Rep:Mod:kgw15
NH3 Optimisation
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -56.55776873
RMS Gradient (au): 0.00000485
The point group of your molecule: C3V
Optimisation Result
Optimised N-H bond distance: 1.01798Å
Optimised H-N-H bond angle: 105.741°
Item Log:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986275D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found. ---------------------------- ! Optimized Parameters ! ! (Angstroms and Degrees) ! -------------------------- -------------------------- ! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
NH3 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Animating the vibrations
Screenshot of the vibration modes is here
Questions
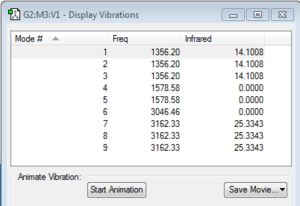
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2&3 and 5&6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Bending: 1,2,3; Stretching: 4,5,6
Which mode is highly symmetric? 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2
Charge Analysis
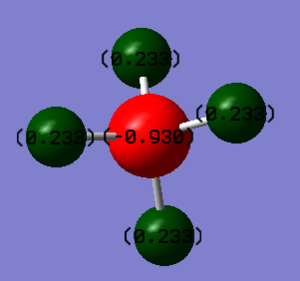
The charge on N is -1.125
The charge on H is 0.375
So the expected charges on N and H are -3 and +1 respectively. The reason N has a negative charge is that it is more electronegative than H.
Reactivity of NH 3
N2 Optimisation
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -109.52412868
RMS Gradient (au): 0.00000060
The point group of your molecule: D*H
Vibration frequency: 2457.33
Item Log:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401039D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
N2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2 Optimisation
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -1.17853936
RMS Gradient (au): 0.00000017
The point group of your molecule: D*H
Vibration frequency: 4465.68
Item Log:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Energy for Haber-Bosch process
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907
ΔE in kJ/mol: -146.47849401
Thus we can see that the product is more stable. (which is comparable to known values)
CH4 Investigation
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -40.52401404
RMS Gradient (au): 0.00003263
The point group of your molecule: TD
Item Log:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256043D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
CH4 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Details on the Molecule
The frequency analysis shows that there are 9 vibrational modes, which is consistent with the expected 3N-6 calculation. However, only 2 peaks should be observed in IR spectrum since some of them are degenerate and some are IR inactive.
The charge analysis predicts that the charges on C & H are -4 and +1 respectively. Once again, this resonates with the fact that C is more electronegative than H and thus has a negative charge.
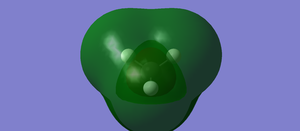
MOs of CH4
The LUMO has energy of 0.11824au. It should be the anti-bond between 2s of C and 1s of H. We can see the nodal plane between the red electron density of C and the green of H.



There are 3 degenerate HOMOs of energy at -0.38831au. They should be made of the 2px, 2py and 2pz of C mixing with the 1s of H.
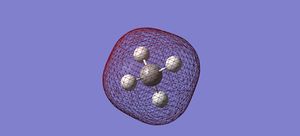

The 2nd lowest MO composes of the 2s of C and 1s of H. Energy: -0.69041au
The lowest MO is only the 1s of C. The 1s of H does not mix with it because the energy gap is too large. Energy: -10.16707au
CN- Investigation
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -92.82453153
RMS Gradient (au): 0.00000704
The point group of your molecule: C*V
Item Log:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000005 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.650389D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1841 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
CN- |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Details on the Molecule
As a linear molecule, the frequency analysis is consistent with the 3N-5 calculation. There is only 1 vibrational mode.
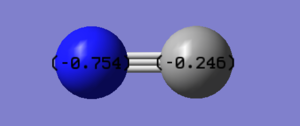
Charge analysis shows that the negative charge is spread unevenly over the molecule, with N having a higher share since it is more electronegative than C. The sum of the charges equals one, the charge we see on the molecule.
Moreover, this also supports our understanding of the molecule in terms of resonance structure. Instead of a -1 charge on an individual atom, as predicted with Lewis structure. We can see that the charge is spread over the molecule.
MOs of CN-
|
|
| 1s of N (-14.00393au) | 1s of C (-9.86720au) |
1s of N has a lower energy than that of C since it has one more proton in its nucleus, thus a higher effective nuclear charge and lowering the energy of the orbital. The two AOs do not form MO since the energy difference is too large.
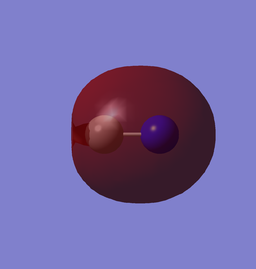
|
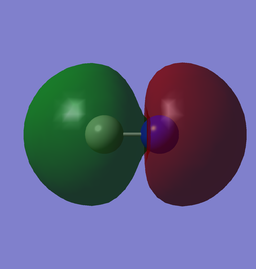
|
| 3σ (-0.56195au) | 4σ* (-0.10636au) |
These MOs are formed from the 2s AOs. Here we can see the higher distribution from N in 3σ and higher from C in 4σ* due to the higher nuclear charge of N, making it closer in energy to the bonding MO and further to anti-bonding MO.

|
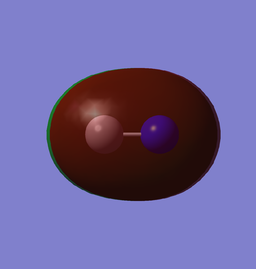
|
| x (-0.01696au) | y (-0.01696au) |
The 1π MOs are formed from the 2p, they are degenerate and orthogonal to each other.
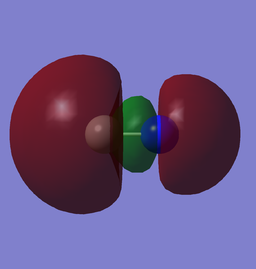
|
| (0.01857au) |
The HOMO is from the overlapping of the 2pz along the bond. The reason we see the lobe pointing away the molecule being larger, despite being a bonding MO is that it is mixed with the 3σ orbital in a out-of-phase fashion. This is also the reason C has a larger lobe.
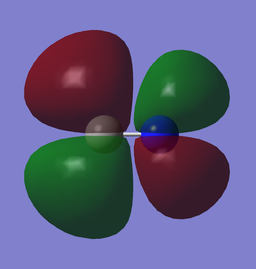
|
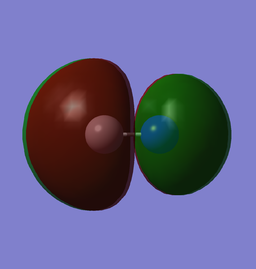
|
| x (0.35435au) | y (0.35435au) |
The LUMO is a 2π* from the anti-phase overlapping of orthogonal 2p orbitals.
Thank you for your time.
