Rep:Mod:YL9210
Optimisation and Analysis of simple molecules
Optimization Analysis
Optimisation of BH3 using 'B3LYP, 3-21G'
Calculations
The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of 3-21G.
The method BLYP determines the type of approximations in solving the Schrodinger equation. The basis set determines the accuracy, 3-21G has a very low accuracy, however the time for the calculations should be short. The keyword of calculation was # opt b3lyp/3-21g geom=connectivity.
Results
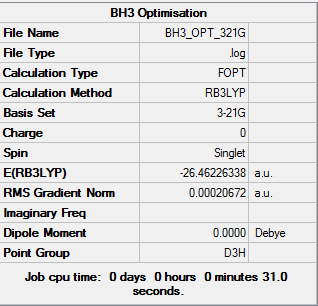
The log file of BH3 Optimisation (3-21G): BH3_OPT_321Gyjl.LOG
Summary of BH3 Optimisation (3-21G)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 3-21G |
| Final Energy | -26.46226338 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00020672 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 31.0 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000413 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000271 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001610 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.001054 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.071764D-06
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
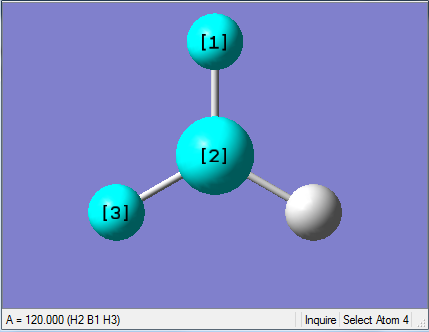
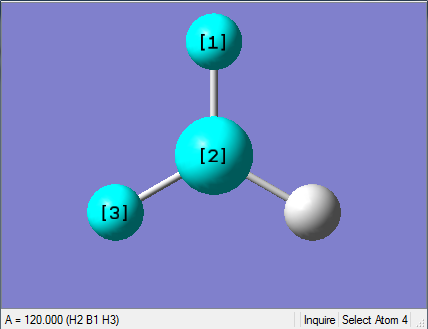
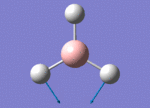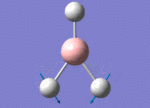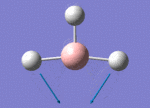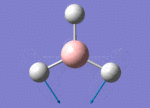
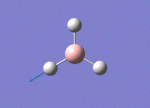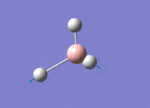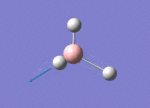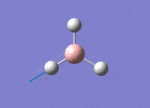
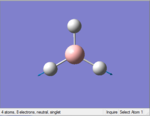
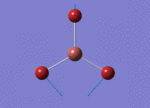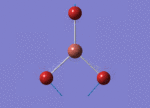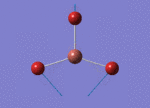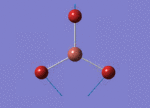
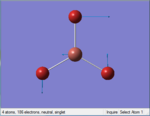
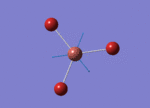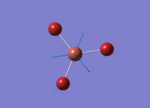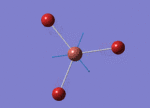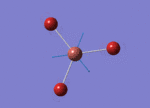
The Image of Bond Angle
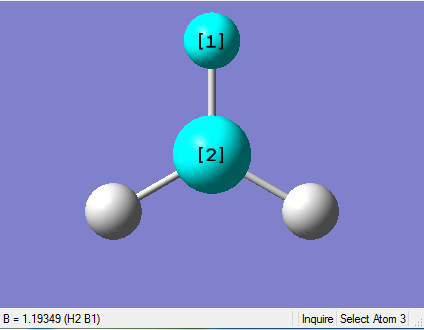
The Image of Bond Length
B-H bond length = 1.193 Å
H-B-H bond angle= 120.0°
Discussion
Forces and displacements were converged as shown in the "item" table. All B-H bond lengths and H-B-H angles were equivalent as shown in the two images.
Optimisation of BH3 using 'B3LYP, 6-31G(d,p)'
Operations
The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of 6-31G(d,p).
Basis set 6-31G(d,p) has a higher accuracy than that of 3-21G.The keyword of calculation was # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d,p) geom=connectivity.
