Rep:Mod:mg4417
Miren Gami (CID:01206786)
Introduction to Molecular Modelling 2 wiki report
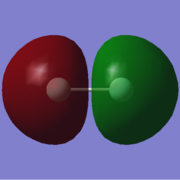
Optimised NH3 molecule
Key Information
Optimisation Summary
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point group: C3V
Geometric Information
Bond angle: 105.741°
Bond length: 1.01798 Å
"Item" table
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy= -5.986294D-10
Jmol and LOG file
Optimised ammonia molecule |
Analysis
Frequency

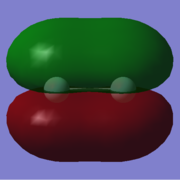
"Umbrella" mode in ammonia |
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?: 6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?: 2 and 3; 5 and 6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?: 1,2 and 3 are "bending" vibrations, 4,5 and 6 are "bond stretch" vibrations
Which mode is highly symmetric? 1 and 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2
Charge
Charge on N is -1.125
Charge on H is 0.375

These charges are as expected. The nitrogen atom is expected to be negatively charged since it is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms and pulls electron density from them. The hydrogen atoms would therefore be positively charged.
Optimised N2 molecule
Key Information
Optimisation Summary
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000365 a.u.
Point group: D∞H
Geometric Information
Bond angle: 180°
Bond length: 1.10550 Å
"Item" table
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000006 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000006 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000002 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000003 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy= -1.248809D-11
Jmol and LOG file
Optimised nitrogen molecule |
Analysis
Frequency

Bond stretching in the nitrogen molecule |
Charge
N2 is a homonuclear diatomic molecule so both atoms have the same electronegativity and the electron density is equally distributed between them. As a result, the atomic charge on either atom is zero.
Optimised H2 molecule
Key Information
Optimisation Summary
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853930 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00012170 a.u.
Point group: D∞H
Geometric Information
Bond angle: 180°
Bond length: 0.74309 Å
"Item" table
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000211 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000211 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000278 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000393 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy= -5.852867D-08
Jmol and LOG file
Optimised hydrogen molecule |
Analysis
Frequency analysis

Bond stretching in the hydrogen molecule |
Charge
H2 is a homonuclear diatomic molecule so both atoms have the same electronegativity and the electron density is equally distributed between them. As a result, the atomic charge on either atom is zero.
Haber-Bosch reaction energies
• E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
• 2*E(NH3)=2*-56.55776873 a.u. = -113.11553746 a.u.
• E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
• E(H2)= -1.17853930 a.u.
• 3*E(H2)=3*-1.17853930 a.u.= -3.5356179 a.u.
• ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579088 a.u.
-0.05579088 a.u.= -146.48 kJ/mol
For 1 mol of NH3: -73.24 kJ/mol
This is an exothermic reaction, the gaseous NH3 is lower in energy than the products and therefore more stable.
Optimised F2 molecule
Key Information
Optimisation Summary
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -199.49825218 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00007365 a.u.
Point group: D∞H
Geometric Information
Bond angle: 180°
Bond length: 1.40281 Å
"Item" table
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000128 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000128 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000156 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000221 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy= -1.995025D-08
Jmol and LOG file
Optimised fluorine molecule |
Analysis
Frequency analysis

Bond stretching in the fluorine molecule |
Charge
F2 is a homonuclear diatomic molecule so both atoms have the same electronegativity and the electron density is equally distributed between them. As a result, the atomic charge on either atom is zero.
Molecular Orbitals
- First 12 MOs in the optimised fluorine molecule (hover over image for further information)
-
1. energy=-24.7973016000, fully occupied.
-
2. energy=-24.7973016000, fully occupied.
-
3. energy=-1.3365938700, fully occupied.
-
4. energy=-1.0904729200, fully occupied.
-
5. energy=-0.5875332540, fully occupied.
-
6. energy=-0.5233218740, fully occupied.
-
7. energy=-0.5233218740, fully occupied.
-
8. energy=-0.3918998830, fully occupied.
-
9. energy=-0.3918998830, fully occupied.
-
10. energy=-0.1267921140, unoccupied.
-
11. energy=0.8392253090, unoccupied.
-
12. energy=0.9647877580, unoccupied.
Five interesting orbitals
2: σ* orbital with ungerade symmetry formed from an out-of-phase combination of 1s atomic orbitals on both fluorine atoms. This is an antibonding orbital that is very deep in energy with an energy of -24.7973016000. It is doubly occupied. It will have no effect on bonding due to its low energy.
5: σ orbital with gerade symmetry formed from an in-phase combination of 2px atomic orbitals on both fluorine atoms. This is a bonding orbital that is slightly lower in energy than the HOMO/LUMO region with an energy of -0.5875332540. It is doubly occupied. It participates in bonding.
9: π* orbital with gerade symmetry formed from an out-of-phase combination of 2pz atomic orbitals on both fluorine atoms. This is an antibonding orbital that is in the HOMO/LUMO region with an energy of -0.3918998830. It is doubly occupied and is therefore the HOMO, along with MO 8, which is degenerate. It does not have an effect on bonding.
10: σ* orbital with ungerade symmetry formed from an out-of-phase combination of 2px atomic orbitals on both fluorine atoms. This is an antibonding orbital that is in the HOMO/LUMO region with an energy of -0.1267921140. It is unoccupied and is therefore the LUMO. It does not have an effect on bonding as it is completely unoccupied.
11: σ orbital with gerade symmetry formed from an in-phase combination of 3s atomic orbitals on both fluorine atoms. This is a bonding orbital that is high in energy with an energy of 0.8392253090. It is unoccupied and does not have an effect on bonding.