 13.5558 13.5561
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 7 0.12 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.02 -0.06 0.00 0.06 -0.02
2 1 -0.53 -0.21 0.00 -0.07 -0.04 0.73 0.25 0.14 0.19
3 1 -0.53 0.11 0.18 0.25 -0.24 -0.02 -0.07 -0.61 0.40
4 1 -0.53 0.11 -0.18 -0.18 0.52 0.18 -0.18 -0.41 -0.36
IR Spectrum of NH3
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
Molecular Orbitals of NH3
Open the chk file for optimised NH3 from previous steps and save a copy. The NH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
NH3 MO Analysis Summary Table
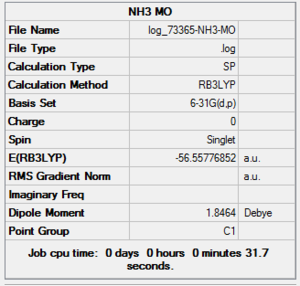
| File Name | log_73365-NH3-MO |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776852 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8464 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 31.7 seconds |
MO Analysis Log File of NH3
The MO analysis file is linked to here
Discussion
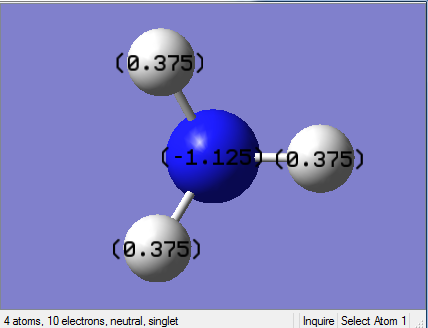
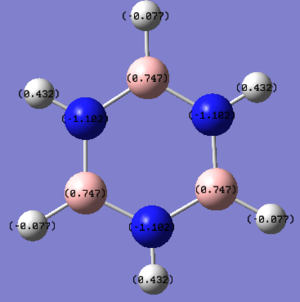
NBO Analysis of NH3
select type: NBO
Charge Distribution by Colour(range between -1.125 and 1.125)
Charge Distribution by Numbers
Ammonia-Borane
Optimisation of NH3BH3
Create a NH3BH3 molecule. The NH3BH3 molecule was then optimised with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation on HPC service.
NH3BH3 Optimisation Summary Table
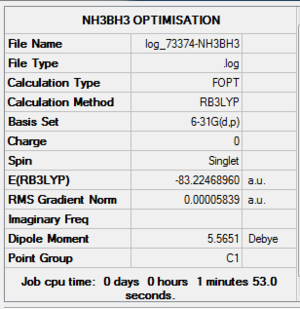
| File Name | log_73374-NH3BH3 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -83.22468960 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00005839 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 5.5651 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 53.0 seconds. |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for NH3BH3
Optimised B-H bond distance 1.21005 angstrom. Optimised N-H bond distance 1.01860 angstrom. Optimised N-B bond distance 1.66807 angstrom Optimised H-B-H bond angle 113.87427 degree. Optimised H-N-H bond angle 107.86829 degree.
Optimisation Log File of NH3BH3
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for NH3BH3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000124 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000057 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000660 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000304 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.649603D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,7) 1.21 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(2,7) 1.21 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(3,7) 1.21 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(4,8) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(5,8) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R6 R(6,8) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R7 R(7,8) 1.6681 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(1,7,2) 113.8754 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(1,7,3) 113.8742 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(1,7,8) 104.5931 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(2,7,3) 113.8743 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(2,7,8) 104.5962 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,7,8) 104.6001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(4,8,5) 107.8698 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(4,8,6) 107.8683 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,8,7) 111.0271 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(5,8,6) 107.87 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(5,8,7) 111.0319 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(6,8,7) 111.0285 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(1,7,8,4) 179.998 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(1,7,8,5) -60.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(1,7,8,6) 60.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(2,7,8,4) -60.0027 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,7,8,5) 59.9983 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,7,8,6) 180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(3,7,8,4) 59.9984 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(3,7,8,5) 179.9994 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,7,8,6) -59.9983 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Frequency Analysis of NH3BH3
Open the log file for optimised NH3BH3 (6-31G) from previous steps and save a copy. The NH3BH3 molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
NH3BH3 Frequency Analysis Summary Table

| File Name | log_73376-NH3BH3-FREQ |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -83.22468959 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00005841 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 5.5651 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 5.1 seconds |
Frequency Analysis Log File of NH3BH3
The Frequency Analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for NH3BH3 Optimisation
Low frequencies --- -0.0015 -0.0011 -0.0009 16.7610 22.0475 39.0806
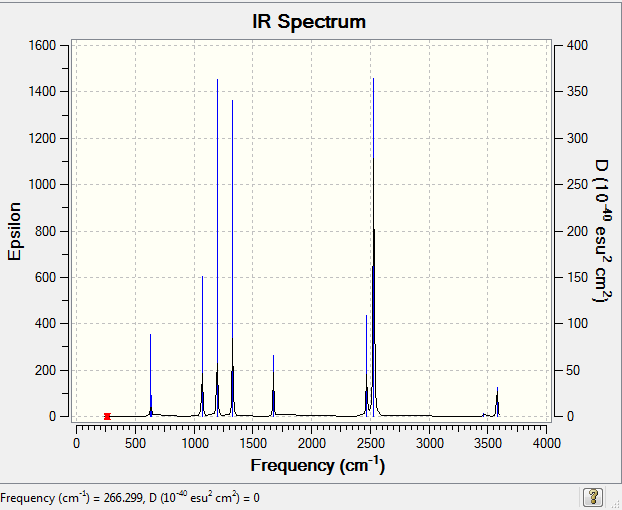
Low frequencies --- 266.2999 632.2669 638.6816
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 266.2993 632.2667 638.6816
Red. masses -- 1.0078 4.9955 1.0452
Frc consts -- 0.0421 1.1766 0.2512
IR Inten -- 0.0000 14.0138 3.5557
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 1 -0.11 -0.35 0.00 0.03 -0.01 0.28 0.10 0.11 -0.25
2 1 0.36 0.08 0.00 -0.01 0.03 0.30 0.12 0.08 -0.21
3 1 -0.24 0.27 0.00 -0.02 -0.03 0.28 0.09 0.07 0.46
4 1 -0.14 -0.43 0.00 0.00 -0.01 -0.37 0.14 0.14 -0.32
5 1 -0.30 0.33 0.00 0.00 -0.01 -0.37 0.14 0.11 0.58
6 1 0.44 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.34 0.17 0.12 -0.27
7 5 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.48 -0.02 -0.02 0.00
8 7 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.36 -0.04 -0.03 0.00
IR Spectrum of NH3BH3
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
Association Energy Analysis
The association energy is calculate by subtracting the energy of starting materials from the product.
