Rep:Mod:felicmod1
The basic techniques of molecular mechanics and semi-empirical molecular orbital methods for structural and spectroscopic evaluations
The Hydrogenation of Cyclopentadiene Dimer
The Moleuclar Mechanics (MM2) option is used to optinised the geometries and the total energies are calculated.
Exo Dimer 1
 Total Energy: 34.0014kcal mol-1
Total Energy: 34.0014kcal mol-1
Endo Dimer 2
 Total Energy: 31.8843kcal mol-1
Total Energy: 31.8843kcal mol-1
The two forms of dimers have different energies, and by the calculationes it is suggested that the Exo dimer has higher energy than the Endo dimer (34.0014kcal mol-1 and 31.8843kcal mol-1) This means the Exo dimer process more strain in the ring thermodynamically while the Endo dimer is observed to be more stable kinetically due to transition state stability and secondary orbital interactions. The torsion energy of isomer 2 is much higher than in 1 this can be due to the extra eclipsed hydrogen pair in 2, Oerall the stereo is determined by the electronic properties.The cyclodimerisation reaction happeens within the LUMO of the dienophile and the HOMO of the diene. In this siutuation the carbon atoms which process the highest coefficients in the frontier orbitals will react and this will be the main factor that determine the sterio of the substituent.
Dihydro Derivative 3
 Total Energy: 34.9709kcal mol-1
Total Energy: 34.9709kcal mol-1
Dihydro Derivative 4
 Total Energy: 29.2539kcal mol-1
Total Energy: 29.2539kcal mol-1
After comparing the total energy of the dihydro derivatives, it is shown that derivative 4 has a lower energy and it should be more thermodynamically favourable than derivatives 3, And the derivative 3 is more strained.
Relative contributions of different energy terms for the dihydro derivatives
| Energy Terms | Dihydro derivative 3(kcal mol-1) | Dihydro derivative 4(kcal mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Stretch | 1.2464 | 1.1378 |
| Torsion | 11.1903 | 12.4202 |
| Bending | 19.0416 | 13.0223 |
| VdW | 5.7950 | 4.4324 |
| Dipole/Dipole | 0.1623 | 0.1410 |
All energies are higher for derivative 3 than derivative apart from the Torsion energy, this is true esperically on the bending and the VdW energies.
Stereochemistry of Nucleophilic additions to a pyridinium ring (NAD+ analogue)
For each molecule, MM2 calculation is used to minimise the energy, different starting point are tried and the one with the lowest energy is used.
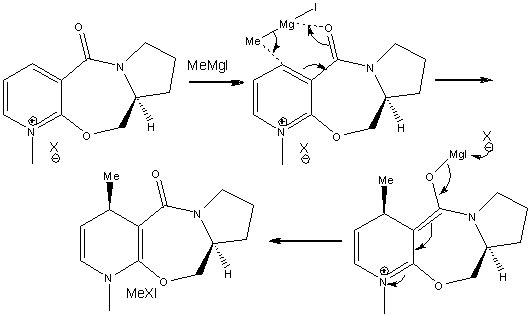
Mechanism for conversion of 5 to 6
- A. G. Shultz, L. Flood and J. P. Springer, J. Org. Chemistry, 1986, 51, 838. DOI:10.1021/jo00356a016
The mechanism shows that the Mg in the Grignard will 1st coordinates with the oxygen in the amide, this happen by oxygen lone pair donating to the emptey d orbital of Mg. As shown from the 3D structure below, there is a 24 degree angle between carbonly group and the pyridine ring, the Mg atom will attact from above to give the enolate. As the outcome the Me grou[ will be above the ring anto to the H (at chiral center).

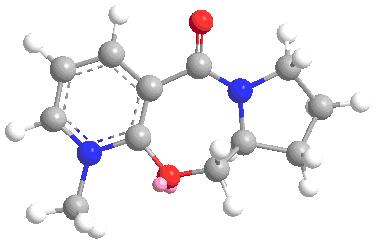
total energy = 26.3534kcalmol-1
If the Grinard reagent MeMgI is included in the model, an error is shown in the MM2 calculation due to the number of ligand attached will not match with the geometry of Mg
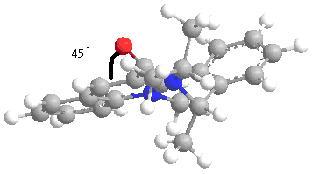
From 7 to 8
Like before, the orientation with the lowest energy is used, it is shown that there is a 45 degree angle between the carbonyl and the ring ( which is anto to the H atom at the chiral center), this means the Gringard will attack from above to give the product due to the same reason as before.
