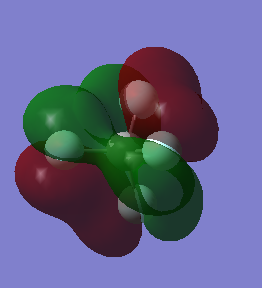Rep:Mod:le1517
Wiki Report for computational models by Lazarus Esayas
NH3
What is the molecule?
NH3
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-56.44397188
What is the RMS gradient?
0.05399560
What is the point group of your molecule?
C3V
Optimised bond length: 1.01798 Angstroms
Optimised bond angle: 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
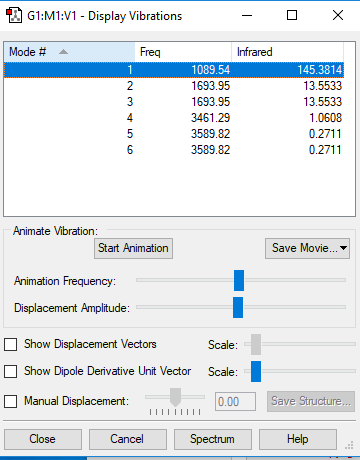
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
2:3, 5:6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bending modes = 1, 2, 3
Stretching modes = 4, 5, 6
Which mode is highly symmetric?
4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2
Charge for N = -1.1.25 Charge for H = 0.375
This is due to high difference in electronegativity between nitrogen and hydrogen and so a negative charge is expected for the hydrogen.
N2
What is the molecule?
N2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-109.52412868
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000060
What is the point group of your molecule?
D*H
Optimised bond length: 1.10550 Angstroms
Optimised bond angle: 180
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
List the frequencies and confirm that there are no negative frequencies
2457.33, therefore no negative frequencies
Nitrogen |
H2
What is the molecule?
H2
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-1.17853936
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000017
What is the point group of your molecule?
D*H
Optimised bond length: 0.74279 Angstroms
Optimised bond angle: 180
4465.68cm-1 , therefore no negative frequencies
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Hydrogen |
Energy Calculations of Reaction
E(NH3)=
-56.44397188
2*E(NH3)=
-112.88794376
E(N2)=
-109.52412868
E(H2)=
-1.17853936
3*E(H2)=
-3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=
-112.88794376 - (-109.52412868 + -3.53561808) = 0.171803
= 451.068811 kJ mol -1
Since energy of reaction is positive, the reactants are less stable than the product of NH3
CF4
What is the molecule?
CF4
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-437.47627267
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00004048
What is the point group of your molecule?
TD
Optimised bond length: 1.32939 Angstroms
Optimised bond angle: 109.471
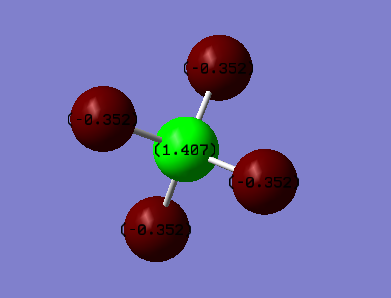
Charge on F = -0.352 Charge on H = 1.407
This is due to the highly electronegative fluorine atoms withdrawing electron density from the carbon atom.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000078 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000042 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000133 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000071 0.001200 YES
CF4 |
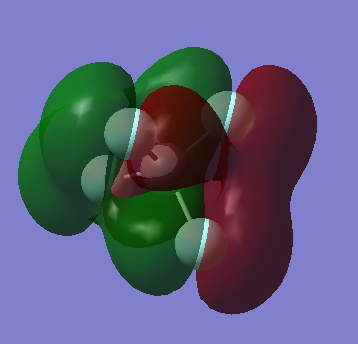
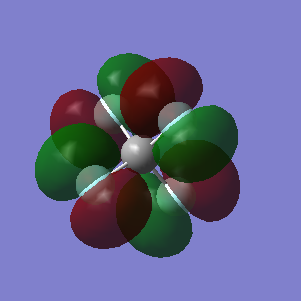
This molecular orbital is a result of the overlap between the π orbitals of each of the fluorine atoms and is around the LUMO region.
Node along each of the bonds and so it can be seen that these are anti-bonding orbitals coming from the fluorine p orbitals.
Another π orbital, anti-bonding orbital with contributions from fluorine atoms, overlap between non bonding atoms.
Bonding orbital using the πz orbital from the fluorine atom and the σ orbital from the carbon which is low in energy
Overlap of σ orbitals from all 5 atoms in the molecule and so can be judged to be a bonding orbital and is deeper in energy than the rest of the bonding orbitals.