| E(NH3) | E(BH3) | E(NH3BH3) |
|---|---|---|
| -56.55776856a.u. | -26.61532335a.u. | -83.22468960a.u. |
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]=-83.22468960-[(-56.55776856)+(-26.61532335)]=-0.05159769a.u.=-135.4697155kJ/mol
Week 2 Mini Project: Investigating Aromaticity
Benzene
Create and optimise Benzene
Create a benzene molecule and then optimise with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Benzene Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23773
Benzene Optimisation Summary Table
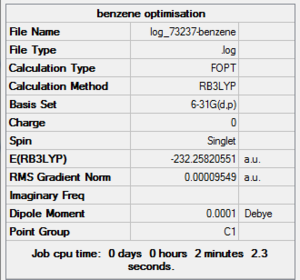
| File Name | log_73237-benzene |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -232.25820551 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00009549 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0001 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 2 minutes 2.3 seconds. |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for Benzene
Optimised C-H bond distance 1.08605 angstrom.
Optimisd C-C-H bond angle 120.00857 degree.
Optimisation Log File of Benzene
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for Benzene Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000212 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000085 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000991 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000315 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.157454D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,6) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R3 R(1,7) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R5 R(2,8) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R7 R(3,9) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R8 R(4,5) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R9 R(4,10) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R10 R(5,6) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R11 R(5,11) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R12 R(6,12) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,6) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,7) 119.9949 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(6,1,7) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,8) 119.9881 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,8) 120.004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,9) 120.0086 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,3,9) 119.9966 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(3,4,5) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,10) 119.9934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(5,4,10) 120.0094 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(4,5,6) 120.0083 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(4,5,11) 120.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(6,5,11) 119.9904 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(1,6,5) 119.9946 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(1,6,12) 120.0106 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,6,12) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(6,1,2,3) -0.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(6,1,2,8) 180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(7,1,2,3) -180.01 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(7,1,2,8) -0.0019 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,6,5) -0.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,6,12) -179.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(7,1,6,5) -180.0013 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(7,1,6,12) 0.007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) 0.0117 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,9) -179.9914 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(8,2,3,4) 180.0036 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(8,2,3,9) 0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,5) -0.0062 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,10) -180.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(9,3,4,5) 179.9969 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(9,3,4,10) -0.0028 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,5,6) -0.0051 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,5,11) 180.0058 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(10,4,5,6) -180.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(10,4,5,11) 0.0054 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(4,5,6,1) 0.011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(4,5,6,12) 180.0027 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,6,1) -179.9999 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,6,12) -0.0082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Discussion
