Rep:Mod:danbanh
BH3
B3LYP/6-21G level
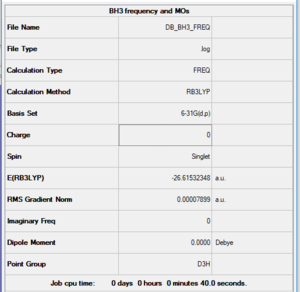
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000158 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000079 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000622 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000311 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies
Low frequencies --- -0.2456 -0.1129 -0.0054 44.0270 45.1846 45.1853 Low frequencies --- 1163.6049 1213.5924 1213.5951
Link to log file: here
BH3 Jmol image
BH3 |
Link to log file: here
Vibrations
| Stretching frequency (1/cm) | Stretching intensity (%) | Type of vibration | IR Active? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1164 | 92 | Bend out of plane | Yes |
| 1214 | 14 | Bend in plane | Yes |
| 1214 | 14 | Bend | Yes |
| 2580 | 0 | Symmetric stretch | No |
| 2713 | 126 | Asymmetric stretch | Yes |
| 2713 | 126 | Asymmetric stretch | Yes |
Whilst there are 6 vibrations for BH3, there are fewer than 6 IR peaks present in the IR spectrum. There are 3 peaks present, 2 of which correspond to 2 degenerate vibrational modes. There are degenerate modes at: 1214/cm and 2713/cm. The final peak present corresponds to an out of plane bend at 1164/cm.
Ng611 (talk) 14:09, 27 May 2019 (BST) What about the non-IR active stretch at 2580 wavenumbers?
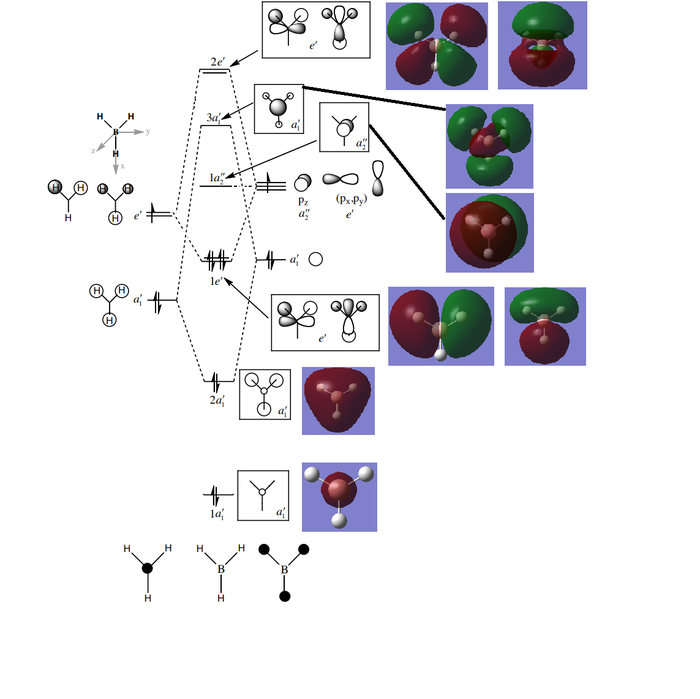
BH3 MO diagram
Ng611 (talk) 14:14, 27 May 2019 (BST) One of your e' orbitals (the right hand one) doesn't seem correct. Pay close attention to the phase relationship.
The LCAO MO description is a reasonably accurate general picture of the distribution of electron density. However, it isn't a perfect description or the real MOs. The real MOs are more diffuse and spread out compared to the LCAO model which constrains electron density to orbitals on atoms rather than across the whole molecule. This shows that qualitative MO analysis is accurate, and useful, but not perfect due to the lack of precision about the distribution of electron density across the whole molecule.
Ng611 (talk) 14:14, 27 May 2019 (BST) There's a more significant discrepancy between the qualitative and quantitative MO theory that you've missed. What do you think it could be?
-Diagram adapted from: Professor T.Hunt, Imperial College London, Lecture_4_Tut_MO_diagram_BH3
Association Energy
NH3

Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-9.843852D-11
Low frequencies --- -0.0138 -0.0032 -0.0015 7.0783 8.0932 8.0937 Low frequencies --- 1089.3840 1693.9368 1693.9368
Link to log file: here
NH3 |
Link to log file: here
NH3BH3

Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000121 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000057 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000507 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000295 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.613116D-07
Low frequencies --- -0.0252 -0.0030 0.0008 17.0357 17.0380 36.8914 Low frequencies --- 265.7448 632.2122 639.3345
Link to log file: here
NH3BH3 |
Link to log file: here
Association energy calculation
E(NH3)= -56.55776873, E(BH3)= -26.61532349, E(NH3BH3)= -83.22468892, ΔE= E(NH3BH3)- [E(NH3)+ E(BH3)], ΔE= -0.0515967 au ΔE= -135 KJ/mol
The calculated energy of the B-N bond is low. This means that the dative B-N bond can be considered as weak. C-C has a bond strength of 346 KJ/mol whilst the weak F-F bond has a bond strength of 155 KJ/mol [1].
Ng611 (talk) 14:16, 27 May 2019 (BST) Good calculation and good bond comparison! Try to use a source from a textbook or databook, rather than the web.
NI3
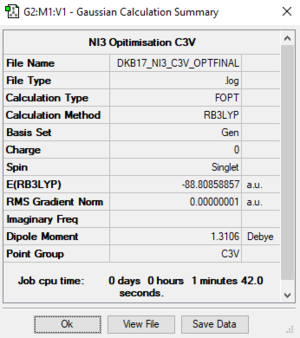
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000015 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000010 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000001 0.000060 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.000040 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.540748D-14
Low frequencies --- -12.5584 -12.5522 -6.0136 -0.0040 0.0191 0.0663 Low frequencies --- 100.9979 100.9986 147.3400
Link to log file: here
N-I bond length: 2.030 Å
Ng611 (talk) 14:18, 27 May 2019 (BST) Slighly off the correct value here. Did you repeat your optimisation?
NI3 |
Link to log file: here
Ionic Liquids
[N(CH3)4]+

Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000073 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000018 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000277 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000088 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.328712D-08
Low frequencies --- 0.0007 0.0010 0.0013 35.6290 35.6290 35.6290 Low frequencies --- 215.5240 315.1230 315.1230
Link to log file: here
[N(CH3)4]+ |
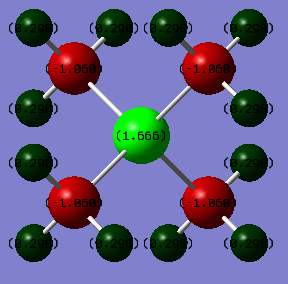
[P(CH3)4]+

Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000138 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000035 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000718 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000298 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.829332D-07
Low frequencies --- -0.0042 -0.0041 -0.0017 51.6355 51.6355 51.6355 Low frequencies --- 188.7480 213.6021 213.6021
Link to log file: here
[P(CH3)4]+ |
Charge Distribution Analysis
| Atom | Charge (C) |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen | -0.296 |
| Carbon | -0.483 |
| Hydrogen | 0.269 |
| Atom | Charge (C) |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus | 1.666 |
| Carbon | -1.060 |
| Hydrogen | 0.298 |
In the valence model of [N(CH3)4]+, the positive charge would be localised on the Nitrogen atom. However, as Nitrogen is highly electronegative, the inductive effect pulls electron density from the methyl groups towards the Nitrogen centre, thus, resulting in a more negative charge distribution around the centre of the molecule. Positive charge is therefore localised on the Hydrogen atoms. The Phosphorus, however, has a local positive charge. This is due to Phosphorus being more electropositive compared to the Carbon atoms resulting in electron density being pulled away from the Phosphorus centre.
Ng611 (talk) 14:21, 27 May 2019 (BST) Good discussion of electronegativity. What about the effect of symmetry? You should also discuss the charge on the carbon atoms in NMe4+ and the breakdown of the formal charge picture.
MO Visualisation
| MO | LCAO | Real MO |
|---|---|---|
| MO8 | 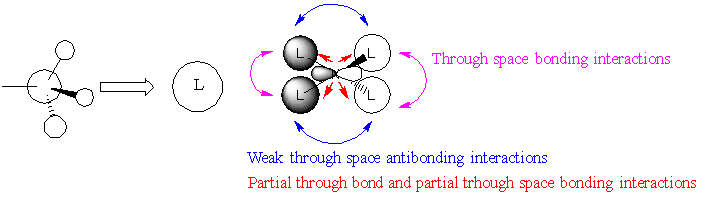 |
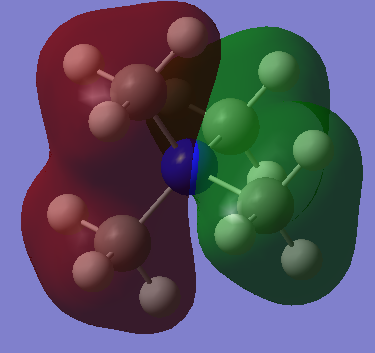
|
| MO10 |  |
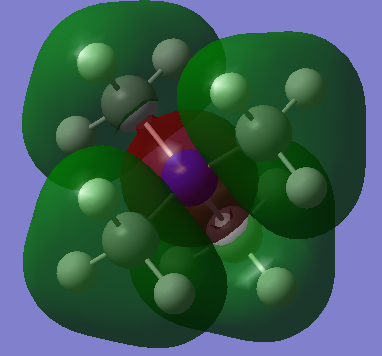
|
| MO21 | 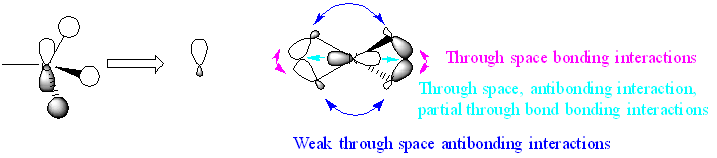 |
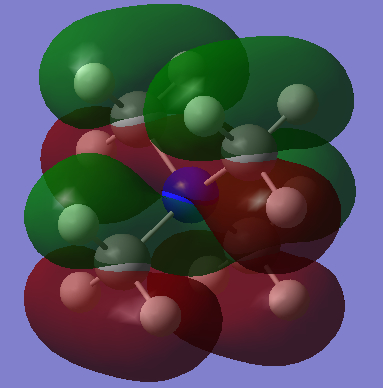
|
Ng611 (talk) 14:28, 27 May 2019 (BST) Your FOs for MO10 should be s-type, not p-type. Otherwise, outstanding LCAO analysis.
References
[1]: Strength of Covalent bonds, Chemistry Libretexts: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_Chemistry_-_The_Central_Science_(Brown_et_al.)/08._Basic_Concepts_of_Chemical_Bonding/8.8%3A_Strength_of_Covalent_Bonds (Accessed 19/05/19)


![400px]](/images/8/8f/Dkb17_N_Charge_distribution.PNG)