Rep:Mod:ft614
Introduction
In order to locate the transition states of different Diels Alder Reactions ([4+2]cycloaddition), the reaction profiles of butadiene and ethane, benzoquinone and cyclopentadiene, xylylene and SO2 are explored and analysed by using Gaussview.
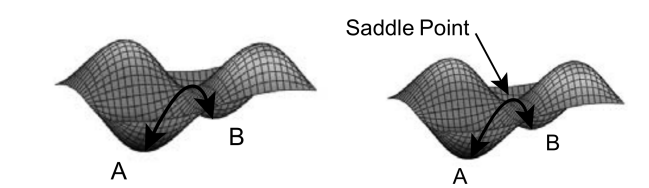
The main reasons to use Gaussview is optimizing, frequency calculation and intrinsic reaction coordinate(IRC) analyzing based on the analysis of Potential Energy Surface(PES). PES is a mathematical function to calculate the energy of a molecule as a function of its geometry1. Optimizing refers to that the optimization the reactants from highly distorted geometry(high energy) to highly stable geometry (minimum energy state) leads to locate the energy levels of reactants, transition states and products. Three kinds of stationary points are shown on the PES, including the minimum, maximum and saddle points. The Minimum points correspond to reactants or products(A) because they are very stable and low in energy, which are found when the first derivatives are equal to zero, and the second derivatives are positive.The transition states correspond to the saddle points(B) with energy decreases in all directions, zero first derivatives and negative second derivatives.Frequency calculation refers to determine the frequency of all the vibrational modes in the reaction pathway .The number of vibrational modes is calculated as (3N-6), N is the number of atom. One negative(imaginary) frequency will be obtained from the frequency calculation due to the transition state structure, a stationary point at which has the maximum potential energy as well as the highest number of internal degrees of freedom. IRC analysing is based on the optimization of transition states, which leads to the calculation of the the sum of electronic and thermal energy of reactants, transition states and products.
01:08, 18 November 2016 (UTC) Your definition of a TS is strange. essentially every other vibrations mode has a positive curvature. but the bond forming/breaking mode has a negative (hence imaginay frequency) and that is the lowest energy pathway over a reaction barrier. in 2D this can be visualised as a saddle point. In higher dimensions you cant.
Exercise 1
- Construction and visualization of Molecular orbitals
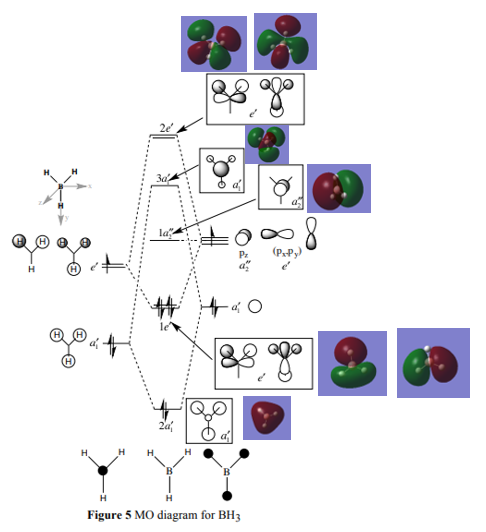
Firstly, in order to figure out which orbitals in the reactants are involved in the product formation,the construction of the Molecular Orbital(MO) diagram will be necessary. Molecular orbitals are formed by two smaller molecular orbitals with one orbital empty of electrons and with the same symmetry. Therefore the orbital overlap integral will be zero for ungerade-gerade interactions,non-zero for gerade-gerade and ungerade-ungerade interactions. The HOMO orbital of butadiene interacts with the LUMO orbital of dienophile, and the LUMO orbital of butadiene interacts with the HOMO orbital of dienophile. However the later one is less favourable because of the higher energy difference between two interacting orbitals.
Secondly, Gaussview is used to visualise the three-dimension and confirm the correct orbitals interacted. Here are the HUMOs and LUMOs of transition states.
| energy level | MO diagram | symmetry | Jmol object | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| highest | 
|
gerade | |||
| HOMO | 
|
ungerade | |||
| LUMO | 
|
ungerade | |||
| lowest | 
|
gerade |
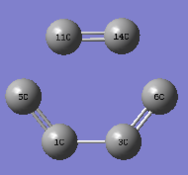
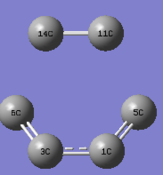
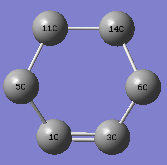
- C-C bond length measurement
Measuring the C-C distance of the reactants, transition states and products can partly reflect how the orbitals of C-atom interact in the reaction pathway.