Frequency analysis for Benzene
Open the log file for optimised benzene 6-31G(d,p) from last step and save a copy. The benzene molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Benzene Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23790
Benzene Frequency Summary Table

| File Name | log_73261-benzene-freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -232.25820551 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00009549 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0001 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 5 minutes 37.1 seconds. |
Frequency Analysis Log File of Benzene
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for Benzene Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -17.2788 -14.5868 -9.6527 -0.0009 -0.0007 -0.0005
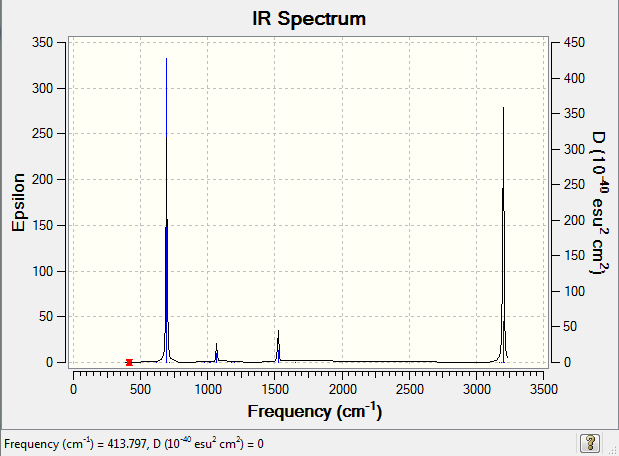
Low frequencies --- 413.7971 414.4697 620.8545
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 413.7971 414.4697 620.8540
Red. masses -- 2.9404 2.9434 6.0705
Frc consts -- 0.2966 0.2979 1.3786
IR Inten -- 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 6 0.00 0.00 -0.15 0.00 0.00 0.19 0.23 -0.26 0.00
2 6 0.00 0.00 0.24 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.16 0.05 0.00
3 6 0.00 0.00 -0.09 0.00 0.00 -0.22 0.22 0.19 0.00
4 6 0.00 0.00 -0.15 0.00 0.00 0.19 -0.23 0.26 0.00
5 6 0.00 0.00 0.24 0.00 0.00 0.03 -0.16 -0.05 0.00
6 6 0.00 0.00 -0.09 0.00 0.00 -0.22 -0.22 -0.19 0.00
7 1 0.00 0.00 -0.32 0.00 0.00 0.42 0.30 -0.17 0.00
8 1 0.00 0.00 0.52 0.00 0.00 0.07 -0.20 0.11 0.00
9 1 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.48 0.30 -0.05 0.00
10 1 0.00 0.00 -0.32 0.00 0.00 0.42 -0.30 0.17 0.00
11 1 0.00 0.00 0.52 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.20 -0.11 0.00
12 1 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.48 -0.30 0.05 0.00
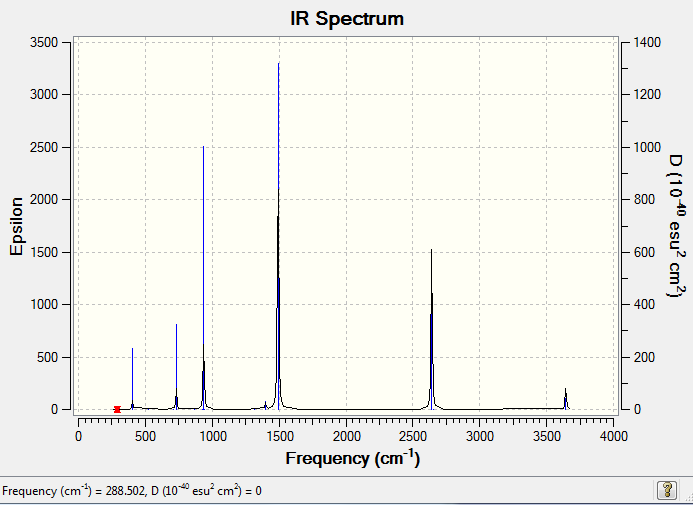
IR Spectrum of benzene
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
Discussion
MO Analysis of Benzene
Open the chk file for optimised benzene from previous steps and save a copy. The benzene molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
Benzene MO Analysis Summary Table
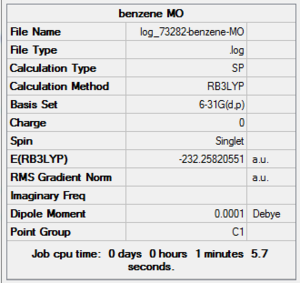
| File Name | log_73282-benzene-MO |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -232.25820551 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0001 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 5.7 seconds |
Benzene Population Analysis "D-space" File
The Population Analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23883
MOs of Benzene
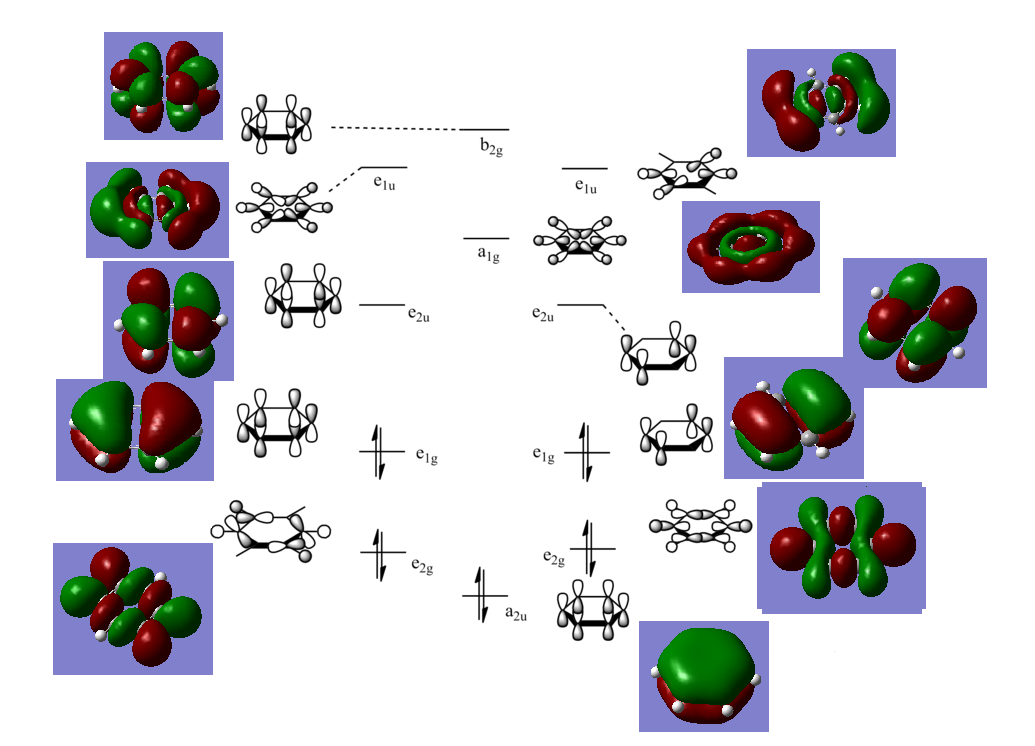
NBO Analysis of Benzene
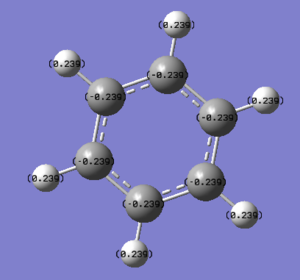
select type: NBO
Charge Distribution by Colour(range between -0.239 and 0.239)
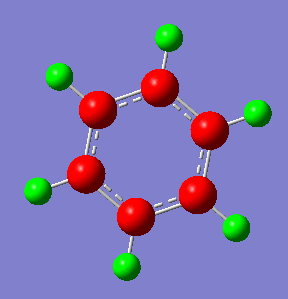
Charge Distribution by Numbers
Boratabenzene
Create and optimise Boratabenzene
Create a boratabenzene molecule and then optimise with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Boratabenzene Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23885
Boratabenzene Optimisation Summary Table
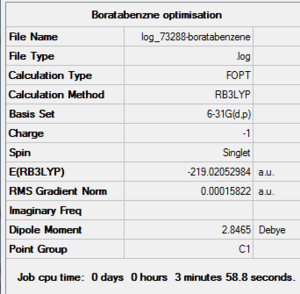
| File Name | log_73288-boratabenzene |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | -1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00015822 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 2.8465 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 3 minutes 58.8 seconds. |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for Boratabenzene
Optimised B-H bond distance 1.21848 angstrom.
Optimised C-H bond distance 1.09698; 1.09677; 1.09165 angstrom.
Optimised B-C bond distance 1.51381;1.51375 angstrom.
Optimised C-C bond distance 1.39890;1.40528;1.40532;1.39887 angstrom.
Optimisd C-B-H bond angle 122.44818;122.44225 degree.
