Rep:Mod:hz1995
I investigated the energetics of the Haber process. To do this, I optimised the molecules NH3, N2 and H2 using GaussView 5.0. I then extracted the molecular information, including charge, bond length and vibration properties, and looked at the dynamic images for all three. Having worked out the energetics, I applied a similar method to a molecule of my choice, Cl2. In addition to the molecular information, I also analysed the Molecular orbitals and the relevant Atomic orbitals responsible for these MOs.
Ammonia Molecule
Summary
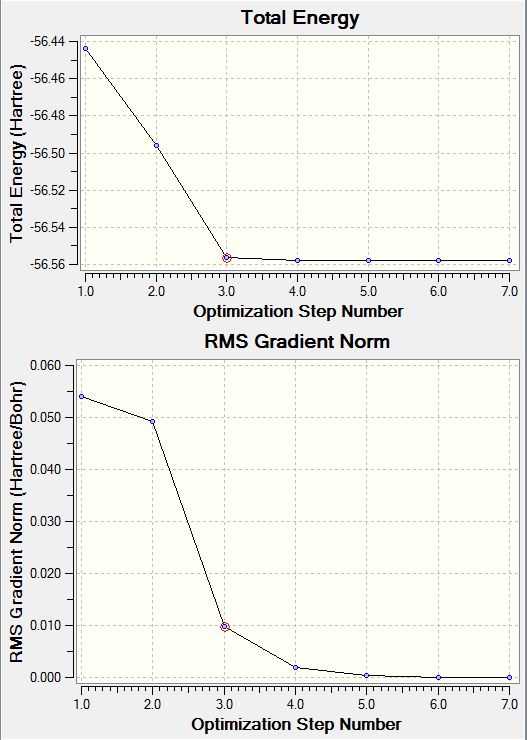
File Name: Haaris - optimised NH3 File Type: .log Calculation Type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p) Charge: 0 Spin: Singlet E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000485 a.u. Imaginary Freq: 0 Dipole Moment: 1.8466 Debye Point Group: C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986278D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimisation graph
Dynamic Image
Optimised NH3 molecule |
Link to completed optimisation file File:HAARIS - OPTIMISED NH3.LOG
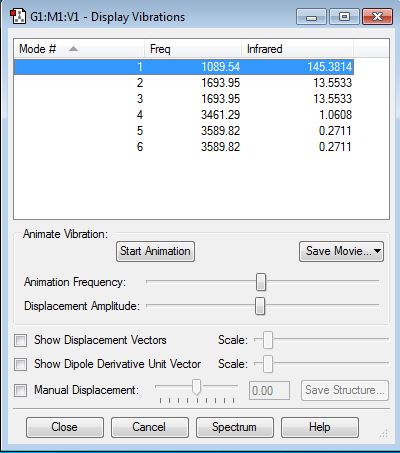
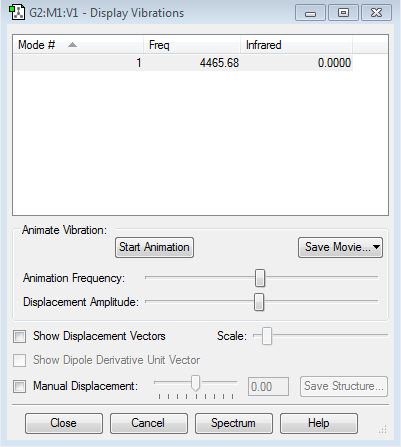
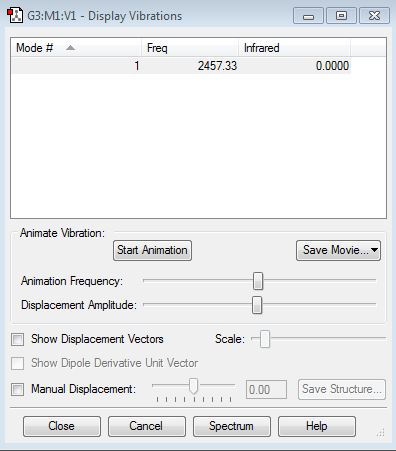
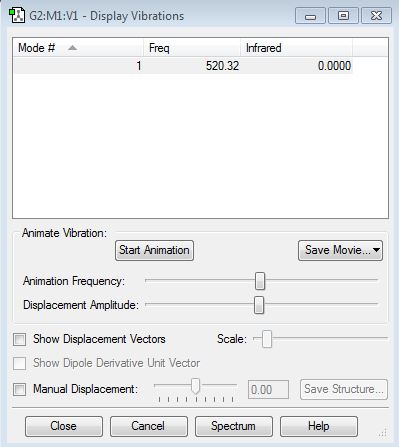
Vibration properties
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? - (3x4)-6 = 6 modes.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? - Modes 2 and 3 (Freq 1693.95), and 5 and 6 (Freq 3589.82).
