Rep:Mod:XYZ8890
Huriye Korkmazhan 01356570
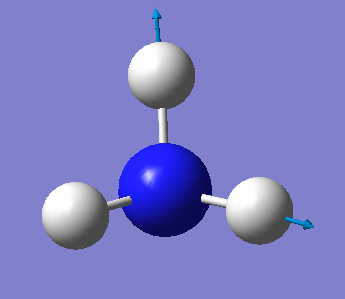
NH3 Molecule
Optimised bond angle
105.741°
Optimised bond length
1.01798 au
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Summary Information
| Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) (au) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -56.55776873 | C3V |
Jmol Image
Ammonia |
Answers to Questions
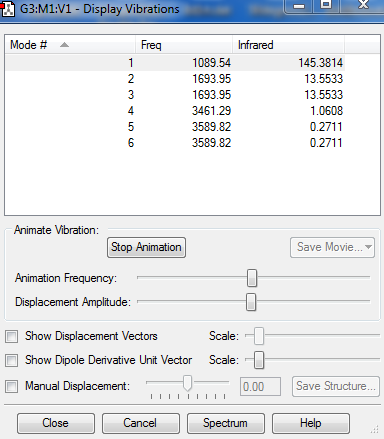
Vibrations
1)6 vibrational modes are expected according to the 3N-6 rule.
2)There are two pairs of degenerate states. While one of the pairs is 2nd and 3rd modes, the second pair is in 5th and 6th modes.
3)While first 3 modes are bending, the last 3 are stretching vibrations.
4)4th mode is highly symmetric.
5)1st mode is the umbrella mode.
6)2 bands are expected to be seen in the IR spectrum of gaseous ammonia. Only first two bending vibrations are seen in the spectrum since they are the only ones that result in change in dipole moment.
Charge
The charge value calculated for Nitrogen is -1.135 and 0.375 for each Hydrogen. Nitrogen receiving the more negative number is expected because of its relatively higher electronegativity. Since Nitrogen is highly electronegative, electrons are found closer to the Nitrogen resulting in a negative value for Nitrogen atom and a positive value for Hydrogen atoms.
Link to Optimisation
The optimisation file is linked to Media:HKORKMAZHAN_NH3_OPTF_POP.LOG
N2 Molecule
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Summary Information
| Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) (au) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -109.52412868 | D*H |
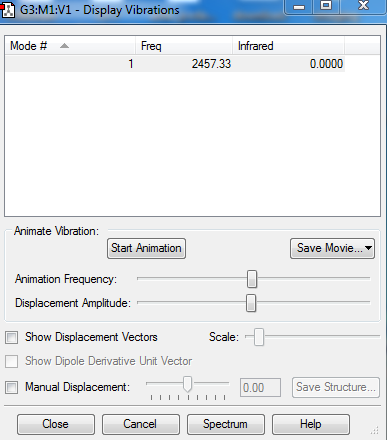
Vibrations
The absence of any negative frequency value indicates optimisation. Since N2 is a linear diatomic molecule, which shares its electrons equally, and thus gives no change in dipole moment when it vibrates, it is IR inactive.
Link to Optimisation
The optimisation file is linked to Media: HKORKMAZHAN_N2_OPTF_POP.LOG
H2 Molecule
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Summary Information
| Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) (au) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -1.17853936 | D*H |
Vibrations
The absence of any negative frequency value indicates optimisation. Since H2 is a linear diatomic mo0lecule, which shares the electrons in the covalent bond equally, there is no change in dipole moment which makes it IR inactive.
Link to Optimisation
The optimisation file is linked to Media:HKORKMAZHAN_H2_OPTF_POP.LOG
Haber-Bosch process
Energy Calculations
| E(NH3) (au) | 2*E(NH3) (au) | E(N2) (au) | E(H2) (au) | 3*E(H2) (au) | ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] (au) | ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -56.55776873 | -113.1155375 | -109.52412868 | -1.17853936 | -3.53561808 | -0.5579074 | -146.4785879 |
The energy change for this reaction is -146.48 kJ/mol. The energy change's being negative indicates that Ammonia is more stable than Nitrogen and Hydrogen. Ammonia is at a more negative energy level relative to the reactants which makes it more stable.