total energy = 15.7021kcalmol-1
Key literature
- Leleu, Stephane; Papamicael, Cyril; Marsais, Francis; Dupas, Georges; Levacher, Vincent. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2004, 15, 3919-3928 DOI:10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.11.004
- A. G. Shultz, L. Flood and J. P. Springer, J. Org. Chemistry, 1986, 51, 838. DOI:10.1021/jo00356a016
A general problem of this model is that the N is shown as trigonal planar this is due to the fact that this Cham£D does not include the lone pair of the Nitrogen into consideration in the molecule. If it was incluede this will incresae the overall energy of the molecule.
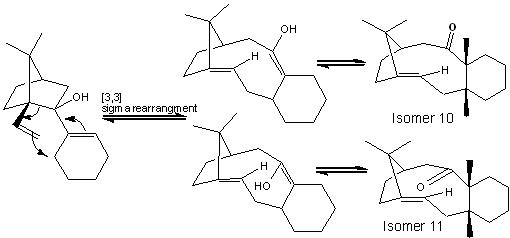
Stereochemistry and Reactivity of an Intermediate in the Synthesis of Taxol
Isomer 10
 total energy = 49.9877 kcal mol-1
total energy = 49.9877 kcal mol-1
Isomer 11
 total energy = 49.9864 kcal mol-1
total energy = 49.9864 kcal mol-1
The two isomers have very similar energies, for the double bond next to the bridgehead will be more stable as the ring size increase. In this case the ring is quite large and therefore the double bond will have a relatively low energy and therefore will be stable. To convert one isomer to another, the carbonyl group has to be fliped upside down, this requires the rotation of the bond which is highly strained and restricted. This transition is illustred by the diagram below which represents the middle of the transformation forom isomer 10 to 11. This molecule will have a very high energy. And because of this energy barrier the transformation is basically impossilbe and therefore making the 2 isomers to be atropisomers.
 total energy = 89.7546 kcal mol-1
total energy = 89.7546 kcal mol-1
literature suggests that this oxy-cope rearrangement can establishes an equilibrium.
Key literature
- J. G. Vinter and H. M. R. Hoffman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1974, 96, 5466 (DOI:10.1021/ja00824a025 DOI:10.1021/ja00824a025 ) and 95, 3051 for another nice example of atropisomerism.
- Pelayo Camps, Francesc Perez and Santiago Vdzquez, Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 28, 9727-9734 (DOI:10.1016/S0040-4020(97)00595-4
How One Might Induce Room Temperature Hydrolysis of a Peptide
Both isomers with the N-substituent oriented axial/equatorial is drawn and the energies is calculated. for both isomer the molecule with the lowest energy is chosen.
Isomer 13
this isomer has the N-substitutent axial to the decalin ring.
Isomer 14
this isomer has the N-substitutent equatorial to the decalin ring.
Kinetically isomer 13 will undergo reaction faster than isomer 14 as the OH group is axial and it can apprach the carbonyl peptide bond which is also axial much easier. For isomer 14 energy must be put into for the OH and carbonyl bond which is further apart to react.
The esterification of both isomers ids intromolecular via cyclisation step, this can be done with a relief of strain in the ring, this will be usually very fast and this might be the reason why the rate of reaction is quite fast for both isomers as the system is not strained.
Key literature
- Dr. M. I. Page, Angew. Chem. lnr. Ed. Engl., 1977, 16, 7, 449-459
Modelling Using Semi-empirical Molecular Orbital Theory
Regioselective Addition of Dichlorocarbene
Part 1
The geometry and the total energy of the molecule is determined using the MM2 option. This however does not gives account on the electronic properties ( strain, steric). MM2 only taken the quantitative aspects into account. The electron of the molecule has to be taken into account that cos they influces the bonding and spectroscopic properties.
total energt: 17.8984kcal mol-1)
The HF/STO-3G self-consistent-field MO method is the applied to create an approximate valence electron MO function.
Finished @ Energy = -548182.95 Kcal/Mol (-873.585857 Hartrees)
HOMO-1
Part 2
A hydrogenated version of compound 12 is drawn and it's geometry is optimised using MM2.
