Rep:Mod:YLS15
Ammonia, NH3
Gaussian Calculation Summary
- Molecule Name: Ammonia, NH3
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis set:6-31G(d,p)
- Final energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
- RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
- The point group of your molecule: C3v
- H-N-H bond angle:105.7412°
- H-N bond length: 1.018Å
The optimisation file of NH3 is linked here
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986284D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found. ---------------------------- ! Optimized Parameters ! ! (Angstroms and Degrees) ! -------------------------- -------------------------- ! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NH3 Molecule |
Vibration Modes
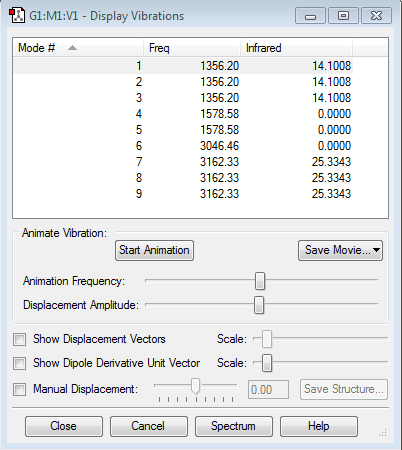
The animations of the different vibrations modes of the NH3 molecule Mode 1 Mode 2 Mode 3 Mode 4 Mode 5 Mode 6
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6 Vibration modes.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate. Also modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Modes 2 and 3 are "bending" vibrations, mode 4 is symmetrical stretching, modes 5 and 6 are asymmetrical stretching.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Modes 1 and 4 is highly symmetrical.
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2 Bands at 1089.54 cm-1 and 1693.95 cm-1
Charge Distribution
The charge on the Nitrogen atom is expected to be negative and the charge on the Hydrogen atom is expected to be positive as Nitrogen is more electronegative than Hydrogen so the electron density is pulled toward the Nitrogen atom resulting in the negative charge.
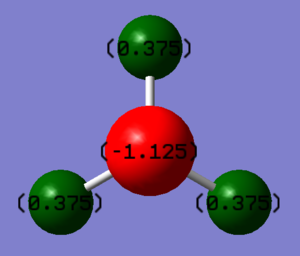
Charge on the Hydrogen atom: +0.375
Charge on the Nitrogen atom: -1.125
Comparison with Literature Values
The literature values of bond length and bond angles is taken from the [NIST Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark DataBase].
| Property | Literature Value | Calculated value | Difference from the Literature value | % Difference compared to the Literature value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-N-H Bond Angle | 106.6700° | 105.7412° | -0.9288° | -0.87% |
| H-N Bond Length | 1.0124Å | 1.0180Å | +0.0056Å | +0.55% |
The calculated bond angle and bond length is very close to the literature value. The reason why the values does not match completely is because the basis set is 6-31G(d,p) which only has medium accuracy. This basis set was used so the calculation is quick. For more accurate results, a basis set with higher accuracy should be used however the time taken to complete the calculation would be longer.
Nitrogen, N2
Gaussian Calculation Summary
- Molecule Name: Nitrogen, N2
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis set:6-31G(d,p)
- Final energy E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u.
- RMS Gradient: 0.00000217 a.u.
- The point group of your molecule: D∞h
- N≡N bond angle: 180°
- N≡N bond length: 1.1055Å
The optimisation file of N2 is linked here
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000001 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000002 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.428714D-12
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
One vibration mode occurs at 2457.34 cm-1
The charge on the two Nitrogen atom is 0. The electrons are distributed evenly since as the two atoms have the same electronegativity as they are the same so there is no net dipole moment.
Hydrogen, H2
Gaussian Calculation Summary
- Molecule Name: Hydrogen, H2
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis set:6-31G(d,p)
- Final energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
- RMS Gradient: 0.00000017 a.u.
- The point group of your molecule: D∞h
- H-H bond angle: 180°
- H-H bond length: 0.7428Å
The optimisation file of H2 is linked here
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
One vibration mode occurs at 4465.68 cm-1
The charge on the two Hydrogen atom is 0. The electrons are distributed evenly since as the two atoms have the same electronegativity as they are the same so there is no net dipole moment.
Reaction Energy of the Haber-Bosch process
- E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
- 2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
- E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
- E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
- 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.4784828 kJ moɭ -1
ΔE is a negative value which indicated that the gaseous product is more stable.
Methane, CH4
Gaussian Calculation Summary
- Molecule Name: Methane, CH4
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis set:6-31G(d,p)
- Final energy E(RB3LYP): -40.52401404 a.u.
- RMS Gradient: 0.00003263 a.u.
- The point group of your molecule: Td
- H-C-H bond angle:109.4712°
- C-H bond length: 1.092Å
The optimisation file of CH4 is linked here
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256106D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CH4 Molecule |
Vibration Modes
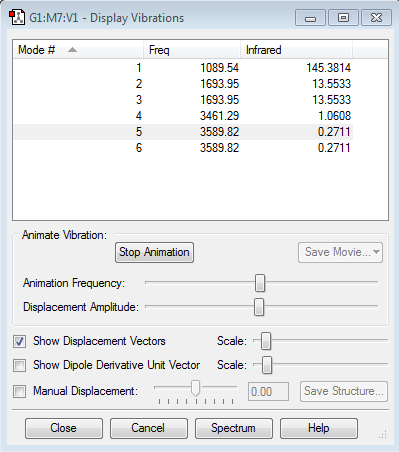
Using the 3N-6 rule, the methane molecule is expected to have 9 vibrational modes.
The animations of the different vibrations modes of the CH4 molecule Mode 1 Mode 2 Mode 3 Mode 4 Mode 5 Mode 6 Mode 7 Mode 8 Mode 9
Modes 1, 2 and 3 are degenerate. Modes 4 and 5 are degenerate. Modes 7, 8 and 9 are also degenerate.
̈Modes 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 are "bending vibrations. Mode 6 is symmetrical stretching. Modes 7 and 8 are asymmetrical stretching.
Charge Distribution
The charge on the Carbon atom is expected to be negative and the charge on the Hydrogen atom is expected to be positive as Carbon is more electronegative than Hydrogen so the electron density is pulled toward the Carbon atom resulting in the negative charge.

Charge on the Hydrogen atom: +0.233
Charge on the Carbon atom: -0.930
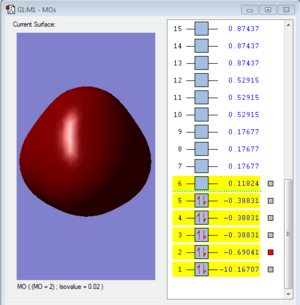
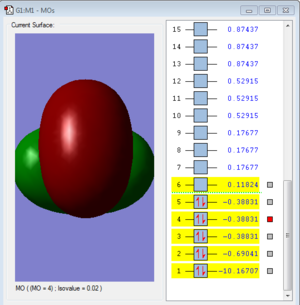
Molecular Orbital
Molecular orbitals 3, 4 and 5 are degenerate.