Cl2 Molecule
Optimised Bond Angle
180°
Optimised Bond Length
2.04174 au
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Summary Information
| Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) (au) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -920.34987886 | D*H |
Jmol Image
Chlorine |
Molecular Orbitals
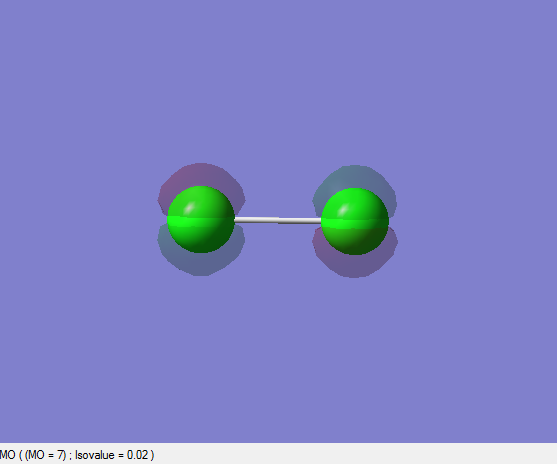
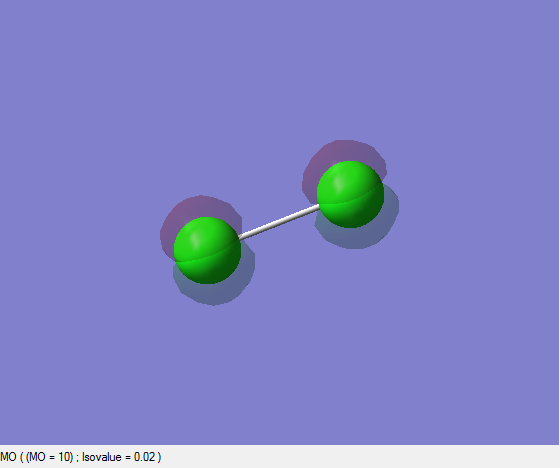
2pz, 2py and 2px Non-bonding Orbitals (Extra Work)
| 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -7.2704310400 | -7.2704310400 | -7.2704545200 | -7.2704545200 | -7.2859153000 | -7.2859158300 |
| 5 | 4 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| -7.2623173500 | -7.2623173500 | -7.2856751100 |
The first and second pictures illustrate the 2pz orbitals. The last two shows either 2px or 2py orbitals and there is one another pair that is either 2px or 2py orbitals. Those six orbitals are non-bonding orbitals since there is no interaction and thus no overlap between them. They are occupied orbitals and all are degenerate having almost the same energies when compared to the atomic orbital energies of Chlorine atom alone. Since there is almost no change in energies of those orbitals when the molecule is formed this indicates that there is no interaction between the atomic orbitals.
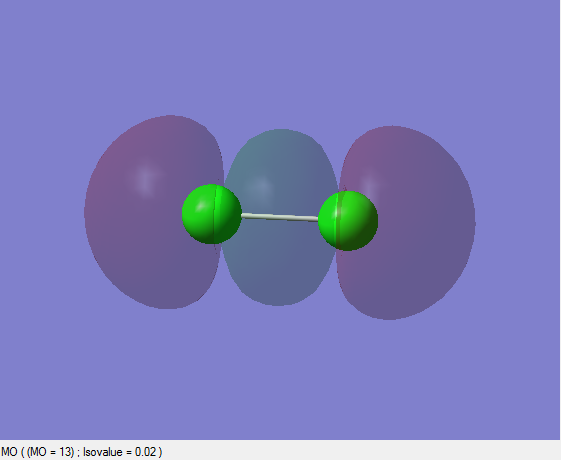
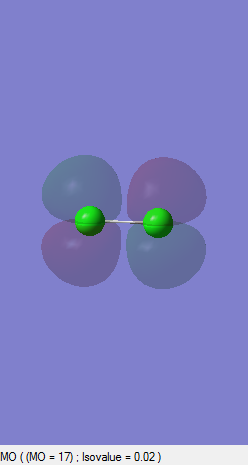
Bonding pi Orbital
This picture illustrates the constructive interference of either 3px-3px or 3py-3py orbitals and has another degenerate pair of the former or latter. Since those p orbitals are in x and y axes, they are perpendicular to the one in z-axis and thus the edge-to-edge overlap between them forms pi orbitals. Both of those two bonding degenerate orbitals are occupied.
