Rep:Mod:kemiwiki
My NH3 Molecule
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776873 |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 |
| N-H bond length | 1.3 Amstrong |
| H-N-H bond Angle | 109.47 |
| Point Group | C3V |
Item Table for NH3
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
My Jmol NH3 Image
Optimised NH3 |
File:OPTIMISATION NH3 1 kemi.LOG
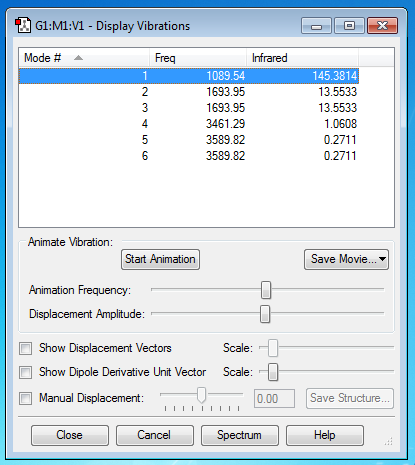
Vibrations of NH3
Answers to Questions
The number of modes expected from 3N-6 rule is 6.
The degenerate modes are modes 2&3 and 5&6.
The umbrella mode is mode 1.
Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
In a gaseous ammonia spectra, the expected number of bands is 2.
Charge of Atoms
The charge on the each hydrogen is 0.375. The charge on the nitrogen atom is -1.125.
As nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, is has a greater ability to attract the bonding electron pairs to itself. This is why it is negative charged, while the hydrogen atoms are positively charged.
Hydrogen and Nitrogen molecules
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy | -1.15928020 |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 |
| Point Group | D infinity |
test molecule |
Hydrogen Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy | -109.524 |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.0000006 |
| Point Group | D infinity |
test molecule |
Nitrogen Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Energies calculated( all in atomic units):