| distance | Reactants | TS | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| c1-c5 , c3-c6 | 1.33 | 1.38 | 1.5 |
| c1-c3 | 1.47 | 1.41 | 1.34 |
| c11-c14 | 1.32(sp2 C=C) | 1.38 | 1.54(sp3 C-C) |
| c5-c11, c6-c14 | - | 2.11 | 1.54 |
|
|
|
Firstly, in the reactants, C11-C14 (ethene) is typical sp2 C-C bond length(1.32Å), C1-C3(single bond,1.47Å)is longer than others due to the lack of p_orbital interaction. Secondly, in the transition state, due to the movements of electron density from butadiene to dienophile to butadiene , the bond lengths among carbons change obviously: bonds are partly formed in the pairs of C5-C11 and C6-C14(2.11Å), and bond length of C3-C6 and C1-C5(1.38Å) elongates due to the loss of pi-electron interactions, while C1-C3(1.41Å) becomes shorter. Lastly, there is only one double bond(C1-C3,1.34Å) in the product, so C11-C14,C5-C11 and C6-c14 are typically sp3 C-C bond lengths(1.54Å)lengths. The Van der Waals radius of the C atom is 1.70Å .3
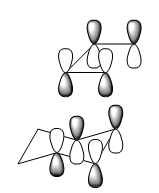
- Synchronous bond formation
Here are two diagrams illustrating two vibrational modes, the right one is with lowest positive frequency and the left is with negative frequency.
Because the energy of transition structure is located at the maximum point of the PES, so the force constant, which is also the second derivative(k) of the surface, is negative. The vibrational frequency(v) is calculated from the k,
v=1/2π √(k/μ),μ is reduced mass
so the frequency for transition state will be negative. From the vibration diagram, it is clear that in the transition structure, C5,C6 and C11,C14 are stretching towards in the same place simultaneously, the interaction between C5,C11 and C6,C14 will be the same, so the bond formation is synchronous. However, in the right one, at the same time when the interaction between C5, C11 becomes stronger, C6,C14 move in an opposite direction and interact less.
Nf710 (talk) 01:14, 18 November 2016 (UTC) This section was done very well, however be careful your MOS in those jmols are not the optimized ones. you need to set the correct frame. excellent knowledge of the 1D harmonic oscilator.
Exercise 2
- MO illustration
Compare with exercise 1, this reaction is much easier to happen because of the addition of EWG (electron withdrawing group: carbonyl group: reasonace effect), which makes the dienophile more electrophilic, therefore it is a normal demand Diels-Alder reaction, also it is deducible that addition of electron donating group(EDG) to the nucleophile will be favourable, and the reactions involves EWG-containing diene and EDG_containing dienophile will be inverse demand. The product structure can be either exo- or endo- due to the secondary orbital interaction, happening between C=O p-orbitals from diene and the two p-orbitals of dienophile , nevertheless there are no bonds forming between them. Here is the MO diagram of HOMOs and LUMOs of exo- and endo- transition states.
| MO | exo | MO illustration | endo | MO illustration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUMO | 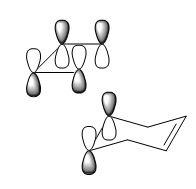
|
| ||||||
| HOMO | 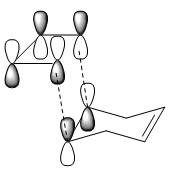
|
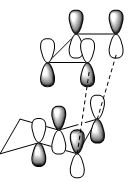
|
(Change the isovalue for the MOs so that the secondary orbital overlap becomes more obvious Tam10 (talk) 11:43, 10 November 2016 (UTC))
- Kinetic and theromdynamic product
From the HOMOs of exo- and endo- structure, it is clear that there is the additional p-orbital overlap in the endo-structure, which means, this extra overlap can help to stabilize the transition state and lower its energy and lower the activation energy. Hence the endo-structure product will be more kinetically stable. However, it is still not enough to determine which one is the thermodynamically favorable. So Gaussview is used to calculate the sum of the electronic and thermal energy of reactants, transition states and products.( 1 hartree/particle= 2625.8 KJ/mol)
| hatree | Reactants | transition state | Products | activation energy/ KJ/mol | change in gibbs free energy/ KJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| exo | 0.130709 | 0.181212 | 0.109351 | 132.610 | 56.0818 |
| endo | 0.130709 | 0.180249 | 0.108078 | 130.082 | 59.4244 |
Therefore, it can be confirmed again from the calculation of the activation energy of two products that the endo-structure is more kinetically favourable and is the major product. Also, exo- structure is the thermodynamically favoured because of the smaller Gibbs free energy difference between reactants and product.
- Comparison of two different optimization method(PM6 and B3LYP)
| EXO | PM6 | B3LYP |
|---|---|---|
| reactants | 0.130709 | -575.418824 |
| transition state | 0.181212 | -575.381307 |
| products | 0.109351 | - |
| ENDO | PM6 | B3LYP |
|---|---|---|
| reactants | 0.130709 | -575.418824 |
| transition state | 0.180249 | -575.383855 |
| products | 0.108078 | - |
Hence it is can be observed that the gibbs free energies of different energy levels calculated by B3LYP are much lower than PM6. Although the activation energy calculated by B3LYP is higher than PM6, the results are the same: endo-structure is kinetically preferred, and exo-structure is thermodynamically preferred.
