Rep:Mod:ZY3915
NH3 molecule
N-H bond distance: B=1.01798
H-N-H bond angle: A=105.741
| Molecule name | Ammonia |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873au |
| Point group | C3V |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
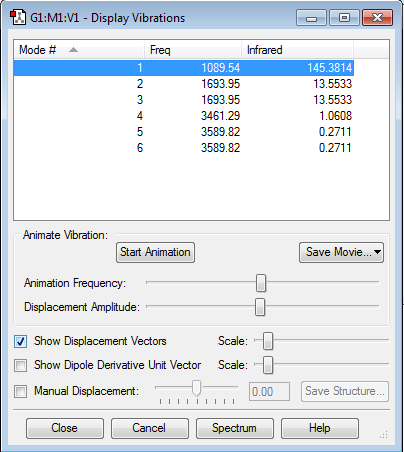
Vibrations
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
3*4-6=6; so,6 modes
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
mode2 and mode3(both have frequency of 1693.95); mode5 and mode6(frequency of 3589.82)
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
mode1 2 3 are "bending"; mode4 5 6 are "bond stretch"
Which mode is highly symmetric?
mode1 and mode4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
mode1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2, because mode1 2 and 3 have strong infrared signals while signals of the rest are negligible so those(mode4 5 and 6)will not be there in the experimental spectrum. However the total number of bands will be 2, as mode2 and mode3 are identical in frequency.
Charges
| 1(N) | 2(H) | 3(H) | 4(H) |
|---|---|---|---|
| -1.125 | 0.375 | 0.375 | 0.375 |
The Haber-Bosch process
H2
Molecule name Hydrogen Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) Charge 0 Spin Singlet E(RB3LYP) -1.17853936 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000222 a.u. Imaginary Freq 0 Dipole Moment 0.0000 Debye Point Group D∞H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000005 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000007 0.001200 YES
N2
Molecule name Nitrogen Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) Charge 0 Spin Singlet E(RB3LYP) -109.52412868 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000001 a.u. Imaginary Freq 0 Dipole Moment 0.0000 Debye Point Group D∞H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
E(NH3)=-56.5577687au
2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375au
E(N2)=-109.5241287au
E(H2)=-1.1785394au
3*E(H2)=-3.5356181au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557907au=-146.47849401kJ/mol
so the energy for converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia gas is -146.47849401kJ/mol, which means the ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants
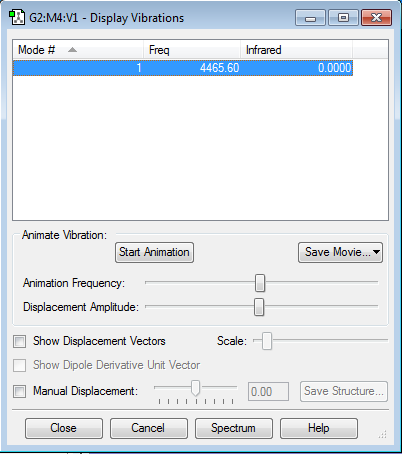
CO molecule
test molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Molecule name Carbon monoxide Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) Charge 0 Spin Singlet E(RB3LYP) -113.30945314 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000002 a.u. Imaginary Freq 0 Dipole Moment 0.0599 Debye Point Group C∞V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
There is only one mode of vibration (bond stretch) for this molecule as the only band in the experimental spectrum and this mode is highly symmetric.
Charges
| 1(C) | 2(O) |
|---|---|
| 0.506 | -0.506 |
Moleuclar Orbitals
HOMO-6:1σ bonding orbital(contributed by 1s orbital of carbon and 1s orbital of oxygen) This orbital is occupied by two electrons,and is very deep in energy (-19.25805) that AOs do not have much overlap.
HOMO-2:1π bonding orbital(contributed by 2p orbital of carbon and 2p orbital of oxygen) The energy of this orbital is deep in energy (-0.46743) but very close to that of HOMO and the orbital is occupied by two electrons.
HOMO-1:2π bonding orbital(contributed by 2p orbital of carbon and 2p orbital of oxygen) This orbital is occupied by two electrons and it has the same energy as HOMO-2(-0.46743).
HOMO:3σ bonding orbital(contributed by 2p orbital of carbon and 2p orbital of oxygen) This orbital is the HOMO that contribute the most to the C-O bond and it has two electrons in it.
LUMO+2:3σ* antibonding orbital(contributed by 2p orbital of carbon and 2p orbital of oxygen) This orbital has no electron in it and the calculated shape is not consistent with the prediction on text books due to optimisation focusing on orbitals with electrons in it.