Rep:Mod:longjohnsilver359
‘DAY 1
BH3
H-B bond length = 1.19435 Å
HBH angle = 120.0°
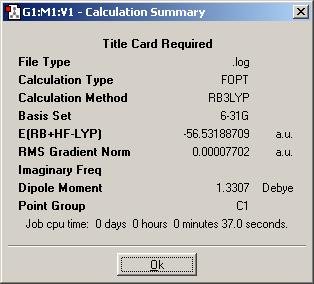
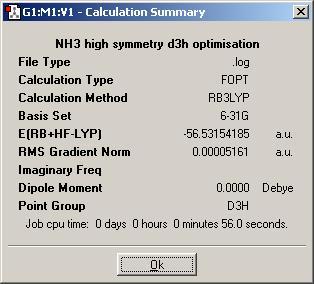
What is the file type? Plain textfile
What is the calculation type? Geometry optimization? Search for Minimum on hypersurface. I'm not sure about the answer expected
What is the calculation method? DFT/b3lyp
What is the basis set? 3-21g
What is the final energy in atomic units (au)? -26.4622643765
What is the dipole moment? 0
What is the point group of your molecule? D3H
How long did your calculation take? 25s CPU time
BCl3
Cl-B bond length = 1.86592 Å
ClBCl angle = 120.0°
What is the file type? Plain textfile
What is the calculation type? Geometry optimization? Search for Minimum on hypersurface. I'm not sure about the answer expected
What is the calculation method? DFT/b3lyp
What is the basis set? lanl2mb
What is the final energy in atomic units (au)? -69.4392811
What is the dipole moment? 0
What is the point group of your molecule? D3H
How long did your calculation take? 13s CPU time
Small molecule
Analysis of a small molecule in similar fashion
Animating the vibrations
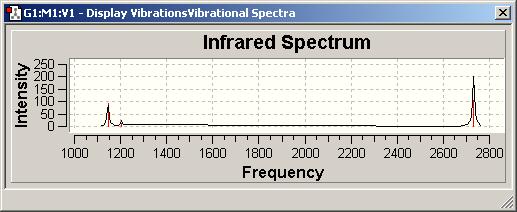
| no. | form of the vibration | frequency | intensity | symmetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x | 1145.72 | 92.6991 | A“2 |
| 2 | x | 1204.66 | 12.3789 | E' |
| 3 | x | 1204.66 | 12.3814 | E' |
| 4 | x | 2592.79 | 0 | A'1 |
| 5 | x | 2731.31 | 103.837 | E' |
| 6 | x | 2731.31 | 103.83 | E' |
Number of vibrations:
- Has to contain x,y or z
- degenerated vib. appear as one
MO
MO diagram (to be nicked from a student)
- MOs in good agreement.
- Different order of MOs
very valuable for qualitative understanding.
DAY 2
geometry
Ecis-Etrans=-7,69 kJ/mol
| parameter | cis | trans |
|---|---|---|
| r(MoP) | 2.652 | 2.572 |
| r(MoC)trans | 2.032 | 2.029 |
| r(MoC)cis | 1.983 | |
| r(CO)trans | 1.188 | 1.190 |
| r(CO)cis | 1.191 | |
| a(MoPMe) | 114.1 | 117.2 |
a more bulky ligand might change the relativ energy in favour of the trans geometrie
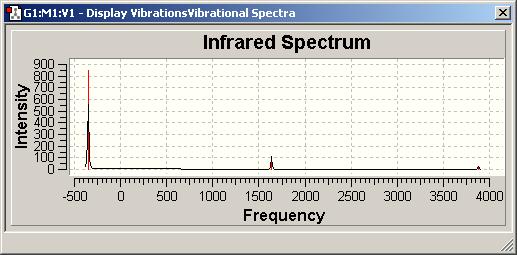
Vibrational Spectra
trans CO: 1838,6;1838,8;1882,3;1954,1
DAY 3 Symmetry
has the symmetry made any difference to the final structure obtained?
almost constant bond length. c1/c3v = 100,6pm d3h = 100,5pm. angle c1/c3v = 115,9/116,2
has the symmetry made any difference to the time it took to optimise the geometry?
higher symmetry results in faster calculations for simillar starting geometries. (Though to be 100% precise, none of the three examples can really be compared on this timescale)
what implication does symmetry have for the time it takes to do a calculation?
???
can a molecule "break symmetry" during an optimisation?
No, it can't.
what implications does this have if you enter a high symmetry structure to optimise?
You will not be able to find a lower lying minimum of lower symmetry.
which is the lowest energy geometry?
C3v
what is the energy in kJ/mol of the other two isomers above the energy of the lowest energy structure? Hint: take ΔE=E(high energy)-E(low energy), the energy units are reported in atomic units so you will need to convert the energy difference to kJ/mol. is the energy differences between these structures significant? Explain why.
ΔE=0,91 kJ/mol; activation energy of inversion (-> transition state)
MP2
how long do these calculations take compared to your lower level ones?
they take between 0 and 20 seconds longer.
determine the barrier height to inversion by finding the relative energy at this level of calculation ΔE=E(D3h)-E(C3v) in kJ/mol
20,48 kJ/mol
has ΔE changed much between the B3LYP/6-31G and MP2/6-311+G(d,p) sets of calculations?
it is by a factor or 22,6 or 19,58kJ/mol larger.
how do your results compare to the experimentally determined barrier which is 24.3 kJ/mol?
they are in reasonably good agreement, and it might be possible to improve them by using a third and better method.
IR
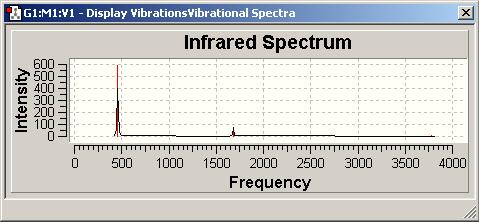
how many positive frequencies are there for the C3v and the D3h structures?
C3v=458,5;2*1681,0;3575,7;2*3776,6 D3h=(-351,8;)2*1636,8;3657,9;2*3877,6 Signal at 3657 has intensity 0
draw the vibrational modes for both structures (visualise them with gaussview) and match them up, ie which vibrational modes have the same character of motion for the C3v and D3h structures
same order.
compare the calculated frequencies for the C3v structure to those obtained experimentally (you will have to look them up). The C3v structure is the ground state structure, ground state structures always have all positive frequencies.
The D3h structure is a transition state structure, transition states always have only one negative frequency, what is the value of negative frequency? which vibration in the C3v and D3h structures "follows" the inversion reaction path?
follows the A2/A1
value: -351,8