Results
The log file of BH3 Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): BH3_OPT_631GDPyjl.LOG
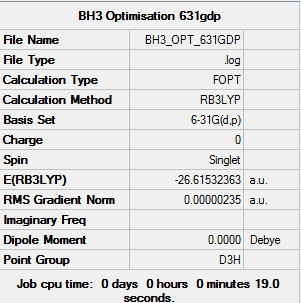
Summary of BH3 Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000235 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 19.0 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000019 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000012 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.304899D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
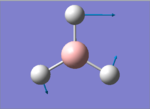
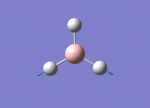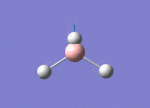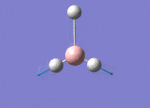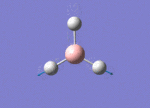
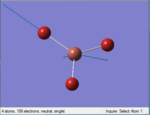
The Image of Bond Angle
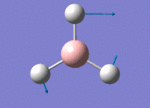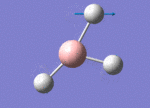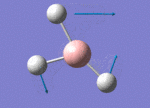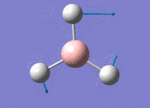
The Image of Bond Length
B-H bond length = 1.192 Å
H-B-H bond angle= 120.0°
Discussion
Forces and displacements were converged as shown in the "item" table. All B-H bond lengths and H-B-H angles were equivalent as shown the two images. The bond length was slightly shorter than that of optimisation using 3-21G as a basis set, while the bond angles remained the same. The decrease of bond length could be explained by the decrease in energy when 6-31G(d,p) was used as a basis set. The total energy for the 6-31G(d,p) calculation was a more negative energy, the energy difference was 0.15306025 a.u, which equaled to 401.9 kJ/mol-1. There was a large energy decrease when 6-31G(d,p) was used as a basis set.
| Basis Set | Energy /a.u. |
|---|---|
| 3-21G | -26.46226338 |
| 6-31G(d,p) | -26.61532363 |
| Change in Energy | 0.15306025 |
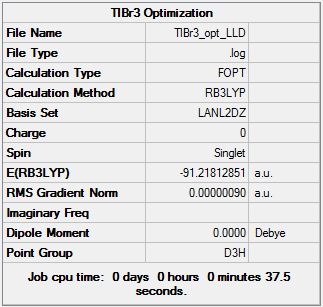
Optimisation of TlBr3 using 'B3LYP, LAN2DZ'
Operations
For the heavier molecule TLBr3, calculations were submitted to HPC to avoid long time calculation. The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of LANL2DZ.
The basis set LANL2DZ is in "medium" level.The keyword of calculation was # opt b3lyp/lanl2dz geom=connectivity.
Results
The log file of TlBr3 optimisation (LAN2DZ): DOI:10042/21608
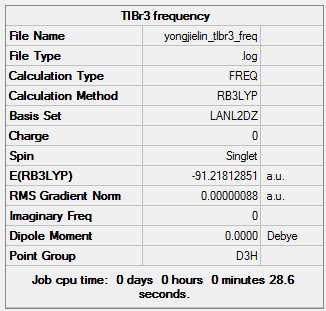
Summary of TlBr3 Optimisation (LANL2DZ)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Final Energy | -91.21812851 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000090 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 37.5 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.084085D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
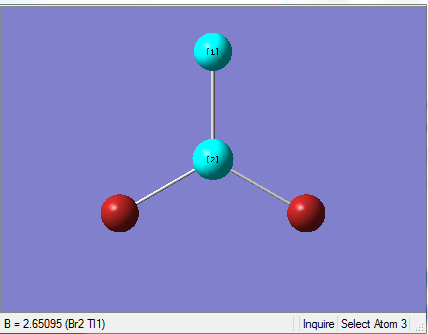
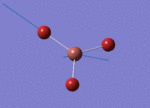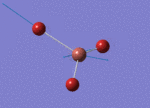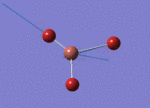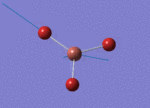
The Image of Bond Length
The Image of Bond angle
Tl-Br bond length = 2.651 Å
Br-Tl-Br bond angle= 120.0°
The Tl-Br bond length From optimisation equals to 2.651 Å, which slightly different from 2.512 Å in literature1.
Discussion
Forces and displacements were converged as shown in the "item" table. All B-H bond lengths and H-B-H angles were equivalent as shown the two images.
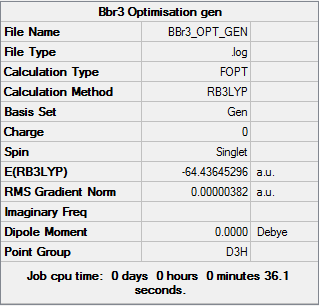
Optimisation of BBr3 using 'B3LYP, GEN'
Operations
The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of GEN. "pseudo=read gfinput" was used as an additional keyword, # opt b3lyp/gen geom=connectivity gfinput pseudo=read was the keyword in calculations.
Results
The log file of BBr3 optimisation (GEN):DOI:10042/21625
Summary of BBr3 Optimisation (GEN)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | GEN |
| Final Energy | -64.43645296 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000382 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 36.1 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000023 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.027599D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The Image of Bond Angle
The Image of Bond Length
B-Br bond length = 1.933 Å
Br-B-Br bond angle= 120.0°
Discussion
Forces and displacements were converged as shown in the "item" table. All B-H bond lengths and H-B-H angles are equivalent as shown the two images.
Comparison of Bond Lengths and Bond Angles
| Molecule | Bond Length /Å | Bond Angle/Degree |
|---|---|---|
| BH3 | 1.19349 | 120.0 |
| BBr3 | 1.9340 | 120.0 |
| TlBr3 | 2.65095 | 120.0 |
From the structures provided in the previous sections, BH3, BBr3 and TlBr3 all adopt trigonal planar structure, so the bond angle remianed as a constant although the atoms in the molecules were changed. When the H ligands in BH3 were changed to be Br ligands to form BBr3, the bond length increased. H and Br are similar in the way of bonding to the central elements, they both formed single bond with the central elements.In contrast, Br has a large size with lone pairs of electrons in the outer most shell, while H is small with only one electron. Hence, the bond length increased from BH3 to BBr3. When the central element B in BBr3 was changed to be Tl to form TlBr3, the bond length increased.B and Tl are both from the group 13, they both have 3 valent electrons and able to form trigonal planar structures. However, Tl is larger than B, so the bond length increased from BBr3 to TlBr3.
