Rep:Mod:complab97
NH3 Molecule
A model of this molecule was made using the program Gaussview. All 3 bond angles were set to 1.3 Angstrom and the point group set to C3V. The structure of this molecule is an rough estimate, and will be optimised to find the lowest energy structure.
The structure is optimised by Gaussian using a plot of potential energy vs. the positions of the hydrogen atoms relative to to the central nitrogen atom, starting from the estimated structure that has been made. The positions of the hydrogen atoms are changed a small distance in both directions, and compared to gradient of the line (the 1st derivative). If the gradient is now smaller, Gaussian continues to calculate the gradient for small movements in this direction. Using this method, Gaussian attempts to find the positions of nuclei, where the gradient is as close to zero as possible - which is the lowest energy (equilibrium) position of the molecule.
Jmol image of optimised NH3 molecule |
The following parameters were used in the Gaussian optimisation:
Calculation method: B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p) - medium level of accuracy
Type of calculation to do: OPTF (optimise and frequency analysis) - this is used to determine the optimum (lowest energy) positions of the nuclei
Further commands used: pop=(full,nbo) - pop=NBO runs a population analysis to calculate the atomic charges; pop=full calculates all of the MOs
Optimisation Results
Final energy: E(RB3LYP): -56.44397188 au
RMS gradient: 0.05399560 au
Point group: C3V
N-H bond length: 1.01798 angstrom
H-N-H bond angle: 105.741 degrees
Gaussian Calculations
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
The following graph (below right) represents the change in potential energy as Gaussian optimises the structure of the molecule. As the basis set 6-31G(d,p) only has medium accuracy, there are relatively few steps before the optimised structure is reached.
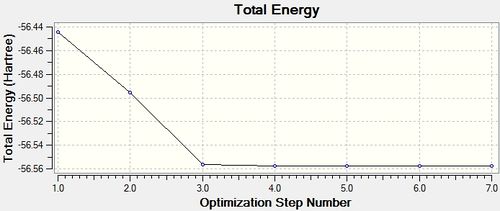
Vibrational Analysis
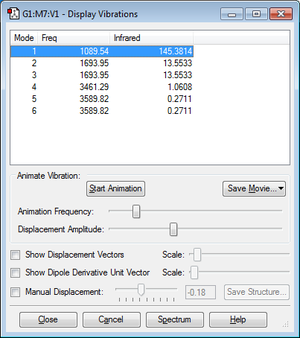
- 6 vibrational modes are expected from the 3N-6 rule
- Modes 2 & 3 are degenerate; so are modes 5 & 6
- The "bending" vibrations are modes 1, 2, and 3
- The "stretching" vibrations are modes 4, 5, and 6
- Mode 4 is the highly symmetric vibrational mode
- Mode 1 is the "umbrella" vibrational mode
- 4 bands would be seen in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia - although there are 6 vibrational modes, due to the degenerate modes, vibrations only occur at 4 different frequency bands
Charge Distribution
Charge of N: -1.125 Charge of H: +0.375
These charges are expected, as nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen
N2 Molecule
Optimisation Results
Final energy: E(RB3LYP): -109.52359111 au
RMS gradient: 0.02473091 au
Point group: D*H
N-N bond length: 1.10550 angstrom
Gaussian Calculations
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrational Modes
There is one vibrational mode for N2, frequency = 2457.33 cm-1
Jmol image of optimised N2 molecule |
H2 Molecule
Optimisation Results
Final energy: E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 au
RMS gradient: 0.00000017 au
Point group: D*H
H-H bond length: 0.74279 angstrom
Gaussian Calculations
Item Value Threshold Converged? Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Vibrational Modes
There is one vibrational mode for H2, frequency = 4465.68 cm-1
Jmol image of optimised H2 molecule |
Energies of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
Units(a.u.)
E(NH3)= -56.44397188
2*E(NH3)= -112.88794376
E(N2)= -109.52359111
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= 0.17126543 au
ΔE = 449.66 kJ/mol-1
CN- Analysis
Jmol image of optimised CN- molecule |
Optimisation Results
Final energy: E(RB3LYP): -92.82453153 au
RMS gradient: 0.00000704 au
Point group: C*V
C-N bond length: 1.18409 angstrom
Gaussian Calculations
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000012 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000005 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
Charge Distribution
The carbon atom has a charge of -0.246; the nitrogen atom has a charge of -0.754. This is expected, nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon so will have a more negative charge, and the total charge adds up to -1.
Vibrational Analysis
This molecule has one vibrational mode, a symmetrical bond stretch at 2139.19 cm-1
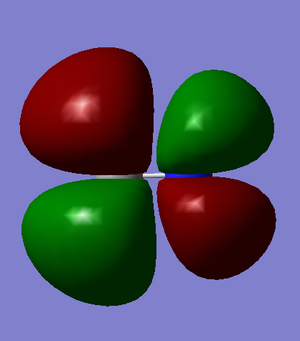
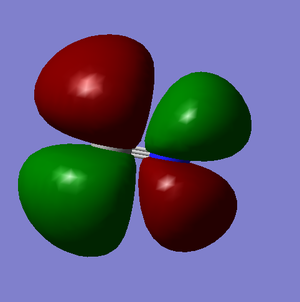
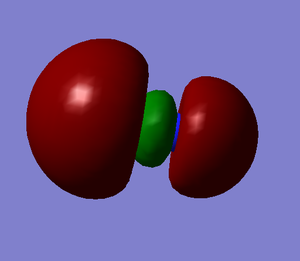
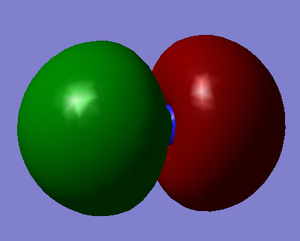
Molecular Orbitals
These images show the LUMO+1, the LUMO, the HOMO, and the 3 orbitals next lowest in energy of the CN- ion. The grey atom is carbon; the blue is nitrogen.