Rep:Mod:dl3715
NH3
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basic Set
6-31G
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)
-56.55776873 a.u. (8 d.p)
RMS gradient
0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group
C3V
Optimised N-H bond length
1.01798 armstrong
Optimised H-N-H bond angle
105.741 degree
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986268D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Jmol image
test molecule |
Link
The optimisation file is liked to here
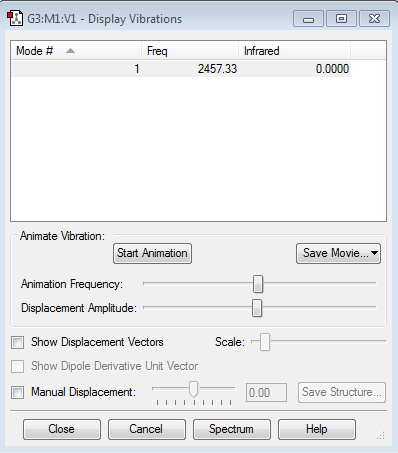
Display Vibrations
Answers to questions
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 3
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? bends(2,3) and asymmetric stretches(5,6)
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? bends:1,2,3 stretchees:4,5,6
which mode is highly symmetric? 1,4
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 4
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?Two bands would be observed on the spectrum since 2,3 are degenerated and 5,6 are degenerated; also, the 4,5 and 6 are not intense enough to be observed. Thus, overall two bands will be observed.
Charge on the N-atom and H-atoms
Nitrogen:-1.125 Hydrogen:0.375 would expect to see a slight negative charge on nitrogen and a slightly positive charge on hydrogen since nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen.
N2
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basic Set
6-31G
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)
-109.52412868 a.u. (8 d.p)
RMS gradient
0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group
D∞h
Optimised N-N bond length
1.10550 armstrong
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401007D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Jmol image
test molecule |
Link
The optimisation file is liked to here
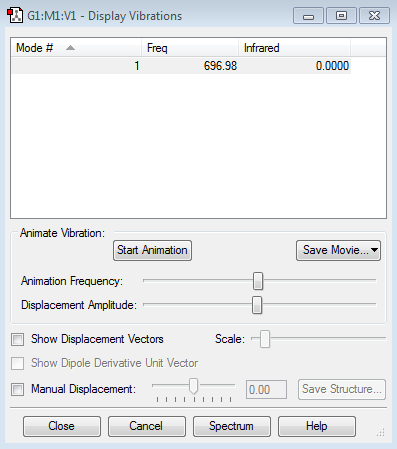
Display Vibrations
Answers to questions
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? 1
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? only one mode which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? stretch:1
which mode is highly symmetric? 1
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? no how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 1
Charges
zero charge on both nitrogen atoms, since same atoms have the same electronegatity.
H2
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basic Set
6-31G
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)
-1.17853936 a.u. (8 d.p)
RMS gradient
0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group
D∞h
Optimised N-N bond length
0.74279 armstrong
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Jmol image
test molecule |
Link
The optimisation file is liked to here
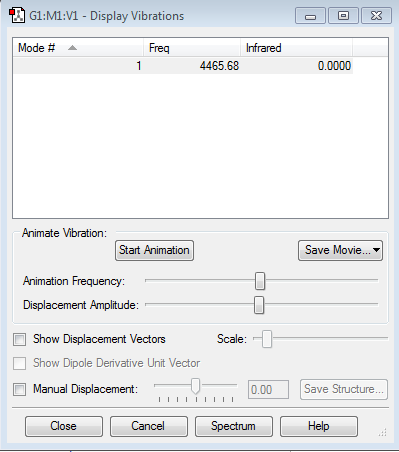
Display Vibrations
Answers to questions
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? 1
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? only one mode which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? stretch:1
which mode is highly symmetric? 1
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? no how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 1
Charges
zero charge on both hydrogen atoms, since same atoms have the same electronegatity.
Energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746
E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557907 a.u.
=-146.8176316 KJmol-1
since the reaction is exothermic, the product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
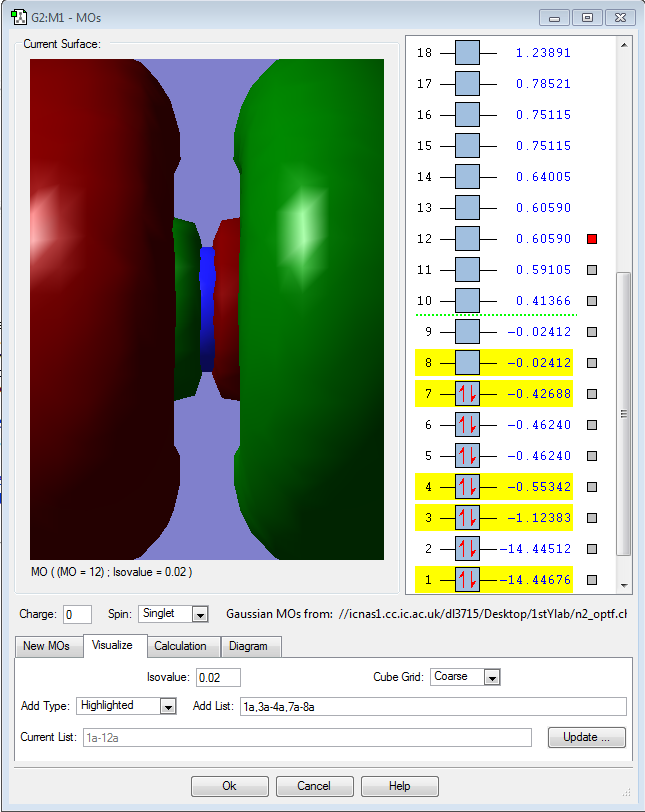
Molecular orbitals for N2
S2
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basic Set
6-31G
final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)
-796.32599779 a.u. (8 d.p)
RMS gradient
0.00000670 a.u.
Point Group
D∞h
Optimised S-S bond length
1.92947 armstrong
Item
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000020 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000028 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-2.290670D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found.
Jmol image
test molecule |
Link
The optimisation file is liked to here
Display Vibrations
Answers to questions
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule? 1
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? only one mode which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? stretch:1
which mode is highly symmetric? 1
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? no how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 1
Charges
zero charge on both sulfur atoms, since same atoms have the same electronegatity.