Rep:Mod:dav16
EX3
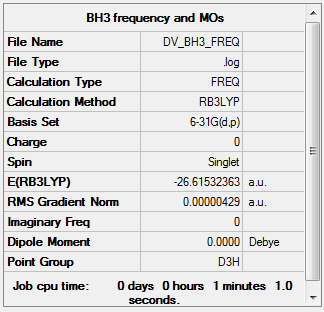
BH3
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000009 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000034 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000017 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -2.2126 -1.0751 -0.0054 2.2359 10.2633 10.3194 Low frequencies --- 1162.9860 1213.1757 1213.1784
Link to log file File:DV BH3 FREQ.LOG
BH3 |
| Mode | Wavenumber /cm-1 | Intesity/Arbitrary Units | IR active | Symmetry | Vibration Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
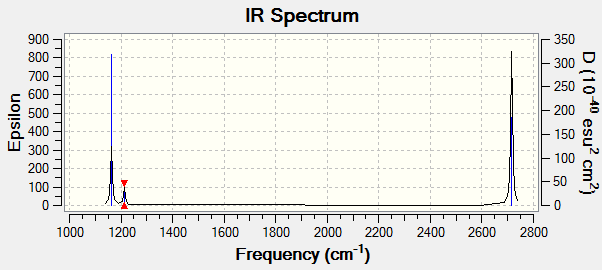
| 1 | 1163 | 92 | yes | A2 | out of plane bending |
| 2 | 1213 | 14 | yes | E' | rock bend |
| 3 | 1213 | 14 | yes | E' | rock bend |
| 4 | 2582 | 0 | no | A1' | symmetric stretch(no change in dipole moment) |
| 5 | 2715 | 126 | yes | E' | Asymetric stretch |
| 6 | 2715 | 126 | yes | E' | Asymmetric stretch |
The obtained computational results there are 6 vibrational modes, it is expected 3 modes following the 3N-6 rule. The spectrum above only shows 3 peaks, modes 2&3 and modes 5&6 have degenerate energy relative to one another, so only appear as one peak in the spectrum. On the other hand, mode 4 corresponds to a symmetric stretch which does not appear in the spectrum because there's no change in dipole moment involved. That gives two peaks so far, such that the remaining peak is due to non-degenerate out of plane bending.
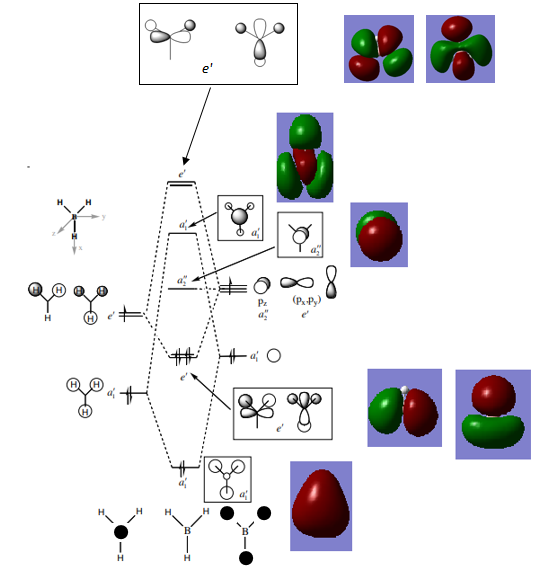
MO Analysis
By comparing the quantified MOs obtained in Gaussian to those expected by applying LCAO, it is seen that the MOs come out as expected in terms of shape and phases. This is a simple MO diagram because there are only 4 atoms involved in a symmetric arrangement in an 8 electron system. It is seen that for the higher energy MOs the electron density is more diffuse and the shape of the MOs becomes harder to interpret relative to the MOs expected from theory.
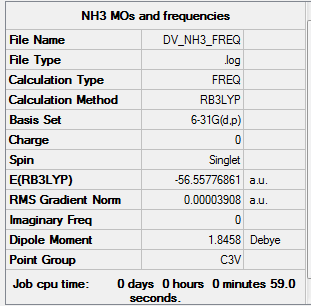
NH3
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000092 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000039 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000304 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000101 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -32.4128 -32.3999 -11.4544 -0.0040 0.0076 0.0521 Low frequencies --- 1088.7642 1694.0248 1694.0252
Link to log file File:DV NH3 FREQ.LOG
NH3 |
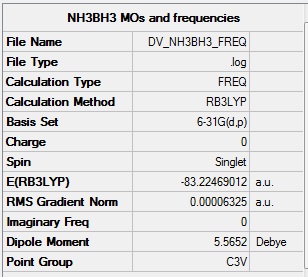
NH3BH3
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000114 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000063 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000621 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000355 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -0.0617 -0.0457 -0.0067 21.6783 21.6842 40.5400 Low frequencies --- 266.0169 632.3610 640.1360
Link to log file File:DV NH3BH3 FREQ.LOG
NH3BH3 |
•E(NH3)= -56.55777 a.u.
•E(BH3)= -26.61532 a.u.