01:20, 18 November 2016 (UTC) Dont base facts on chemically intuition alone. You should use the numbers to determine if the endo is the kentic product. IT is meaninglyess to compare levels of theory they have completely different Hamiltonians. And This ant the optimised orbitals your havent choosen the correct frmae. Dont worry I can manually look at it.
Nf710 (talk) 01:29, 18 November 2016 (UTC) You should have shown the energy barriers and Reaction energy for B3LYP!!!!!!! its a better level of theory.. and used PM6 for an IRC to give you you the geometries of the reactants and products (because B3LYP takes ages) then optimised these geometries with B3LYP unfortunately because you used PM6 you have come out with the incorrect conclusion because it is not a good level of theory. BUt your arguments are good.
exercise 3
Compare with the reaction in exercise 2, there is not only Diels-Alder reaction happening, but also possible for a cheletropic reaction to happen, in which S atom donates two electrons and bond to two C atoms at the same time.
- Visualisation of the reaction coordinate by IRC calculation
| Diagram | DA_exo | DA_endo | cheletropic_exo |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRC | 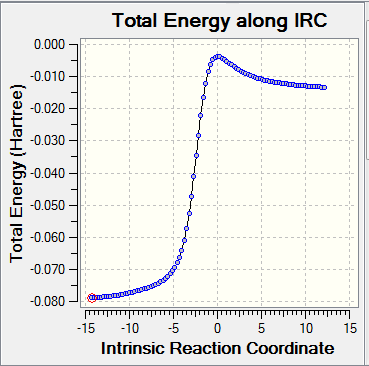
|
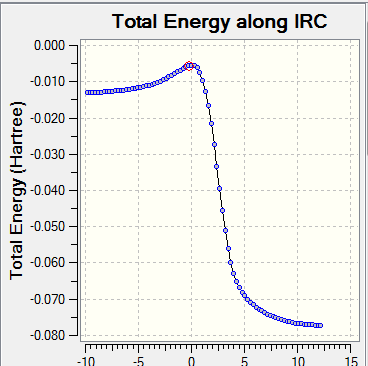
|
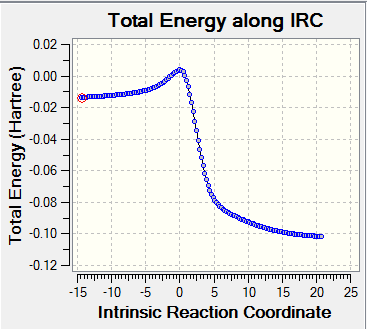
|
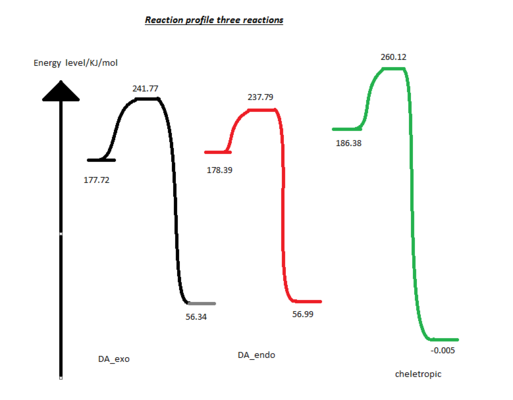
- Calculation the activation and reaction energies (kJ/mol)
| reactant/hartree | transition state/hartree | product/hartree | activation energy/ KJ/mol | change in gibbs free energy/ KJ/mol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sum of electronic and thermal energy | DA_exo | 0.067684 | 0.092077 | 0.021455 | 64.0521 | 121.388 |
| DA_endo | 0.067963 | 0.090559 | 0.021704 | 59.40175 (kinetically favorable) | 121.466 | |
| chele_exo | 0.070981 | 0.099064 | -0.000002 | 73.74146 | 186.387 (thermodynamically favorable) |
- reaction profile drawing
(It's ok to just use straight lines to connect the energy levels. Also, it's easier to read if everything is normalised. Typically they are normalised from the same starting point which can be the reactants at infinite separation Tam10 (talk) 11:43, 10 November 2016 (UTC))
The diagrams and data above shows the endo-structure from DA reaction is the kinetically favoured and the product from cheletropic reaction is the thermodynamically favoured.
Conclusion
The use of Gaussview is extremely helpful in the transition state determination, particularly the energy calculation of different energy states. The varity of products and speed of Diels Alder reaction can be achieved by the choices of the reactants. Firstly, is the addition of electron-donating group to diene or the electron-withdrawing group( exercise 2) to dienophile. And the reaction is speed of reaction can be accelerated when secondary orbital interactions exist between reactants. Secondly, when CO, N2, or SO2 (lone pair available) work as electrophiles, cheletropic reaction is possible to happen, which will produce the most thermodynamically favorable product.
reference
1. http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/teaching_comp_chem_year4/L4_PES.pdf
2. http://rossi.chemistry.uconn.edu/workshop/files/pes_ts_mep_exercises.pdf
3.Van der Waals Radii of Elements,S. S. Batsanov, Center for High Dynamic Pressures, Mendeleevo, Solnechnogorskii raion, Moscow oblast, 141570 Russia , February 14, 2001