A bond represents the interactions between two atoms. There are a number of factors can affact the strength of a bond, such as bond length, the charges on atoms, and the sizes of atoms. In some structures gaussview does not draw in the bonds represents the interactions between two atoms is too weak to be shown as a bond in stead of no bond formimg.
Frequency, Population, and Association Energy Analysis
Frequency analysis of BH3
Operations
The frequency calculation of BH3 was based on the 6-31G(d,p) BH3 optimisation file. The keyword in the calculation was # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p)geom=connectivity.
Results
The log file of frequency of BBr3: YONGJIELIN_BH3_FREQyjl.LOG
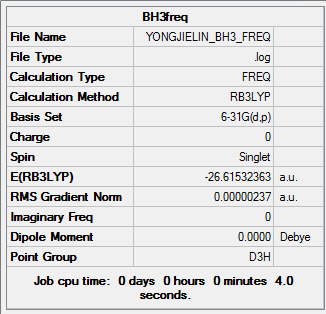
Summary of BH3 Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000237 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 4.0 s |
"Low frequencies table"
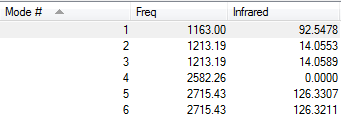
Low frequencies --- -0.9033 -0.7343 -0.0054 6.7375 12.2491 12.2824 Low frequencies --- 1163.0003 1213.1853 1213.1880
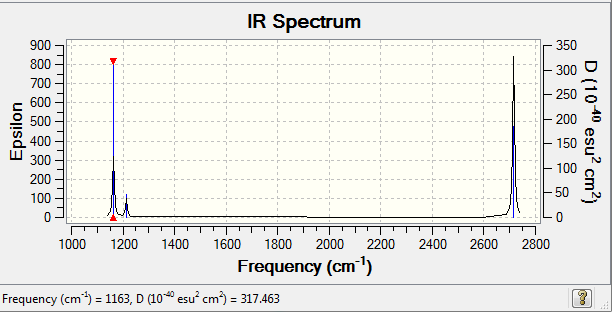
IR Spectrum of BH3
Frequency Table of BH3
Discussion
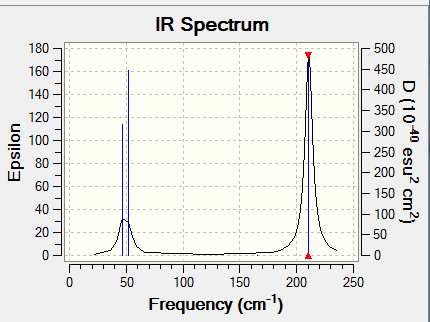
There are only 3 main peaks shown in the IR spetrum while there are 6 vibration modes disscussed in the table above.The fisrt reason of this is there are two pairs of vibrations with similar values vibration frequencies. Two absoptions with similar values of frequencies combines together to show one main peak.The second reason is the fourth vibration mode has 0 intensity, so it not shown in the IR spetrum. Hence, there are 3 main peaks shown in the IR spetrum.
Frequency analysis of TlBr3
Operations
For the heavier molecule TLBr3, calculations were submitted to to HPC to avoid long time calculation. The frequency calculation was based on the TlBr3 'B3LYP, LAN2DZ' file. The keyword was # freq b3lyp/lanl2dz geom=connectivity.
Results
The log file of The log file of frequency of TlBr3:DOI:10042/21608
Summary of TlBr3 Frequency
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Final Energy | -91.21812851 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000088 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 28.6 s |
"Low frequencies table"
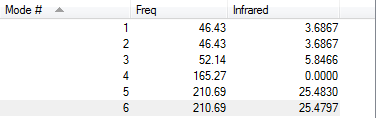
Low frequencies --- -3.4213 -0.0026 -0.0004 0.0015 3.9367 3.9367 Low frequencies --- 46.4289 46.4292 52.1449
IR Spectrum of TlBr3
Frequency Table of TlBr3
Discussion
The lowest "real" normal mode is the mode with lowest frequency. The lowest "real" normal mode of BH3 is the mode at 1113cm-1, which is Wagging. The lowest "real" normal mode of TlBr3 is the mode at 46 cm-1, which is Symmetrical Stretching.
Frequency analysis
| Form of vibration | BH3/cm-1 | TlBr3/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetrical Stretching | 1113 | 46 |
| Rocking | 1113 | 46 |
| Wagging | 1163 | 52 |
| All atoms move in and out motion | 2582 | 165 |
| Asymmetrical Stretching | 2715 | 211 |
| 2 Symmertrical, 1asymmetrical Stretching | 2715 | 211 |
The vibration frequencies of BH3 are much higher than those of TlBr3. This indicates that the bond energy of BH3 is much higher than that of TlBr3, which agrees with the discussion of bond length comparison above.