•E(NH3BH3)= -83.22469 a.u.
•ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)] = -83.22469 - (-26.61532-56.55777)
•ΔE = -0.05160 a.u. = -135 kJmol-1
The B-N bond is of dative covalent nature, though there's a strong dipole moment across the bond due to the difference in electronegativity between boron and nitrogen, by comparing to the strength of C-C bond -348 kJmol -1, B-N is a much weaker bond.
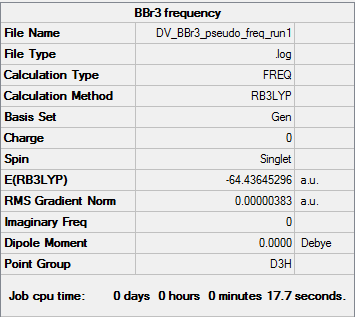
BBr3
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -0.0137 -0.0064 -0.0046 2.4315 2.4315 4.8421 Low frequencies --- 155.9631 155.9651 267.7052
Link to log file File:DV BBr3 pseudo freq run1.log
BBr3 |
Mini Project
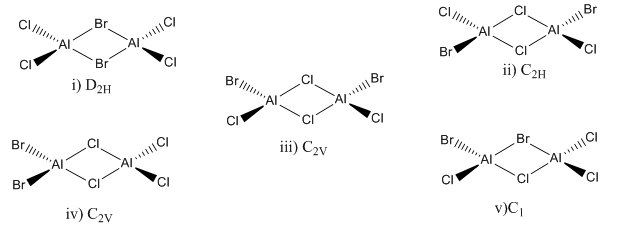
Isomers of Al2Br2Cl4 were investigated in this section
Aluminium and Chlorine atoms optimised with B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) and BR atoms optimised with LanL2DZ pseudopotentials.
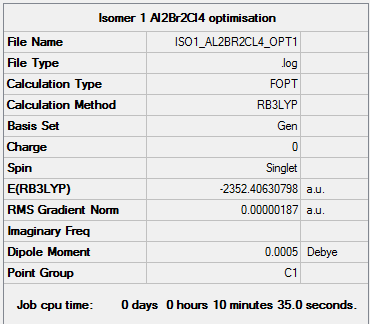
Isomer i (Bridging Br)
Isomer i) energy = -2352.40631 a.u. = -6175067 kJmol-1
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000002 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000604 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000310 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -5.1748 -5.0356 -3.1468 -0.0023 -0.0011 0.0005 Low frequencies --- 14.8260 63.2702 86.0770
Link to log file File:ISO1 AL2BR2CL4 FREQ11.LOG
AL2BR2CL4 Isomer i) |
Isomer ii (Bridging Cl with trans terminal Br)
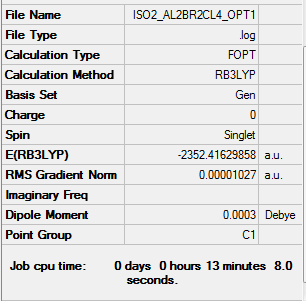
Isomer ii energy = -2352.41630 a.u. = -6175093 kJmol-1
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000010 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000863 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000319 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -4.9721 0.0023 0.0023 0.0027 1.6380 2.3324 Low frequencies --- 18.1768 49.0937 73.0114
Link to log file File:ISO2 AL2BR2CL4 FREQ1.LOG
AL2BR2CL4 Isomer i) |
•isomer i energy = -6175067 kJmol-1
•isomer ii energy = -6175093 kJmol-1
The second isomer in which there are bridging chlorines instead of bromines is more stable. By considering the orbital overlap and match in energy it is seen that there should be better orbital overlap and match in energy between Al and Cl than between Al and Br because the first two are in the same row in the periodic table, whereas the latter two would lead to more diffuse orbital overlap as Br is in row 4 of the periodic table.