Optimisd B-C-H bond angle 123.96970;123.96524 degree.
Optimisd C-C-H bond angle 115.94940;120.42370;117.43697;119.77597;119.77319;117.43516;120.42671;115.95351 degree.
Optimisation Log File of Boratabenzene
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for Boratabenzene Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000159 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000069 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000911 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000335 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.630178D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3989 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,6) 1.097 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,12) 1.5137 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.4053 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0968 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.4053 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0917 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R8 R(4,5) 1.3989 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R9 R(4,9) 1.0968 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R10 R(5,10) 1.097 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.5138 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R12 R(11,12) 1.2185 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,6) 115.9494 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A2 A(2,1,12) 120.0809 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A3 A(6,1,12) 123.9697 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 122.1393 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 120.4237 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 117.437 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 120.4508 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 119.776 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 119.7732 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A10 A(3,4,5) 122.1381 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A11 A(3,4,9) 117.4352 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(5,4,9) 120.4266 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! A13 A(4,5,10) 115.9535 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A14 A(4,5,12) 120.0812 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A15 A(10,5,12) 123.9653 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A16 A(1,12,5) 115.1096 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(1,12,11) 122.4482 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,11) 122.4422 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(6,1,2,3) 180.01 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(6,1,2,7) -0.0042 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(12,1,2,3) 0.0084 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(12,1,2,7) -180.0058 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,12,5) 0.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,12,11) -180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,12,5) -180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,12,11) -0.0017 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) -0.015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) -180.0108 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) -180.0011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) 0.0031 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,5) 0.0116 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,9) 180.0045 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,5) 180.0075 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,9) 0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,5,10) -180.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,5,12) -0.002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,5,10) 0.0018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,5,12) 180.0053 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(4,5,12,1) -0.0042 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(4,5,12,11) -180.0032 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(10,5,12,1) 179.9996 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(10,5,12,11) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Discussion