There has been a reordering of modes between these molecules, this could be explained by the reason that various of molecules could have various sensitivities in one specific mode.
Two IR spectra have a similar shape with two small peaks on the left and one large peaks on the right, because two molecules share the same structure with the vibration modes.
The method BLYP determines the type of approximations in solving the Schrodinger equation while the basis set determines the accuracy.The same method and basis set were used for both the optimisation and frequency calculations in order to have a meaningful comparison with the same approximation and the same level of accuracy.
A frequency analysis is used to check whether the optimisation is done properly. For the case of a successful optimisation, the first derivative should be close to 0. This indicates the potential energy is either at maxima (transition state) or minima(ground state). The second derivative is used to determine whether the points are maxima or minima. If all second derivative are positive, all the stationary points are minima. If one negative value is obtained, it means there is one minimum. If more than one negative values are obtained, it indicates the optimisation is not successful.
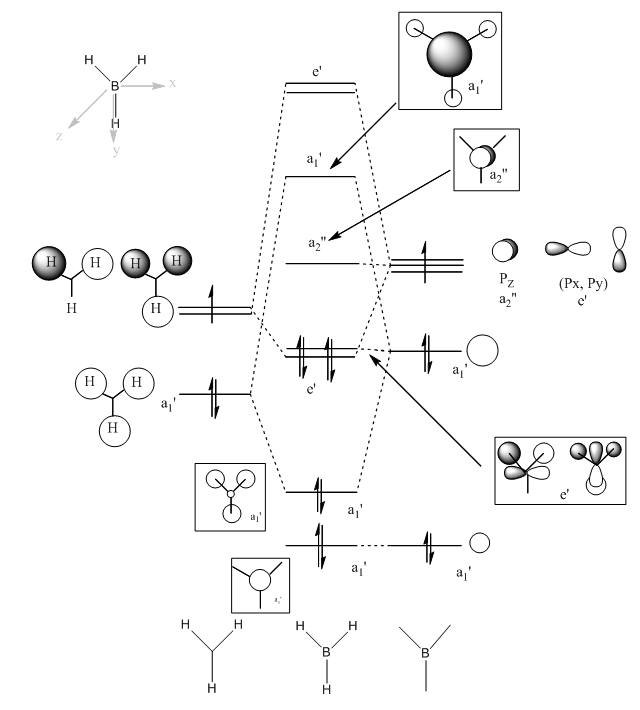
Molecular Orbital Analysis of BH3
Operations
The MO calculation of BH3 was based on the 6-31G(d,p) BH3 optimisation file.'pop=full' was added with type under NBO set to "Full NBO"as additional keywords.
Results
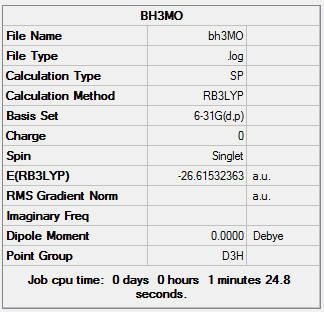
Summary of BH3 Energy Calculation
Summary Table of BH3 Energy Calculation
| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 1 min 24.8 s |
MO Diagram
| Symmetry Labels | Calculated MO | Predicted MO |
|---|---|---|
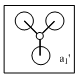
| a1' |  |
|
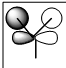
| a1' |  |
|
| e' | 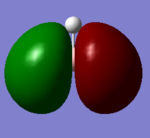 |
|
| e' |  |
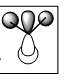
|
| a2' | 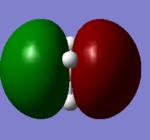 |
|
Discussion
There is no significant difference between the real and LCAO MOs, so it indicates a high accuracy and usefulness of qualitative MO theory.
NBO analysis of NH3
Operations
The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of 6-31G(d,p). "nosymm" keyword was used as an additional keyword. # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) nosymm geom=connectivity was the keywords in the calculations. The frequency and energy calculations were based on the Optimisation in the fisrt step.
results
The log file of NH3 Optimisation (6-31G): NH3OPTLYJ2.LOG
Summary of NH3 Optimisation (6-31G)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776856 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000885 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 19.0 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000024 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000079 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000053 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.629727D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7413 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7486 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7479 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The log file of frequency of NH3: NH3FRELYJ2.LOG
Summary of NH3 Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776856 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00000881 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 12.0 s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -30.7295 -0.0014 -0.0002 0.0013 20.1705 28.2664 Low frequencies --- 1089.5535 1694.1244 1694.1856
The log file of NH3 Energy Calculation:NH3MOLYJ2.LOG
Summary of NH3 Energy Calculation
Summary Table of NH3 Energy Calculation
| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776856 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 4 s |
The color range of NBO analysis
Charge Distribution by Color
Charge Distribution Shown by Number
Association Energy analysis of NH3BH3
Operations
The Optimisation was operated under the method of B3LYP and the basis set of 6-31G(d,p). The frequency calculations was based on the optimisation in the fisrt step.