AlCl2Br
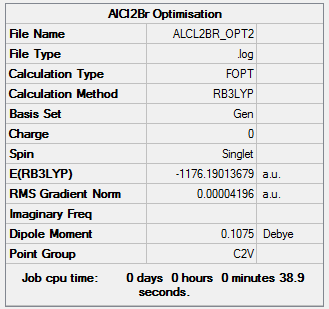
AlCl2Br energy = -1176.19013679 a.u. = -3087499 kJmol-1
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000136 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000073 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000760 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000497 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- 0.0042 0.0049 0.0050 1.3569 3.6367 4.2604 Low frequencies --- 120.5042 133.9178 185.8950
Energy of dimer = -6175093 kJmol-1
Energy of AlCl2Br = -3087499 kJmol-1
Dissociation Energy = 2E(monomer) -E(Isomer) = 95 kJmol-1
Link to log file File:ALCL2BR FREQ RUN3.log
ALCL2BR monomer |
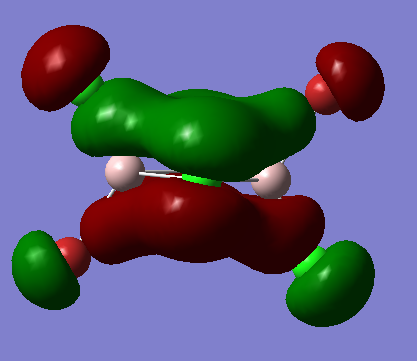
MO analysis
MO 40
Fragment Orbitals
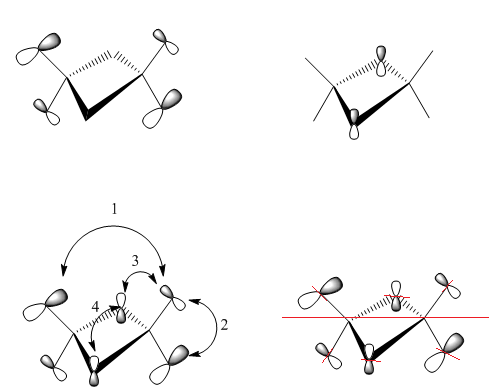
Interactions
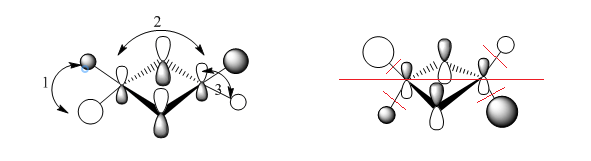
1) medium distance, but s-s orbitals through space antibonding interaction so overall medium antibonding
2) bonding interaction, small distance but p orbitals, so overall strong bonding interaction
3) s-p interaction, short distance, but overlaps out of phase . The terminal orbitals look more like polarised s orbitals than p orbitals. The bonding interactions are outweighed by the antibonding interactions so overall antibonding .
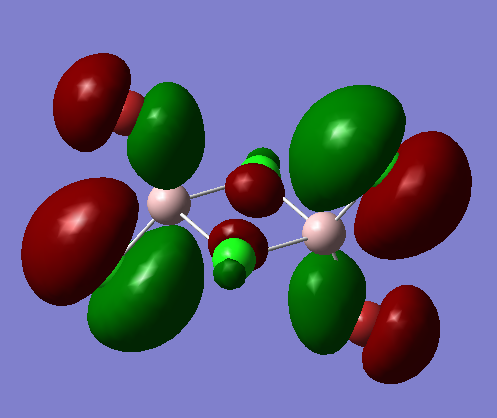
The delocalised pi system prevails in the MO but the other picture on the right shows the nodes on the dimer which also show the MO is overall weakly antibonding̟.
MO 48
Fragment Orbitals
Interactions
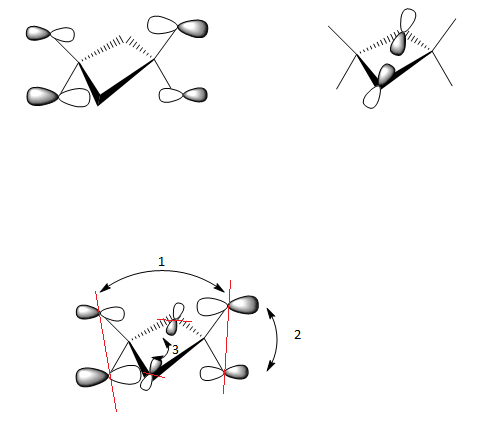
1) Long range, through space orbital interaction but far away so very weakly bonding
2)Medium range, through space orbital interaction therefore weakly bonding
3) Small distance,spatial overlap but orbitals have lower contribution to the MO and are slightly polarised, sigma type so medium bonding
The contributions from the terminal Chlorine p orbitals is greater than that of the terminal bromine p orbitals. The MO is overall weakly bonding.
MO 54
Fragment Orbitals
Interactions
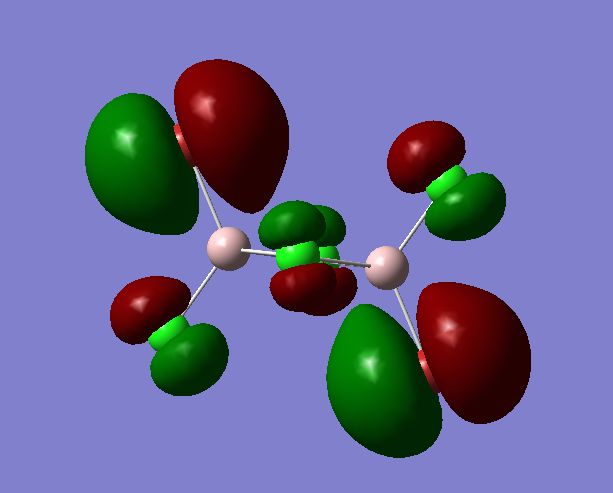
1) Long range, through space orbital interaction but far away so very weakly bonding
2) Medium range, through space orbital interaction, out of phase so weakly antibonding
3) medium range, through space orbital interaction, out of phase so is weakly antibonding
4)small distance, through space orbital interaction, sideways interaction so weakly bonding
The MO is assigned as antibonding, the antibonding interactions outweigh the bonding interactions.