Frequency analysis for Boratabenzene
Open the log file for optimised boratabenzene 6-31G(d,p) from last step and save a copy. The boratabenzene molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Boratabenzene Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23887
Boratabenzene Frequency Summary Table
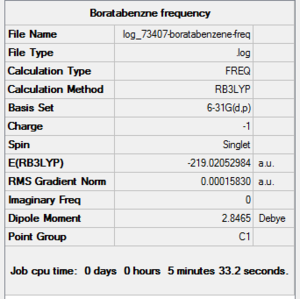
| File Name | log_73407-boratabenzene-freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | -1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00015830 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 2.8465 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 5 minutes 33.2 seconds. |
Frequency Analysis Log File of Boratabenzene
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for Boratabenzene Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -13.1243 -0.0008 -0.0008 -0.0007 15.0607 18.1733
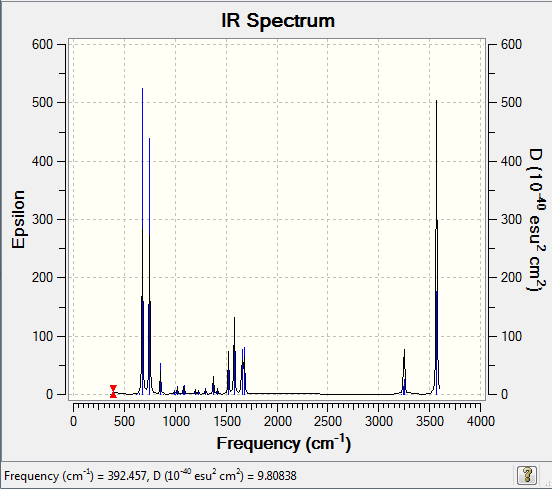
Low frequencies --- 371.3450 404.2340 565.2523
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 371.3449 404.2333 565.2523
Red. masses -- 2.6884 3.2177 5.7648
Frc consts -- 0.2184 0.3098 1.0852
IR Inten -- 2.3000 0.0000 0.1575
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 6 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.23 -0.22 0.21 0.00
2 6 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 -0.22 0.23 0.22 0.00
3 6 0.00 0.00 -0.21 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00
4 6 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.22 0.23 -0.21 0.00
5 6 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00 -0.23 -0.22 -0.21 0.00
6 1 0.00 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.00 0.36 -0.34 -0.06 0.00
7 1 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.52 0.31 0.08 0.00
8 1 0.00 0.00 -0.38 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.21 0.00 0.00
9 1 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.52 0.31 -0.08 0.00
10 1 0.00 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.00 -0.36 -0.34 0.06 0.00
11 1 0.00 0.00 -0.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.29 0.00 0.00
12 5 0.00 0.00 -0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.17 0.00 0.00
IR Spectrum of boratabenzene
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
MO Analysis of Boratabenzene
Open the chk file for optimised benzene from previous steps and save a copy. The benzene molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
Boratabenzene Population Analysis "D-space" File
The Population Analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23889
Boratabenzne MO Analysis Summary Table
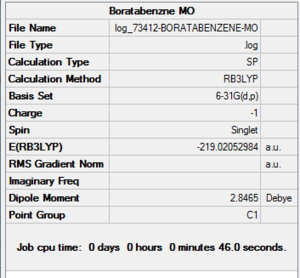
| File Name | log_73412-BORATABENZENE-MO |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | -1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 2.8465 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 46.0 seconds |
MO Analysis Log File of Boratabenzene
The MO analysis file is linked to here
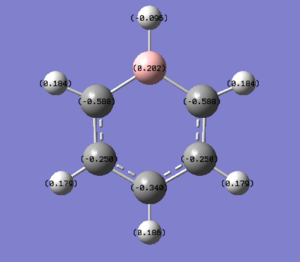
NBO Analysis of Boratabenzene
select type: NBO
Charge Distribution by Colour(range between -0.588 and 0.588)
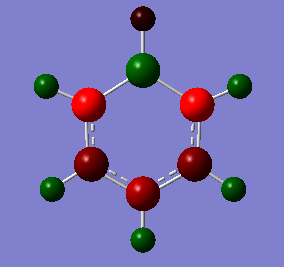
Charge Distribution by Numbers

Pyridinium
Create and optimise Pyridinium
Create a pyridinium molecule and then optimise with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Pyridinium Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23923
Pyridinium Optimisation Summary Table
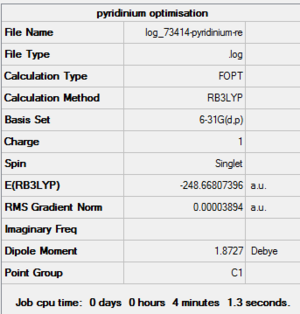
| File Name | log_73414-pyridinium-re |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00003894 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8727 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 4 minutes 1.3 seconds. |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for Pyridinium
Optimised N-C bond distance 1.35237;1.35234 angstrom.
Optimised C-C bond distance 1.38386;1.39876;1.39879;1.38384 angstrom.
Optimised N-H bond distance 1.01692 angstrom.
Optimised C-H bond distance 1.08324; 1.08352; 1.08520 angstrom.
Optimisd C-N-H bond angle 118.34498;138.34624 degree.
Optimisd N-C-H bond angle 116.83192;116.83400 degree.
Optimisd C-C-H bond angle 123.92972;119.41926;121.49880;119.97397;119.97112;121.49597;119.42133;123.93269 degree.