Results
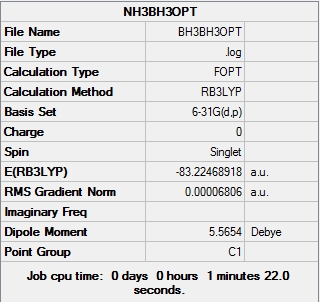
The log file of BH3NH3 Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): BH3NH3OPTLYJ.LOG
Summary of BH3NH3 Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -83.22468918 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00006806 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 5.57 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 mins 22.0 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000137 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000063 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000606 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000336 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.993995D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(2,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(3,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(4,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(5,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R6 R(6,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R7 R(7,8) 1.668 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(1,7,2) 107.87 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(1,7,3) 107.8652 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(1,7,8) 111.0329 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(2,7,3) 107.8697 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(2,7,8) 111.0286 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,7,8) 111.0291 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(4,8,5) 113.8693 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(4,8,6) 113.8721 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,8,7) 104.6003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(5,8,6) 113.8747 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(5,8,7) 104.6003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(6,8,7) 104.5984 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(1,7,8,4) -179.9867 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(1,7,8,5) -59.9892 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(1,7,8,6) 60.0135 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(2,7,8,4) -59.9839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,7,8,5) 60.0136 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,7,8,6) -179.9837 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(3,7,8,4) 60.0161 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(3,7,8,5) -179.9864 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,7,8,6) -59.9837 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
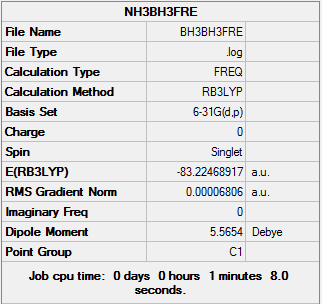
The log file of frequency of BH3NH3: BH3NH3FRELYJ.LOG
Summary of BH3NH3 Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -83.22468917 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00006806 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 5.57 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 68.0 s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -0.0003 0.0014 0.0014 17.1229 22.5486 38.7662 Low frequencies --- 265.8589 632.3779 639.0694
Discussion
Association Energy:
E(NH3)= -56.55776856 a.u. E(BH3)= -26.61532363 a.u. E(NH3BH3)= -83.22468918 a.u.
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)]= -0.05159699 a.u.= -135.467897 kJ/mol-1
Conversely, dissociation energy can be obtained, which is 135.467897 kJ/mol-1. Bond energy equals to dissociation energy, which equals to 135.467897 kJ/mol-1.
Optimisation and Analysis of Aromatic Molecules
Optimisation of Benzene
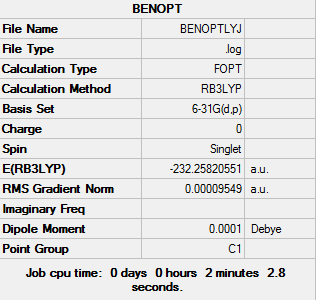
Results
The log file of Benzene Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): DOI:10042/21893
Summary of Benzene Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -232.25820551 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00009549 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 2 mins 2.8 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000212 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000085 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000991 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000315 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.157454D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,6) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R3 R(1,7) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R5 R(2,8) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R7 R(3,9) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R8 R(4,5) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R9 R(4,10) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R10 R(5,6) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R11 R(5,11) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R12 R(6,12) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,6) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,7) 119.9949 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(6,1,7) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,8) 119.9881 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,8) 120.004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,9) 120.0086 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,3,9) 119.9966 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(3,4,5) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,10) 119.9934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(5,4,10) 120.0094 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(4,5,6) 120.0083 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(4,5,11) 120.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(6,5,11) 119.9904 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(1,6,5) 119.9946 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(1,6,12) 120.0106 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,6,12) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(6,1,2,3) -0.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(6,1,2,8) 180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(7,1,2,3) -180.01 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(7,1,2,8) -0.0019 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,6,5) -0.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,6,12) -179.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(7,1,6,5) -180.0013 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(7,1,6,12) 0.007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) 0.0117 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,9) -179.9914 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(8,2,3,4) 180.0036 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(8,2,3,9) 0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,5) -0.0062 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,10) -180.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(9,3,4,5) 179.9969 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(9,3,4,10) -0.0028 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,5,6) -0.0051 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,5,11) 180.0058 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(10,4,5,6) -180.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(10,4,5,11) 0.0054 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(4,5,6,1) 0.011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(4,5,6,12) 180.0027 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,6,1) -179.9999 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,6,12) -0.0082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
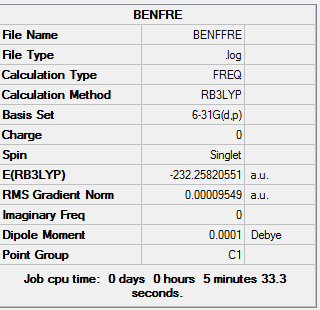
Frequency Analysis of Benzene
Results
The log file of frequency of Benzene: DOI:0042/21929
Summary of Benzene Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -23225820551 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00009549 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 mins 33.3 s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -17.2788 -14.5868 -9.6527 -0.0009 -0.0008 -0.0007 Low frequencies --- 413.7971 414.4697 620.8545