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.33553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.15928020
3*E(H2)= -4.7784060
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= - 0.033002748
Energies Calculated (in Kj/mol)
E(NH3) = 14892.4248
2*E(NH3)= 296984.8436
E(N2) = -287555.5771
E(H2)= -3043.69015
3(H2)= -9131.070495
ΔE= - 86.64871487
As the ΔE is negative, the product (NH3) is lower in energy than the reactants, hence more stable.
My small Molecule: ClF3
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy | -759.38175724 |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00076805 |
| Cl-F Bond length | 1.57 Amstrong |
| F-Cl-F | 120 degrees |
| Charge of Cl atom | 1.355 |
| Charge of F atom | -0.452 |
test molecule |
ClF3 Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000011 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000049 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000032 0.001200 YES
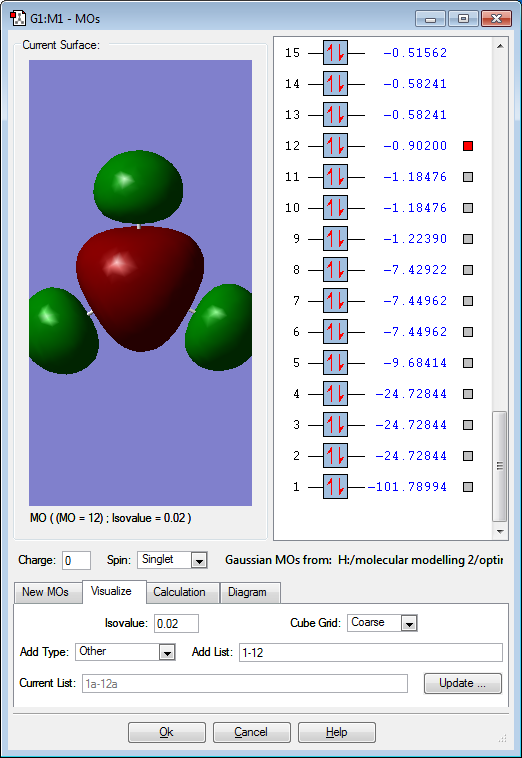
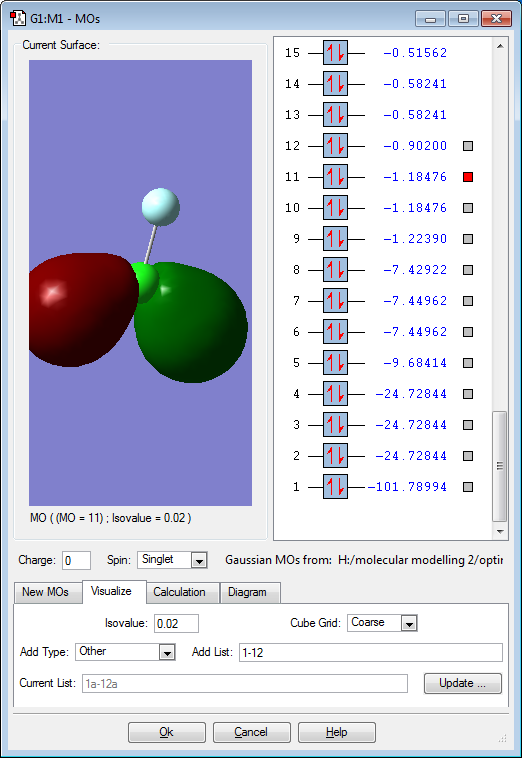
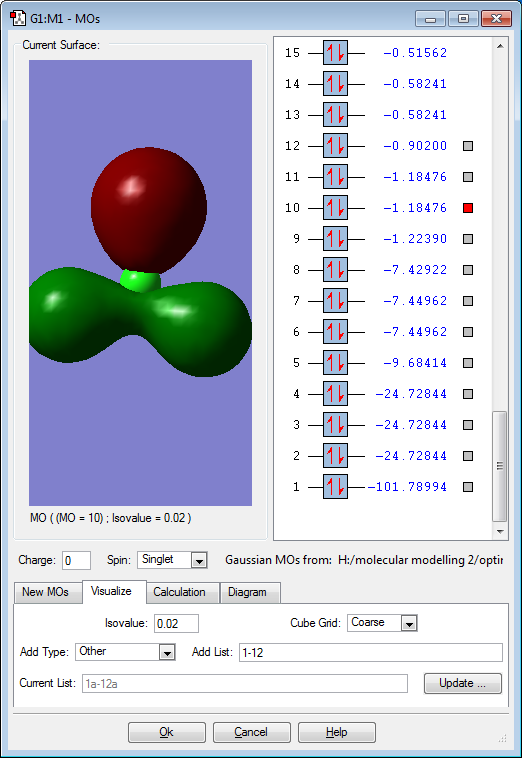
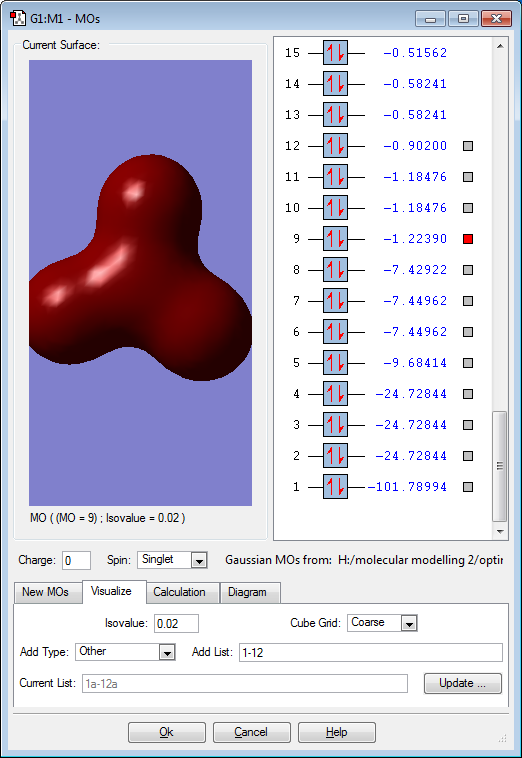
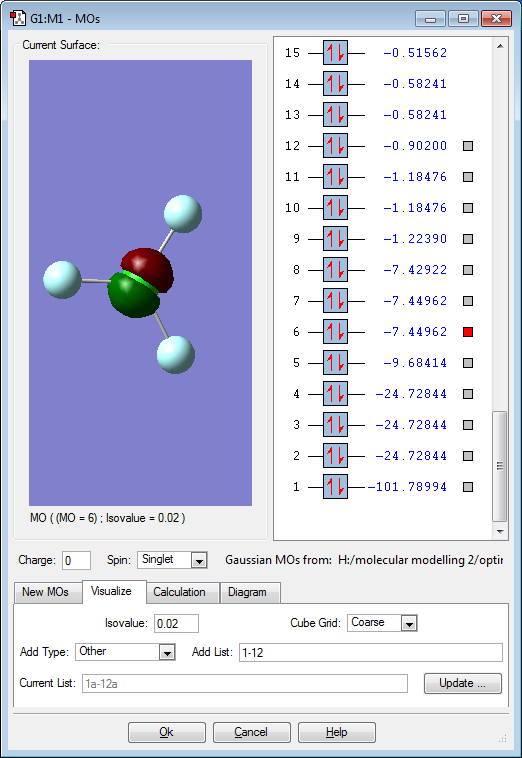
Molecular Orbitals
Red electron clouds are representative of bonding orbitals and green electron density clouds are representative of the anti-bonding orbitals. Orbitals 11 and 10 are degenerate, as well as 8 and 7 as they have the same energy value.