Rep:Mod:awc106 module2 PROJECT
Mini Project: Ammonia-Borane
Ammonia borane NH3BH3 is a Lewis acid-base pair moleucle. NH3BH3 is also under scrutiny as a very promising molecule for the sotrage of hydrogen to be used as a new fuel. Ammonia-borane is 19.6% by weight hydrogen.
is ammonia borane staggered or eclipsed? what is the energy difference between these conformers? how does this energy difference compare to that of ethane? what can you say about the bonding in this compound relative to the organic analogue? what is the stability of ammonia-borane relative to the suggested reactants (NH4Cl and NaBH4), which form NH4BH4 and NaCl, then H2 is released. You should calculate E(reactants)-E(products) ammonia-borane is isoelectronic with ethane. But whereas ethane has an extremely low melting point, the former melts around 110°C. Can you find an explanation? (Hint: is there a way of modelling the solid state of this species? Are any of the techniques described in Module 3 relevant?) Reference:Borane leads the way to alternative fuels an article from Chemistry World (02 July 2008) Reference:Ammonia�borane: the hydrogen source par excellence? Dalton Trans., 2007,�2613 - 2626, DOI: 10.1039/b703053c
Ammonia Borane
Table 1: NH3BH3 | |||||||||||
| Staggered | Eclipsed | ||||||||||
| Results | Image | HOMO | Results | Image | HOMO | ||||||
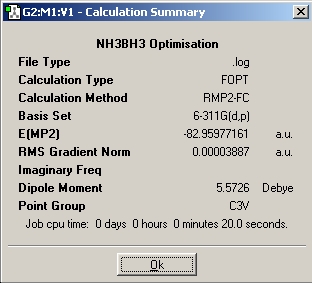
|
|
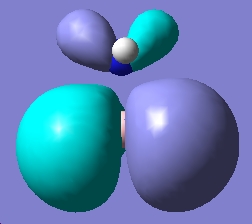
|
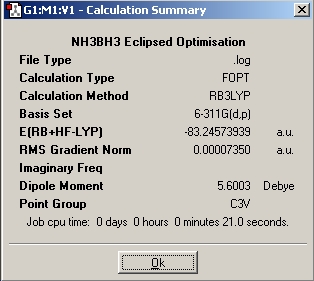
|
|
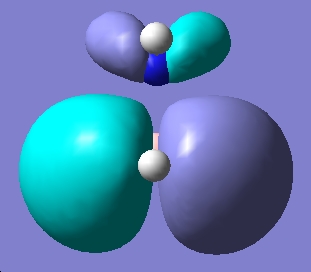
| ||||||
Ammonia-borane is isoelectronic with ethane. It is thus beneficial to compare the two molecules.
Table 2: Ethane | |||||||||||
| Staggered | Eclipsed | ||||||||||
| Results | Image | HOMO | Results | Image | HOMO | ||||||
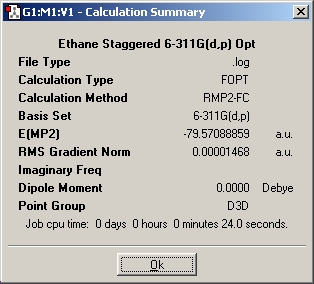
|
|
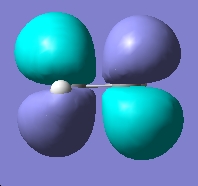
|
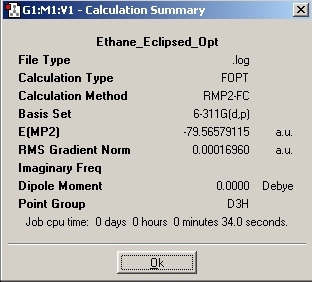
|
|
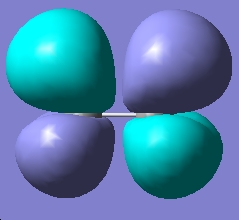
| ||||||
What is the stability of NH3BH3 relative to the reactants? NH3BH3 is synthesised according to the following scheme:
Hydrogen (H2) is the released resulting in NH3BH3. Therefore we must compare the relative energies of the reactants and products and calculate E(reactants)-E(products).
Table 3: Products and Reactants | |||
| NH4+ | BH4- | NH4BH4 | |

|
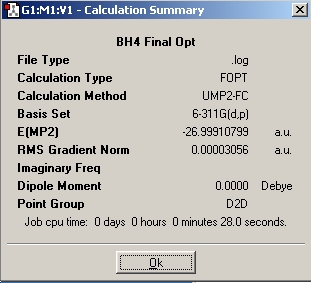
|
File:Gerojj9nh7nimo2.jpg | |
| File:Geroh7jd8nimo2999ij.jpg | File:Ger776jjsd7soh7nimo2.jpg | File:Gejc8rojj9nh7nimo2.jpg | |