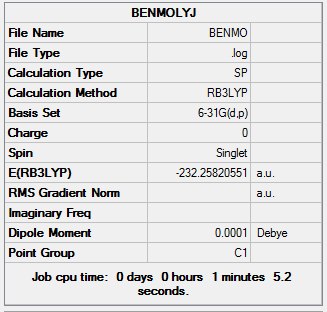
Energy Analysis of Benzene
Results
he log file of frequency of Benzene: DOI:10042/21928
Summary of Benzene Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -232.25820551 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 mins 5.2 s |
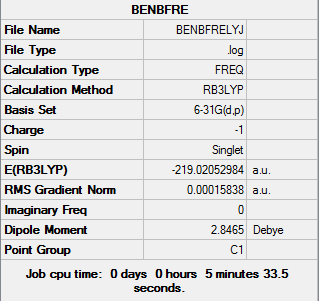
Optimisation of Boratabenzene
Results
The log file of Boratabenzene Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): DOI:10042/21892
Summary of Boratabenzene Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
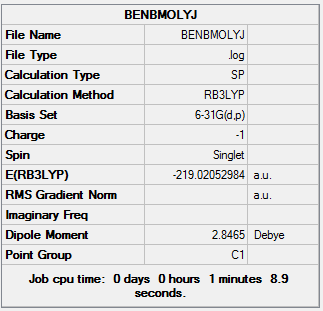
| Final Energy | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00015840 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 2.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 3 mins 58.4 s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000065 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000023 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000826 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000176 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.972574D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,5) 1.3838 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,6) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0852 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(4,9) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R9 R(4,12) 1.3523 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R10 R(5,11) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.3524 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(10,12) 1.0169 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,5) 119.0827 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,6) 121.496 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A3 A(5,1,6) 119.4213 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0549 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 119.9711 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 119.974 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 121.4988 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 119.4192 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A10 A(3,4,9) 123.9297 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,12) 119.2363 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(9,4,12) 116.834 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(1,5,11) 123.9327 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(1,5,12) 119.2354 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(11,5,12) 116.8319 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(4,12,5) 123.3088 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,10) 118.3463 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,10) 118.345 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,1,2,3) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,1,2,7) -180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(6,1,2,3) 180.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(6,1,2,7) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,5,11) -180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,5,12) 0.0021 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,5,11) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,5,12) 180.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) -0.0024 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) -180.0018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) 180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) 0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,9) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,12) 0.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,9) -0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,12) 180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,12,5) 0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,12,10) -180.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,12,5) 180.0025 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,12,10) 0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,5,12,4) -0.0032 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,5,12,10) -180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,12,4) -180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,12,10) 0.0016 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Frequency Analysis of Boratabenzene
Results
The log file of frequency of Boratabenzene: DOI:10042/21925
Summary of Boratabenzene Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00015838 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 2.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5mins 33.5s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -13.1275 0.0004 0.0009 0.0010 15.0447 18.1653 Low frequencies --- 371.3454 404.2334 565.2534
Energy Analysis of Borataenzene
Results
The log file of energy of Boratabenzene: DOI:10042/21930
Summary of Boratabenzene Energy 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -219.02052984 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 2.85 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1mins 8.9s |
Optimisation of Pyridinium
Results
The log file of Pyridinium Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): DOI:10042/21917
Summary of Pyridinium Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
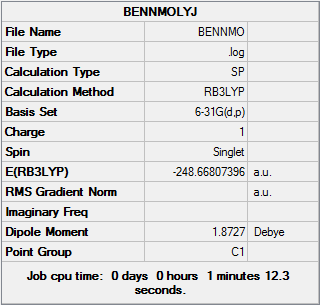
| Final Energy | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00003894 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.87 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time | 3 mins 59.7s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000065 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000023 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000826 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000176 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.972574D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,5) 1.3838 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,6) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0852 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(4,9) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R9 R(4,12) 1.3523 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R10 R(5,11) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.3524 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(10,12) 1.0169 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,5) 119.0827 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,6) 121.496 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A3 A(5,1,6) 119.4213 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0549 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 119.9711 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 119.974 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 121.4988 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 119.4192 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A10 A(3,4,9) 123.9297 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,12) 119.2363 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(9,4,12) 116.834 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(1,5,11) 123.9327 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(1,5,12) 119.2354 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(11,5,12) 116.8319 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(4,12,5) 123.3088 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,10) 118.3463 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,10) 118.345 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,1,2,3) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,1,2,7) -180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(6,1,2,3) 180.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(6,1,2,7) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,5,11) -180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,5,12) 0.0021 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,5,11) -0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,5,12) 180.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) -0.0024 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) -180.0018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) 180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) 0.0012 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,9) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,12) 0.0015 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,9) -0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,12) 180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,12,5) 0.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,12,10) -180.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,12,5) 180.0025 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,12,10) 0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,5,12,4) -0.0032 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,5,12,10) -180.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,12,4) -180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,12,10) 0.0016 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Frequency Analysis of Pyridinium
