Rep:Mod:ma6516
NH3 Molecule
| Type of Molecule | NH3 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -56.55776873 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000323 |
| Point group | C3V |
| NH bond length (A) | 1.01798 |
| HNH bond angle | 105.745 |
A literature value for the HNH bond angle in NH3 is 106.7. This shows that the optimization value is very accurate.[1] A literature value for the NH bond length in NH3 is 1.012. This also shows that the optimization value is very accurate.[1]
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000014 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000009 0.001200 YES
Ammonia |
Media:MA6516PHUNT_NH3_OPTF_POP.LOG

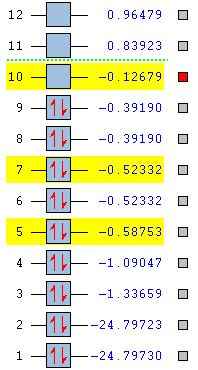
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6 Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? (2 and 3), (5 and 6) Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? bending (1, 2, 3) stretching(4, 5, 6) Which mode is highly symmetric? 4 One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1 How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2. This is due to mode 1 having a strong intensity. Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate and also have relatively strong intensities. The other 3 modes have such small intensities they are probably not visible on the spectrum.

When carrying out calculations it is always good to check your results against your expectations. Write a sentence saying what charge (positive or negative) you would expect for N and H and why. I would expect the hydrogen atoms in ammonia to carry a more positive charge and the nitrogen atom to carry a more negative charge as nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons attached whereas the hydrogen atoms are just positively charged nuclei as they have each shared an electron to form sigma bonds with the nitrogen. Also nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so it is expected that it carries the negative charge. As expected the hydrogen atoms are positively charged and the nitrogen atom is negatively charged.
H2 Molecule
| Type of Molecule | H2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -1.17853936 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Point group | D*H |
| HH bond length (A) | 0.60000 |
A literature value for the bond length in H2 is 0.74 angstrom. This shows that the optimization value is relatively accurate.[2] There is no overall charge in hydrogen as it is a diatomic homonuclear molecule, so no overall charge or polarity arises within the molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES

Hyrdogen |
N2 Molecule
| Type of Molecule | N2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -109.52412868 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 |
| Point group | D*H |
| NH bond length (A) | 1.09200 |
A literature value for the bond length in N2 is 1.10 angstrom. This shows that the optimization value is relatively accurate.[2] There is no overall charge in nitrogen as there it is a diatomic homonuclear molecule, so there is no overall charge or polarity within the molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES

Nitrogen |
Haber-Bosch process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
| E(NH3) | -56.55 |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11 |
| E(N2) | -109.52 |
| E(H2) | -1.18 |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.54 |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -0.06 |
Values above are in Hartrees. Value for ΔE in kJ/mol is -146.48. Identify which is more stable the gaseous reactants or the ammonia product? The ammonia product is more stable as it is overall lower in energy than the gaseous reactants
Project Molecule F2

| Type of Molecule | F2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -199.49825218 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00007365 |
| Point group | D*H |
| FF bond length (A) | 1.40281 |
A literature value for the bond length in F2 is 1.42 angstrom. This shows that the optimization value is relatively accurate.[2]
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Fluorine |
Molecular Orbitals F2

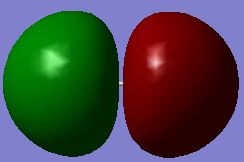
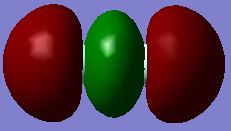

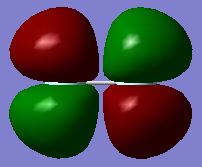

Reaction of fluorine with water
2F2 + 2H2O ==> O2 + 4HF
| E(H2O) | -76.42 |
| E(F2) | -199.50 |
| E(O2) | -150.27 |
| E(HF) | -100.43 |
| 2*E(H2O) | -152.84 |
| 4*E(HF) | -401.71 |
| ΔE=[4*E(HF) + E(O2)] - [2*E(F2) + 2*E(H2O)] | -0.14 |
Values above given in Hartrees. The value for ΔE in kJ/mol is -367.34.
H2O
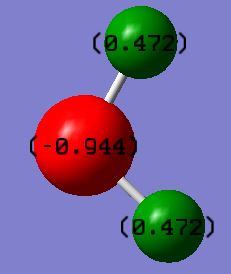
| Type of Molecule | H2O |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -76.41973740 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00006276 |
| Point group | D2V |
| OH bond length (A) | 0.96522 |
| HOH bond angle | 103.745 |
A literature value for the bond length in H2O is 0.96 angstrom. A literature value for the HOH bond angle is 104.5. This shows that the optimization is relatively accurate.[3]
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES

Water |
O2
| Type of Molecule | O2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -150.26605044 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00007560 |
| Point group | D2V |
| OO bond length (A) | 1.16 |
A literature value for the OO bond length is 1.12 angstrom. This shows that the optimization is relatively accurate.[4]. As oxygen is a diatomic homonuclear molecule, there is no overall charge or dipole within the molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000131 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000131 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000081 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000115 0.001200 YES

Oxygen |
HF
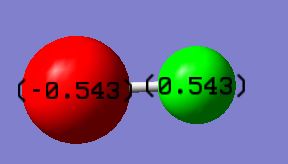
| Type of Molecule | HF |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -100.42746153 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00001092 |
| Point group | C*V |
| HF bond length (A) | 0.88000 |
A literature value for the bond length in HF is 0.92 angstrom. This shows that the optimization is relatively accurate.[3]
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000019 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000019 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000016 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000022 0.001200 YES
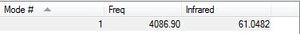
Hydrogen Fluoride |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th ed. http://www.hbcpnetbase.com. Page 9-26.Retrieved 18 June 2013. via https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammonia_(data_page)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Huheey, pps. A-21 to A-34; T.L. Cottrell, "The Strengths of Chemical Bonds," 2nd ed., Butterworths, London, 1958; B. deB. Darwent, "National Standard Reference Data Series," National Bureau of Standards, No. 31, Washington, DC, 1970; S.W. Benson, J. Chem. Educ., 42, 502 (1965).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/o-h-bond-lengths-water-molecule-h20-096-h-o-h-angle-1045o-dipolemoment-water-molecule-185--q279785
- ↑ http://www.science.uwaterloo.ca/~cchieh/cact/c120/bondel.html
