Rep:Mod:littlecutemolecule
NH3 Molecule
Basic Information
A 3D NH3 Molecule |
Molecule Name: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Optimized N-H bond distance: 1.01798 Å
Optimized H-N-H bond angle: 105.741 °
| ITEM | VALUE | THRESHOLD | CONVERGED? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy: -5.986276D-10
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis

There are six modes of vibrations for NH3. Its frequencies spread from 1089.54s-1 to 3589.82s-1. Also, the peak intensities spread from 145.3814 to 0.2711.
Questions
1. How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
A: Six.
2. Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
A: 2&3, 5&6
3. Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
A: Bending: 1,2,3 Bond Stretch: 4,5,6
4. Which mode is highly symmetric?
A: Mode4
5. One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
A: Mode1
6. How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
A: Two.Since 2&3, 5&6 are degenerate, and 4&5&6 have negligible peak intensity, only the peak of mode1 and the peak of mode2&mode3 can be seen.
Atomic Charges
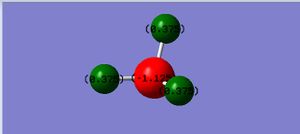
The charge on N is -1.125A and that on H is 0.375A.
Negative charge is expected on nitrogen and positive charge is expected on hydrogen since N is more electronegative than H.
N2 Molecule
Basic Information
A 3D N2 Molecule |
Molecule Name: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -109.52359111 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.02473091 a.u.
Point Group: D∞H
Optimized N-N bond distance: 1.09200 Å
Optimized N-N bond angle: 180.0 °
| ITEM | VALUE | THRESHOLD | CONVERGED? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000001 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000001 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401031D-13
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis
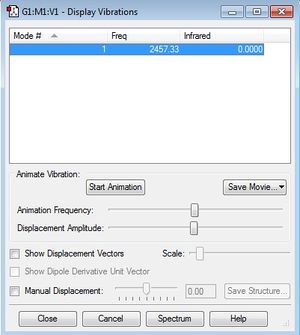
There is only one kind of vibration for N2 molecule. According to the screenshot, there is a peak at 2457.33s-1. However, since the intensity of the peak is 0.0000, no peak is expected to be observed on the spectrum.
Atomic Charges

The charge on N is 0, because it is a diatomic molecule, no electronegative difference.
H2 Molecule
Basic Information
A 3D H2 Molecule |
Molecule Name: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group: D∞H
Optimized H-H bond distance: 0.74279 Å
Optimized H-H bond angle: 105.741 °
| ITEM | VALUE | THRESHOLD | CONVERGED? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000000 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000000 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis

There is only one kind of vibration for H2 molecule. According to the screenshot, there is a peak at 4465.68s-1. However, since the intensity of the peak is 0.0000, no peak is expected to be observed on the spectrum.
Atomic Charges

The charge on H is 0, because it is a diatomic molecule, no electronegative difference.
Haber-Bosch process
Energy Calculations
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52359111 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05632831 a.u.
Unit Conversion= -147.889989171 kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable.
literature value:ΔH298K=-45.7kJ/mol [1]
The literature value is less exothermic than the calculated value.
ClF Molecule
Basic Information
A 3D ClF Molecule |
Molecule Name: ClF
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -559.93737432 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.03767912 a.u.
Point Group: C∞V
Optimized Cl-F bond distance: 1.57000 Å
Optimized Cl-F bond angle: 180.000 °
| ITEM | VALUE | THRESHOLD | CONVERGED? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000246 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000246 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000433 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000613 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy: -1.066055D-07
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis

There is only one kind of vibration for ClF molecule. According to the screenshot, there is a peak at 781.00s-1. However, since the intensity of the peak is 11.6966, one peak is expected to be observed on the spectrum.
Atomic Charges
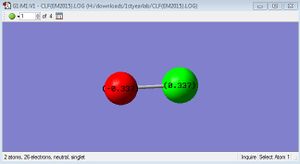
The charge on F is -0.337 and the charge on Cl is 0.337, because F is more electronegative than Cl.
Molecular Orbital





References and bibliography
[1]G Austin,Shreve’s Chemical Process Industries, 5th ed., McGraw-Hill International Editions, New York, 1984.