Results
The log file of frequency of Pyridinium: DOI:10042/21926
Summary of Pyridinium Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00003897 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.87 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 mins 38.6s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -7.2115 0.0002 0.0005 0.0006 17.3444 18.5499 Low frequencies --- 392.4572 404.0614 620.4717
Energy Analysis of Pyridinium
Results
The log file of Energy of Pyridinium: DOI:10042/21927
Summary of Pyridinium Energy 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -248.66807396 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 1.87 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 mins 12.3 s |
Optimisation of Borazine
Results
The log file of Borazine Optimisation (6-31(d,p)): DOI:10042/21987
Summary of Borazine Optimisation (6-31(d,p))
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
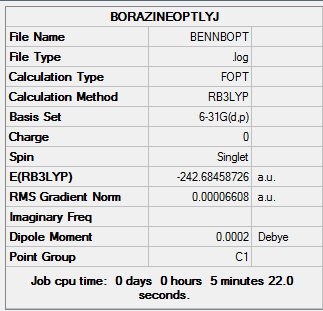
| Final Energy | -242.68458726 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00006608 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 mins 22s |
"Item table"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000093 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000033 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000341 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000096 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.028630D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,9) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R2 R(2,11) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(3,8) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R4 R(4,10) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(5,7) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R6 R(6,12) 1.0097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(7,10) 1.4306 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R8 R(7,12) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R9 R(8,10) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R10 R(8,11) 1.4307 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R11 R(9,11) 1.4307 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(9,12) 1.4306 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(5,7,10) 121.4436 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(5,7,12) 121.4373 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(10,7,12) 117.119 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A4 A(3,8,10) 121.4337 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,8,11) 121.4348 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(10,8,11) 117.1314 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(1,9,11) 121.4399 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(1,9,12) 121.4414 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(11,9,12) 117.1187 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(4,10,7) 118.567 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(4,10,8) 118.5613 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(7,10,8) 122.8717 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(2,11,8) 118.5639 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(2,11,9) 118.5622 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(8,11,9) 122.8739 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(6,12,7) 118.5563 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(6,12,9) 118.5584 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(7,12,9) 122.8853 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,7,10,4) 0.0043 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,7,10,8) -179.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(12,7,10,4) -179.9957 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(12,7,10,8) 0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(5,7,12,6) 0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(5,7,12,9) 179.9967 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(10,7,12,6) -179.9996 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(10,7,12,9) -0.0033 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,8,10,4) 0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(3,8,10,7) -179.9954 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(11,8,10,4) -179.9991 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(11,8,10,7) 0.005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(3,8,11,2) 0.0034 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(3,8,11,9) 179.9928 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(10,8,11,2) -179.997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(10,8,11,9) -0.0075 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(1,9,11,2) -0.0061 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(1,9,11,8) -179.9955 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(12,9,11,2) 179.9942 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(12,9,11,8) 0.0048 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,9,12,6) -0.0025 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,9,12,7) -179.9989 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,9,12,6) 179.9973 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,9,12,7) 0.0009 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Frequency Analysis of Borazine
Results
The log file of frequency of Borazine: DOI:10042/21995
Summary of Borazine Frequency 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
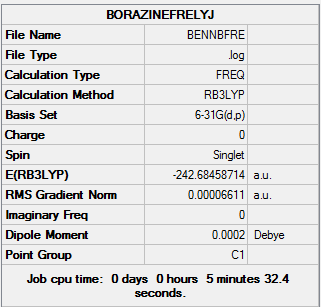
| Final Energy | -242.68458714 a.u. |
| Gradient | 0.00006611 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 mins 32.4 s |
"Low frequencies table"
Low frequencies --- -17.2548 -10.7439 -6.9144 -0.0006 -0.0002 0.0006 Low frequencies --- 288.8565 289.6622 404.1659
Energy Analysis of Borazine
Results
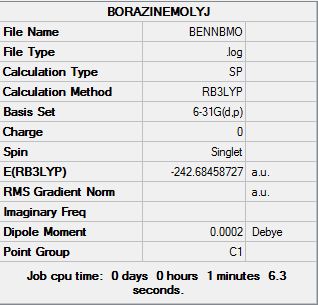
The log file of Energy of Borazine: DOI:10042/21994
Summary of Borazine Energy 6-31G(d,p)
| File type | .log |
|---|---|
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -242.68458727 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 0.00 Debye |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 mins 6.3s |
Discussion
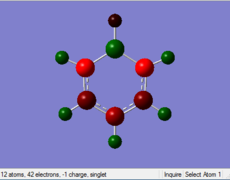
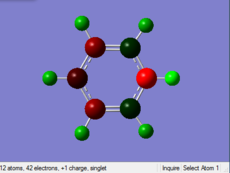
Charge Distribution
| Benzene | Boratabenzene | Pyridinium | Borazine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution
By Charge |

|
|
|

|
| Distribution
By Number |
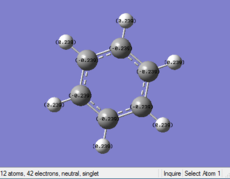
|
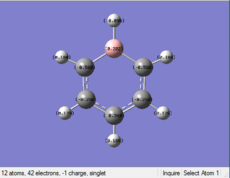
|
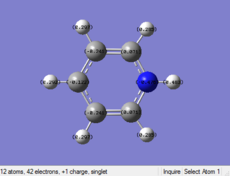
|
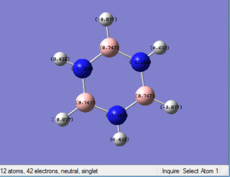
|
| Color Range | [[File:BENNCRLYJ.PNG|230px] |
Benzene: Charge evenly distributes to every sigle C in the benzic ring, the value of charge is -0.239. The H atom attached to C also have same value of charge.