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? - Bending 1,2,3 and stretching 4,5,6.
Which mode is highly symmetric? - 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? - 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? - There are two distinct frequencies for the 6 modes therefore you would expect 2 bands. Two frequencies have a very small value on the y-axis (relative intensity) which would make them difficult to see. They have small intensities because the change in dipole moment is small.
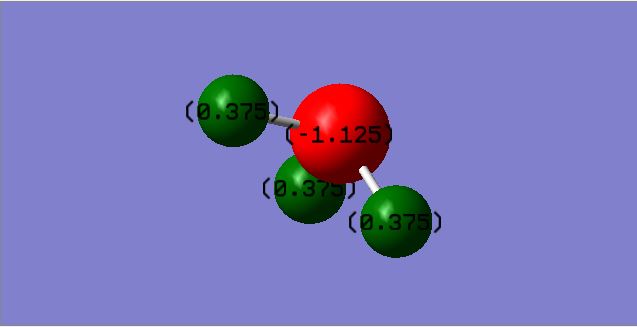
Charge distribution
You would expect Nitrogen to be negatively charged and Hydrogen to be positively charged since Nitrogen is more electronegative and will therefore attract bonding electrons towards itself.
Hydrogen Molecule
Summary
File Name: H2 File Type: .log Calculation Type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p) Charge: 0 Spin: Singlet E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000017 a.u. Imaginary Freq: 0 Dipole Moment: 0.0000 Debye Point Group: D*H Bond Length: 0.74279 A
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164079D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Dynamic image
Optimised H2 molecule |
Link to completed optimisation file - File:HZ H2.LOG
Vibration properties
Nitrogen Molecule
Summary
File Name: HZ_n2_optimised File Type: .log Calculation Type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p) Charge: 0 Spin: Singlet E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000060 a.u. Imaginary Freq: 0 Dipole Moment: 0.0000 Debye Point Group: D*H Bond length: 1.10550 A
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.383811D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Dynamic image
Optimised N2 Molecule |
Link to completed optimisation file - File:HZ N2 OPTIMISED.LOG
Vibration properties
Haber-Bosch Reaction Energy
Calculations
N2 + 3h2--> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074 a.u.
ΔE= -0.05579074 x 2625.5 = -146.4785879 kJ/mol.
The negative energy value shows that energy is released. This indicates that Ammmonia more stable than the mixture of H2 and N2.
Cl2
Summary
File Name: hz_cl2_optimised File Type: .log Calculation Type: FREQ Calculation Method: RB3LYP Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p) Charge: 0 Spin: Singlet E(RB3LYP): -920.34987886 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00002511 a.u. Imaginary Freq: 0 Dipole Moment: 0.0000 Debye Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.277357D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.0417 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Dynamic image
Optimised Cl2 Molecule |
Link to optimised file - File:HZ CL2 OPTIMISED.LOG
Vibration properties
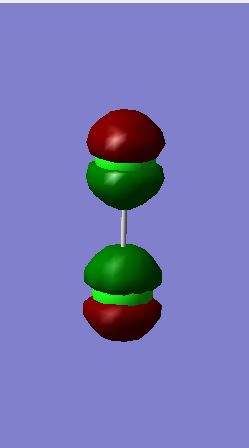
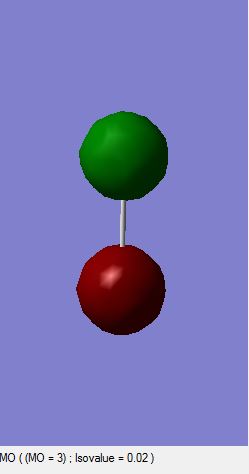
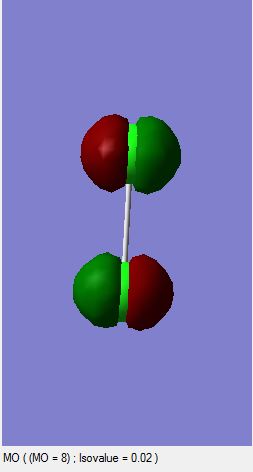
Cl2 Molecular Orbitals