Optimisation Log File of Pyridinium
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for Pyridinium Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000065 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000023 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000826 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000176 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.972574D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,5) 1.3838 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,6) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0852 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(4,9) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R9 R(4,12) 1.3523 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R10 R(5,11) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.3524 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(10,12) 1.0169 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,5) 119.0827 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,6) 121.496 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A3 A(5,1,6) 119.4213 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0549 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 119.9711 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 119.974 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 121.4988 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 119.4192 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A10 A(3,4,9) 123.9297 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,12) 119.2363 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(9,4,12) 116.834 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(1,5,11) 123.9327 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(1,5,12) 119.2354 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(11,5,12) 116.8319 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(4,12,5) 123.3088 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,10) 118.3463 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,10) 118.345 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,1,2,3) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,1,2,7) -180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(6,1,2,3) 180.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(6,1,2,7) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,5,11) -180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,5,12) 0.0021 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,5,11) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,5,12) 180.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) -0.0024 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) -180.0018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) 180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) 0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,9) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,12) 0.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,9) -0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,12) 180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,12,5) 0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,12,10) -180.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,12,5) 180.0025 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,12,10) 0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,5,12,4) -0.0032 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,5,12,10) -180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,12,4) -180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,12,10) 0.0016 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Discussion
Frequency analysis for Pyridinium
Open the log file for optimised pyridinum 6-31G(d,p) from last step and save a copy. The pyridinium molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Pyridinium Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23924
Pyridinium Frequency Summary Table
| File Name | log_73421-pyridinium-freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00003897a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8727 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 5 minutes 38.8 seconds. |
Frequency Analysis Log File of Pyridinium
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for Pyridinium Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -7.2115 -0.0003 -0.0003 0.0009 17.3444 18.5499
Low frequencies --- 392.4572 404.0614 620.4717
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 392.4571 404.0614 620.4717
Red. masses -- 2.9474 2.7453 6.2544
Frc consts -- 0.2675 0.2641 1.4187
IR Inten -- 0.9649 0.0000 0.0144
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 6 0.00 0.00 -0.14 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.03 0.23 0.00
2 6 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.39 0.00 0.00
3 6 0.00 0.00 -0.14 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.03 -0.23 0.00
4 6 0.00 0.00 -0.11 0.00 0.00 0.19 -0.03 -0.20 0.00
5 6 0.00 0.00 -0.11 0.00 0.00 -0.19 -0.03 0.20 0.00
6 1 0.00 0.00 -0.29 0.00 0.00 0.40 -0.25 0.08 0.00
7 1 0.00 0.00 0.61 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.39 0.00 0.00
8 1 0.00 0.00 -0.29 0.00 0.00 -0.40 -0.25 -0.08 0.00
9 1 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.00 0.00 0.51 0.25 -0.01 0.00
10 1 0.00 0.00 0.46 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.35 0.00 0.00
11 1 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.51 0.25 0.01 0.00
12 7 0.00 0.00 0.21 0.00 0.00 0.00 -0.34 0.00 0.00
IR Spectrum of pyridinium
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
MO Analysis of Pyridinium
Open the chk file for optimised pyridinium from previous steps and save a copy. The pyridinium molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
Pyridinium Population Analysis "D-space" File
The Population Analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23926
Pyridinium MO Analysis Summary Table
| File Name | log_73423-pyridinium-MO |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 1 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8727 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 20.9 seconds |
MO Analysis Log File of Pyridinium
The MO analysis file is linked to here
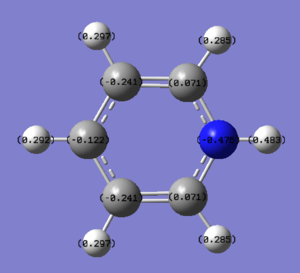
NBO Analysis of Pyridinium
select type: NBO
Charge Distribution by Colour(range between -0.483 and 0.483)
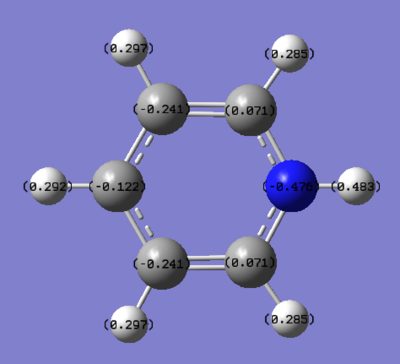
Charge Distribution by Numbers
Borazine
Create and optimise Borazine
Create a borazine molecule and then optimise with calculation:
Job type:optimisation
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Borazine Optimisation "D-space" File
The optimisation "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23927
Borazine Optimisation Summary Table
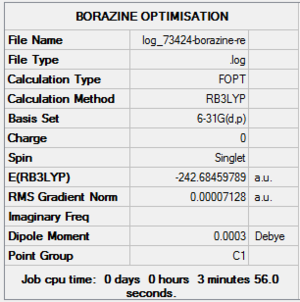
| File Name | log_73424-borazine-re |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -242.68459789 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00007128 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0003 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 3 minutes 56.0 seconds. |
Optimised Bond Length and Bond Angle for Borazine
Optimised N-B bond distance 1.43070;1.43063;1.43066;1.43068 angstrom.
Optimised N-H bond distance 1.00970 angstrom.
Optimised B-H bond distance 1.19488 angstrom.
Optimisd B-N-H bond angle 118.56716;118.56218;118.55542;118.56655;118.56631;118.55983 degree.
Optimisd N-B-H bond angle 121.43140;121.44383;121.43392;121.44572;121.43672;121.43696 degree.