Boratabenzene: Compared with the structure of benzene, one of the C atoms is replaced by B with one negative charge in the Boratabenzene. B is more electropositive than C, so the value of charge on B is higher than that of C atoms. THere is one negative charge on B. By considering the resonance form of the structure, negative charge prefers to be in the positions of Othro and Para. Othro postions are closed to electropositve B, so the charge value on Othro positions is most negative.
Pyridinium: In Contrast, one of the C atoms is replaced by N with one positive charge in the pyridinium. N is more elctronegative than C, so N is distributed more negative charge. There is one positive charge on N. By the consideration of resonance form of the strucute, the Meta postions are relatively electronegative than the other two postions. The C atoms on the Othro positions are closed to electronegative N, so the they are more electropostive than other C atoms.
Borazine: Borazine has a different charge distribution from the previous 3 molecules. 3 of C atoms are replaced by 3 of N atoms, and the other 3 of C atoms are replace by 3 B atoms. All of the B atoms have postive change while all of N atoms have negative charge, this can be more easily to conduct reactions than Benzine, so Borazine is relatively unstable than Benzene.
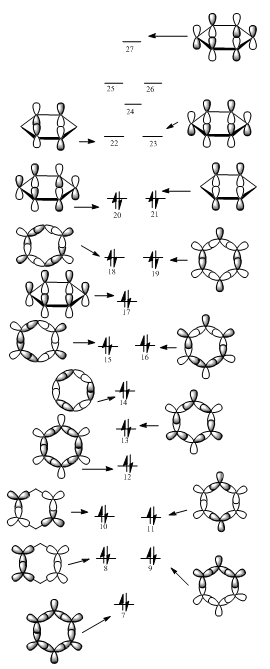
MO Diagram
Aromaticity relates to delocalisation. As can be observed in the MO diagram, there are a number of pair of degenerate orbitals, which can help the electrons delocalise more easily in the molecule. Aromaticity also relates to the total pi electron density. As can be observed in the MO diagram(17, 20, 21, 22, 23, 27 orbitals), 3 pairs of bonding Pi orbitals are full filled, so this molecule is highly aromatic.
| Benzene | Boratabenzene | Pyridinium | Borazine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Sigma | 
|
|
|
|
| E (a.u.) | -0.87677 | -0.60434 | -1.21401 | -0.88852 |
| 17 Pi | 
|
|

|

|
| E (a.u.) | -0.35998 | -0.13208 | -0.64064 | -0.36129 |
| HOMO | 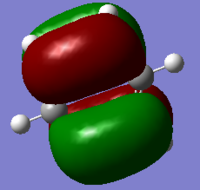
|
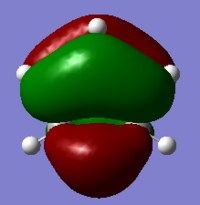
|
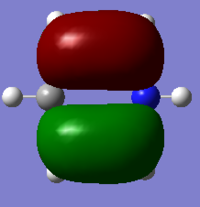
|
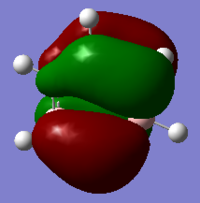
|
| E (a.u.) | -0.24691 | -0.01094 | -0.47885 | -0.27590 |
When the C atoms are substituted in benzene ring, the atoms in LCAOs are no longer equivalent. The energy level in the MO diagram would shift up and down depends on each situation. This can also lead to change of shapes, energy and degeneracy of the orbitals.
Shapes:
MO7:It is a σ all bonding orbital. Benzene shows a symmetrical star shape, while the shapes of pyridinium and boratabenzene are distorted. Borazine has a different shape from those of others, which is a triangle shape. The reason of the shapes of MO formed is similar to the charge distribution discussion above.
MO17 and MO21: These are π bonding orbital.The analogues of benzene all have similar shapes as that of benzene with small distortions. This could be explained by the less interactions on Pi electrons than that of sigma electrons.
Energy:
Compared with benzene, pyridinium and borazine have lower energy while boratabenzene has higher energy. The N in pyridinium is electronegative, so it leads to the energy become lower than C. In contrast, the B in boratabenzene is more electropostive than C, so it causes the energy become higher. Borazine has 3 N atoms and 3 B atoms, the energy change can not be explained by the aspect of electronegativity.
Degeneracy:
Benzine has a number of degenerate orbitals as shown in the diagram, because it has totally symmetric structure. Boratabenzene and pyridinium can no longer have degenerate orbitals, because one of the C is substituted. Borazine has degenerate orbitals as Benzine, because it still has a symmetric structure.
Isoelectronic Disscussion:
The total number of electrons of these four molecules are the same, this could explained by the stablisation energy in the MO diagram. If one more electron was putted into or taken out from the molecules, the molecules would have more anti-bonding orbitals or less bonding orbitals. Hence, 4 of molecules are isoelectronic.
Reference
1.J. Glaser, G. Johansson. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1982, 36a, Pp. 125-135.