Rep:Mod:lem215
Appearance
Part 1
Optimised NH3
Molecule: Optimised NH3 Calculation method: RB3LYP Base set: 6-31G(d.p) Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -56.55776873 RMS gradient: 0.00000485 Point group: C3V Optimized NH bond distance: 1.01798 A Optimized bond angle: 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000070 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000033 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.785188D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
NH3 Optimized |
The optimisation file is liked to here
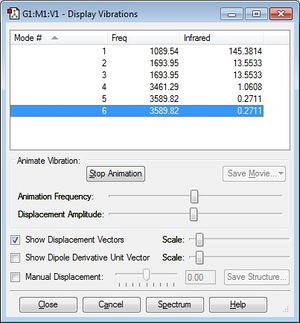
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? Three modes. Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Modes 2 and 3. Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Bending vibrations: 1,2,3. Bond stretch vibrations: 4,5,6. Which mode is highly symmetric? Mode 4. One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? Mode 1. How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 4 different bands. Charge on the N-atom: -1.125 Charge on the H-atoms: 0.375 Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so you would expect nitrogen to have a more negative atomic charge than hydrogen.
Optimised N2
Molecule: Optimised N2 Calculation method: RB3LYP Base set: 6-31G(d.p) Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -109.52412868 RMS gradient: 0.00000060 a.u. Point group: D*H Optimized NH bond distance: 1.10550 A Optimized bond angle: 180.0
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.383792D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
N2 Optimized |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Optimised H2
Molecule: Optimised H2 Calculation method: RB3LYP Base set: 6-31G(d.p) Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -1.17853936 RMS gradient: 0.00000017 a.u. Point group: D*H Optimized HH bond distance: 0.74279 A Optimized bond angle: 180.0
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.167770D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2 Optimized |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 E(N2)= -109.52412868 E(H2)= -1.17853936 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746 - (-109.52412868+-3.53561808)= -0.0557907 a.u. ΔE=-146.47849401 KJ/mol The ammonia products are more stable than the gaseous reactants
Part 2: Independently chosen small molecule, HCl.
Molecule: Optimised HCl Calculation method: RB3LYP Base set: 6-31G(d.p) Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -460.80077875 RMS gradient: 0.00005211 a.u. Point group: C*V Optimized HCl bond distance: 1.28599 A Optimized bond angle: 180.0
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.270754D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.286 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
HCl Optimized |
The optimisation file is liked to here
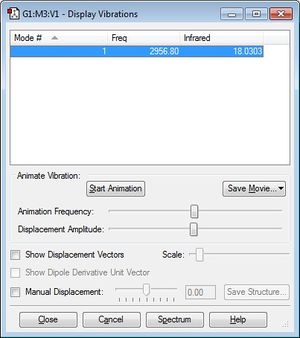
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 (linear) rule? One mode so you would expect HCl to produce one peak in its infrared spectrum. The vibrational mode of HCl is a stretching vibration and therefore highly symmetric.
Atomic charges: H-atom - 0.284 Cl-atom - -0.284 This is as expected because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen.
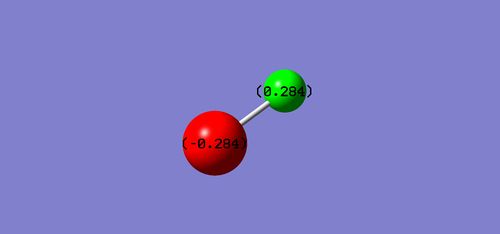
Reaction Energy
H2(g) + Cl2(g) = 2HCl(g) E(H2)=-1.17853936 0.5*E(H2)=-0.58926968 E(Cl2)=-920.34987886 0.5*E(Cl2)=-460.17493943 E(HCl)=-460.80077875 ΔE=(HCl)-[0.5*E(H2)+0.5*E(Cl2)]=-460.80077875-[-0.58926968+-460.17493943]=-0.03656964 a.u. ΔE=-96.013492114 KJ/mol Literature value of ΔE=-92.3 KJ/mol [1]
Molecular Orbitals
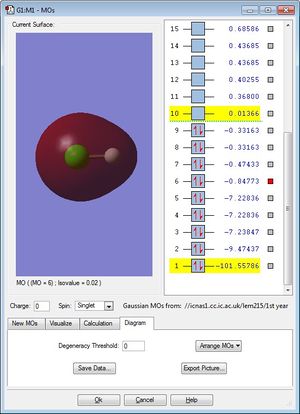
This non-bonding molecular orbital (occupied) is generated by electrons from the Cl 3s orbital and it is deep in energy, -0.84773.
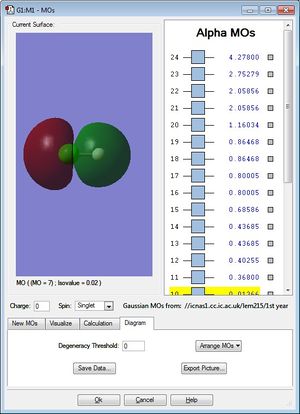
This bonding molecular orbital (occupied) is the HOMO and it is generated by AO mixing from a H 1s electron and a Cl 3p electron and it is deep in energy, -0.47433.
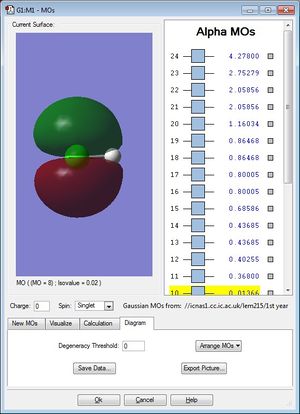
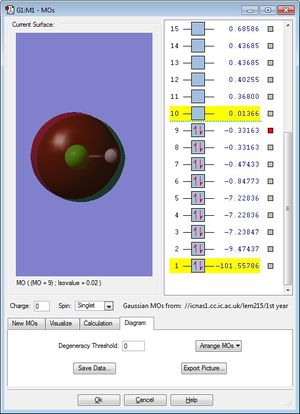
These two non-bonding molecular orbitals (occupied) are generated by electrons from the Cl 3p orbitals. Both of these MOs are degenerate and have energy -0.33163.
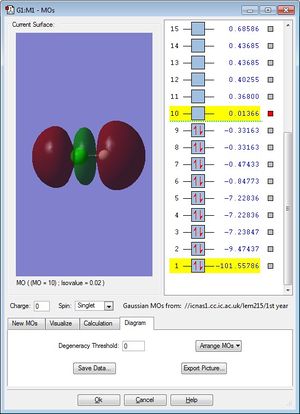
This antibonding molecular orbital is the LUMO and it is generated by AO mixing from a H 1s and a Cl 3p orbtial. It is unoccupied and high in energy, 0.01366.
References
[1] - Course In Chemistry Iit Jee. 2011. Print.