 Total Energy: 22.3519 kcal/mol
Total Energy: 22.3519 kcal/mol
The HF/STO-3G self-consistent-field MO method is the applied to create an approximate valence electron MO function. Finished @ Energy = -548945.59 Kcal/Mol (-874.801205 Hartrees)
HOMO-1
Structure based Mini project using DFT-based Molecular orbital methods
Investigating the regioselectivity of the Baeyer-Villiger reaction
The total synthesis of the natural product (-)-kainic acid (DOI:10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00379-4 ) is investigated [ coumpound 14 to 15)
optiomising the molecule
The compound 15 is drawn using chemdraw 3D, then a gaussian input file is created with Method DFT=mpw1pw91 and basis set 6-31G
The .gjf file is submitted to the SCAN service and to be optimised.#
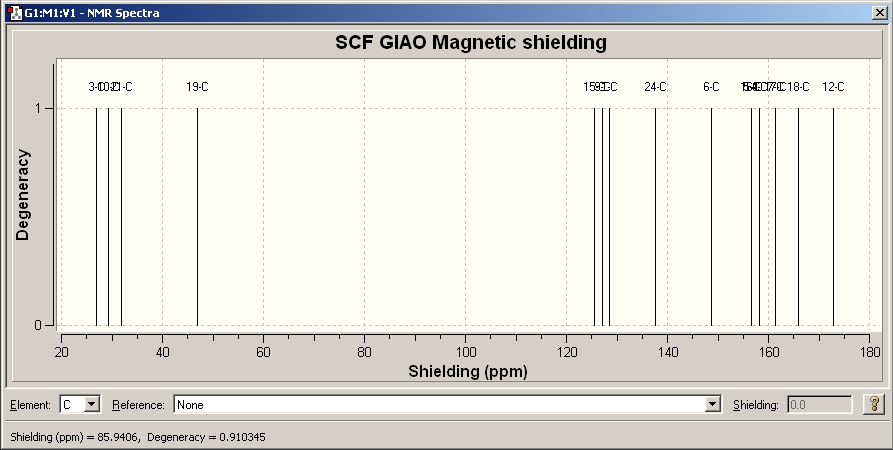
The optimised file is then used to predict its NMR spectrum, IR spectrum and Optical Rotation
NMR predicted
Identifier on Dspace = DOI:10042/to-1674
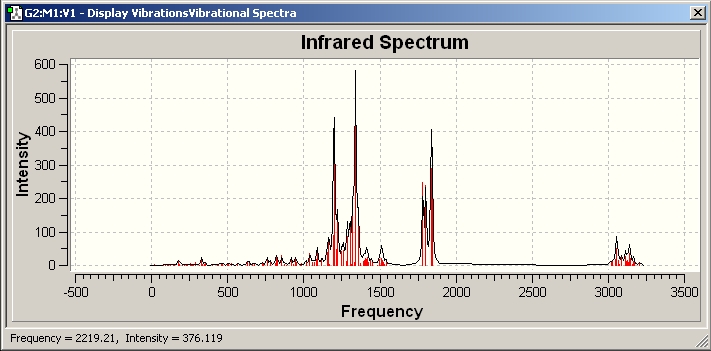
IR predicted
Identifier on Dspace = DOI:10042/to-1708
| No | Form of Vibration | Frequency | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
1781.89 | 248.49 |
| 2 | 
|
1800.94 | 240 |
| 3 | 
|
1835.68 | 290.473 |
| 4 | 
|
1842.4 | 285.518 |
The 4 C=O stretch frequency predicted by Gassian Vmax/cm-1 1781.89, 1800.94, 1835.68 and 1842.4 is a bit higher than the lit value which is Vmax/cm-1 1780, 1755, 1748, 1723
Lit value
optical rotaion= +5(c=0.57) 1H NMR ( 300MHz CDCl3) 4.29 (1H, s, H1, 4.26(1H,dd, J=14.2, 4.4Hz, H5), 4.10 (iH, dd, J=14.2, 7.0 Hz, H5), 3.83 (3H, s, CO2Me), 3.0-2.7 (5H, m, H3a, H4, H8, H8a), 1.51 ( 9H, 2, (CH3)3) IR Vmax/cm-1 1780, 1755, 1748, 1723 (C=O)
Key literature
- K. Mori, The Chemical Record, 2005, ii5, 1-16. DOI:10.1002/tcr.20030
- Synthesis of (−)-kainic acid using chiral lithium amides in an asymmetric dearomatizing cyclization, Jonathan ClaydenCorresponding Author Contact InformationDOI:10042/to-1674