Optimisation Log File of Borazine
The optimisation file is linked to here
Item Table for Borazine Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000117 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000036 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000327 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000104 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.206131D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,9) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(2,11) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R3 R(3,8) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(4,12) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R5 R(5,7) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(6,10) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R7 R(7,10) 1.4307 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(7,12) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R9 R(8,11) 1.4306 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R10 R(8,12) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R11 R(9,10) 1.4306 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(9,11) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(5,7,10) 118.5554 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(5,7,12) 118.5605 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(10,7,12) 122.884 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,8,11) 118.5598 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,8,12) 118.5663 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(11,8,12) 122.8739 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(1,9,10) 118.5621 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(1,9,11) 118.5672 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(10,9,11) 122.8707 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(6,10,7) 121.4339 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(6,10,9) 121.4439 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(7,10,9) 117.1222 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(2,11,8) 121.437 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(2,11,9) 121.4314 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(8,11,9) 117.1316 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(4,12,7) 121.4457 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,8) 121.4367 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(7,12,8) 117.1176 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,7,10,6) -0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,7,10,9) 179.9989 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(12,7,10,6) 179.9979 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(12,7,10,9) -0.0026 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(5,7,12,4) 0.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(5,7,12,8) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(10,7,12,4) -179.9977 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(10,7,12,8) 0.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,8,11,2) 0.0011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(3,8,11,9) -180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(12,8,11,2) 179.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(12,8,11,9) -0.0022 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(3,8,12,4) -0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(3,8,12,7) 179.9995 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(11,8,12,4) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(11,8,12,7) 0.0009 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(1,9,10,6) 0.0011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(1,9,10,7) -179.9984 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(11,9,10,6) -179.9993 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(11,9,10,7) 0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,9,11,2) -0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,9,11,8) 180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(10,9,11,2) -180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(10,9,11,8) 0.0011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Discussion
Frequency analysis for Borazine
Open the log file for optimised borazine 6-31G(d,p) from last step and save a copy. The borazine molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:frequency
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Run calculation using HPC service.
Borazine Frequency Analysis "D-space" File
The frequency analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23928
Borazine Frequency Summary Table
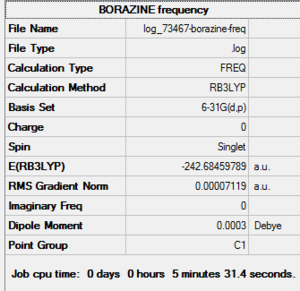
| File Name | log_73467-borazine-freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -242.68459789 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00007119 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0003 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 5 minutes 31.4 seconds. |
Frequency Analysis Log File of Borazine
The frequency analysis file is linked to here
Item Table for Borazine Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -11.1123 -0.0005 0.0003 0.0008 8.6668 11.2356
Low frequencies --- 288.5023 290.4097 404.0141
Harmonic frequencies (cm**-1), IR intensities (KM/Mole), Raman scattering
activities (A**4/AMU), depolarization ratios for plane and unpolarized
incident light, reduced masses (AMU), force constants (mDyne/A),
and normal coordinates:
1 2 3
A A A
Frequencies -- 288.5022 290.4095 404.0136
Red. masses -- 2.9264 2.9236 1.9244
Frc consts -- 0.1435 0.1453 0.1851
IR Inten -- 0.0000 0.0000 23.6788
Atom AN X Y Z X Y Z X Y Z
1 1 0.00 0.00 -0.22 0.00 0.00 -0.15 0.00 0.00 0.16
2 1 0.00 0.00 -0.06 0.00 0.00 0.69 0.00 0.00 0.53
3 1 0.00 0.00 0.24 0.00 0.00 -0.11 0.00 0.00 0.16
4 1 0.00 0.00 -0.57 0.00 0.00 -0.40 0.00 0.00 0.53
5 1 0.00 0.00 -0.02 0.00 0.00 0.27 0.00 0.00 0.16
6 1 0.00 0.00 0.63 0.00 0.00 -0.29 0.00 0.00 0.53
7 7 0.00 0.00 -0.02 0.00 0.00 0.24 0.00 0.00 -0.13
8 7 0.00 0.00 0.22 0.00 0.00 -0.10 0.00 0.00 -0.13
9 7 0.00 0.00 -0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.14 0.00 0.00 -0.13
10 5 0.00 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 -0.09 0.00 0.00 0.10
11 5 0.00 0.00 -0.02 0.00 0.00 0.22 0.00 0.00 0.10
12 5 0.00 0.00 -0.18 0.00 0.00 -0.13 0.00 0.00 0.10
IR Spectrum of borazine
The IR spectrum was shown as follow:
MO Analysis of Borazine
Open the chk file for optimised borazine from previous steps and save a copy. The borazine molecule was then further optimised with calculation:
Job type:energy
Method:DFT B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
NBO: full NBO
Additional keywords:'pop=full'
Run calculation using HPC service.
