Rep:Mod:ks4116
Introduction to Molecular Modelling 2
NH3 Molecule
Summary Information of NH3
Molecule = NH3
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy = -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient = 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group = C3V
Optimised N-H Bond Distance = 1.01798 Angstrom
Optimised H-N-H Bond Angle = 105.741 Degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Image of NH3
NH3 Molecule |
Vibrational Modes and Charges Information
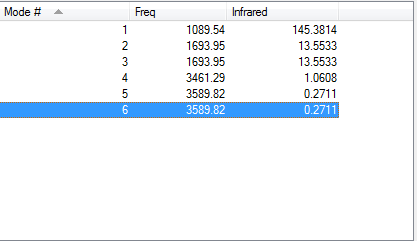
From the 3N-6 rule, 6 modes are expected.
Modes 1,2 and 5,6 are degenerate.
Modes 1 and 2 are bending vibrations where as modes 3,4,5 and 6 are stretch vibrations.
Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
Mode 1 is known as the umbrella mode.
4 bands would be seen in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia due to 4 distinct infrared values given.
The charge on the N-atom is -1.125 and the charge on the H-atom is +0.375. The expected charge on the N would be -1 and +1 on the hydrogens.
N2 Molecule
Summary Information of N2
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy = -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient = 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group = D∞h
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Frequency for N2 = 2457.33 and there are no negative frequencies or charges.
H2 Molecule
Summary Information of H2
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy = -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient = 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group = D∞h
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Frequency for H2 = 4465.68 and there are no negative frequencies or charges.
ΔE of Haber-Bosch Process
E(NH3) = -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3) = -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2) = -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2) = -1.15928020 a.u.
3*E(H2) = -3.4778406 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.11356818 a.u.
This energy in kj/mol is -298.1732566
From this value, it can be see that he reaction is exothermic and so the ammonia product is more stable.
F2 Molecule
Summary Information of F2
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy = -199.49825218 a.u.
RMS gradient = 0.000007365 a.u.
Point Group = D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
F2 Molecule |
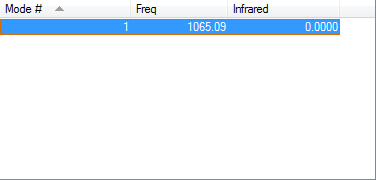
Only one vibrational mode as it's a linear molecule so 3N-5 rule is applied.
The charges on each F atom is 0 due to it being a diatomic molecule.
F2 Molecular Orbitals
This shows the combination of two 2s AO's which are bonding orbitals. The energy is not too deep but the MO is occupied this will result in strong bonding.
This MO is formed by two degenerate p-orbitals, specifically the 2pz orbitals overlapping. It is not deep in energy, nor is it in the HOMO/LUMO region.
This is 2 anti-bonding p orbitals and don't really interact with the bonding of the molecule
This is the overlap of 2 3p AO's forming a bonding MO. This shows the HOMO of F2 and is relatively low in energy.
This shows the LUMO of F2 and is also low in energy.