Borazine Population Analysis "D-space" File
The Population Analysis "D-space" file is linked to DOI:10042/23980
Borazine MO Analysis Summary Table
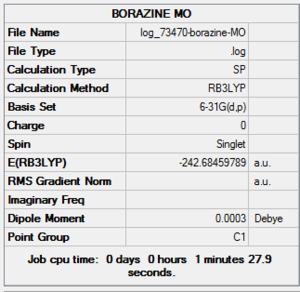
| File Name | log_73470-borazine-MO |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -242.68459789 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0003 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Job CPU Time | 0 days 0 hours 1 minutes 27.9 seconds |
MO Analysis Log File of Borazine
The MO analysis file is linked to here
NBO Analysis of Borazine
select type: NBO
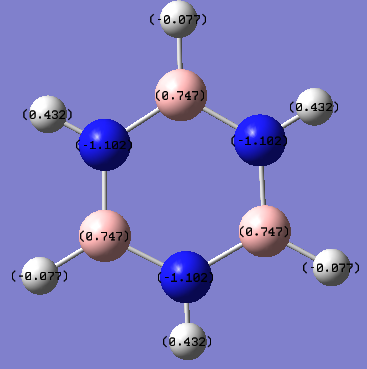
Charge Distribution by Colour(range between -1.102 and 1.102)
Charge Distribution by Numbers
Discussion
Charge Distribution Comparison
| Molecule | Benzene | Boratabenzene | Pyridinium | Borazine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO 21(HOMO) energy | -0.24691 | 0.01094 | -0.47885 | -0.27590 |
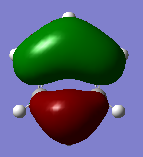
| MO 20 energy | -0.24692 | -0.03493 | -0.50847 | -0.27591 |
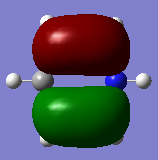
| MO 19 energy | -0.33960 | -0.08387 | -0.57432 | -0.31994 |
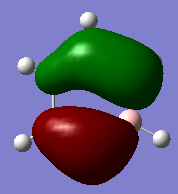
Molecular orbital Comparison
| Molecule | Benzene | Boratabenzene | Pyridinium | Borazine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO 21(HOMO) | 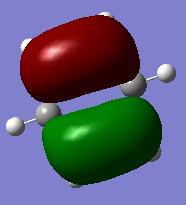 |
 |
 |
|
| MO 20 | 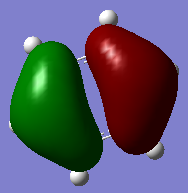 |
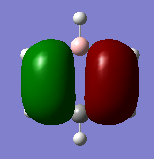 |
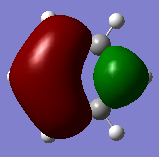 |
|
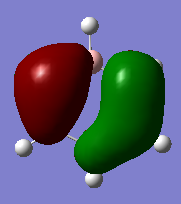
| MO 19 | 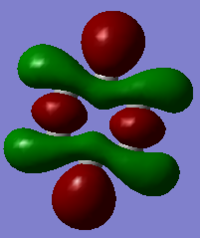 |
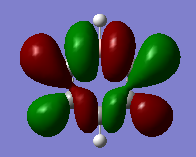 |
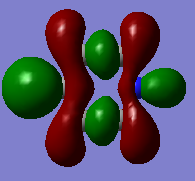 |

|
Aromaticity
The compounds all fulfil Huckel's rules of aromaticity, which are 1)having 4n+2 pi electrons (n=0,1,2,3...), 2)being planar and 3) having a conjugated cyclic pi system perpendicular to the ring. From the MOs of the compounds, we can see that there are indeed pi systems sandwiching the ring. In addition, the molecular orbitals are spread over multiple carbon atoms. There are three bonding orbitals, which correspond to a total of 6 pi electrons.
Charge distribution
The charge distribution in benzene is uniform (-0.225), which is consistent with the fact that all the atoms have the same electronegativity. The negative sign indicates a build up of electron density in the ring, which conforms to the view of a pi electron cloud in the middle of the ring. It is also due to the fact that C is more electronegative than H.
In boratabenzene, the boron atom exhibits electron deficiency (+0.202) as compared to the C atoms (-0.588 to -0.250) due to its lower electronegativity. This is in spite of the fact that we draw a negative charge on the boron atom. This shows that the system of formal charges is merely for our convenience and is not representative of the real charge density that we observe in the molecule. We can also draw resonance forms that place the negative charge on the ortho (-0.588) and para (-0.340) positions, and thus these are more electron rich than the meta positions (-0.250).
This is also the case in pyridinium. In most representations of pydridinium, the positive charge is placed on the N atom, however it is shown to actually possess the most electron density out of all the atoms on the ring due to its high electronegativity (-0.475). Resonance forms place the positive charge on the ortho and para positions and thus these have less electron density (0.071 and -0.122 respectively) as compared to the meta position (-0.241).
In borazine, the alternation of B and N atoms leads to an alternation between electron poor (0.747) and electron rich (-1.102) areas on B and N respectively. As the molecule is symmetrical, the electron density on each of the B and N's are the same.
MOs
The MOs of the four aromatic molecules are roughly similar in terms of the number of lobes and the number of nodal planes. As benzene is symmetric, all its MOs have a certain degree of symmetry. However, the presence of heteroatoms in the other aromatics have an impact on the shape of the Mos.
Comparing boratabenzene to benzene, MO 21 of boratabenzene has a larger lobe on the side with the boron as compared to the side without boron. The p orbital on boron has a large coefficient as it is less contracted due to its lower electronegativity. MO 20 of boratabenzene is similar to MO 21 of benzene as the MO does not involve boron. Breaking the C2 symmetry of benzene also results in breaking of the degeneracy of MOs 20 and 21. MO 19 corresponds to MO 18 of benzene (not shown), which is degenerate with MO 19 of benzene. This degeneracy is broken, and MO 19 is the one higher in energy as there is less electron density on the electropositive B.
For pyridinium, the relative energies of MO 21 and 20 are different. Again the broken C2 symmetry results in this loss of degeneracy. MO 20 has a smaller lobe on the side containing nitrogen. This is because the N 2p orbital is contracted relative to the C 2p orbital as a result of its greater electronegativity. MO 19 has the same shape as its corresponding benzene counterpart, however, the lobe of N is smaller due to the high electronegativity of N.
In the case of borazine, MOs 21 and 20 are again degenerate since it has a C2 axis of symmetry. The shapes are roughly similar to those of benzene. MO 19 also has the same shape has that of benzene, however, the size of the lobes are larger on the B atoms for reasons as mentioned above.