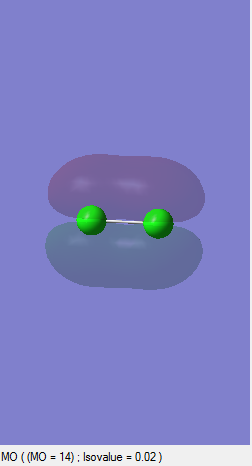
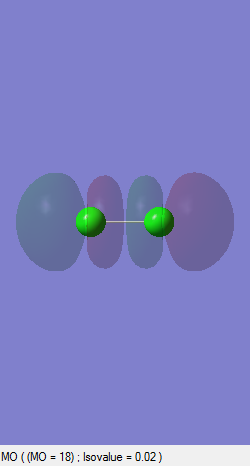
Bonding sigma Orbital (p)
This orbital is formed as a result of in-phase interaction of 3pz orbitals. Because of the orientation of the axis, it overlaps end-to-end giving a sigma orbital which is thus lower in energy than the bonding pi orbitals formed above. This orbital is occupied and bonding.
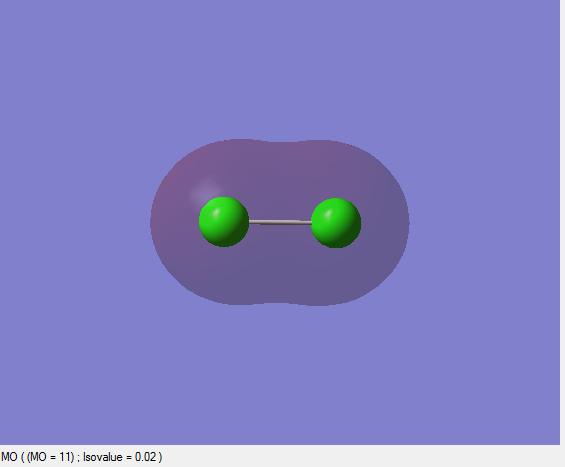
Bonding sigma Orbital (s)
This bonding orbital is occupied and formed as a result of constructive interference of the 3s orbitals resulting in the sigma orbital.
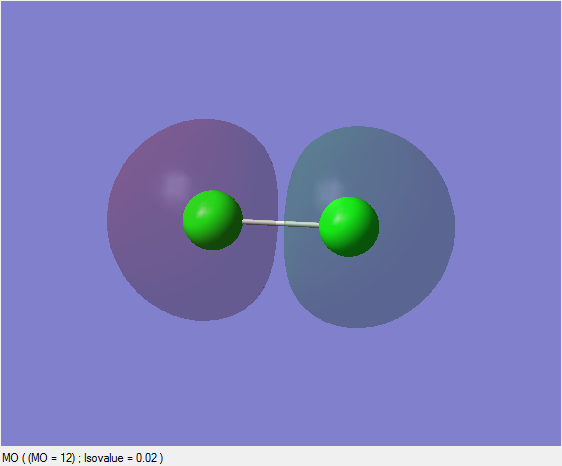
Antibonding sigma* Orbital
In this case this sigma* orbital is formed as a result of out-of-phase interference of 3s orbitals. It is an occupied antibonding orbital.
HOMO orbital
This is the highest occupied bonding orbital. This pi* orbital and also its degenerate pair are formed as a result of out of phase overlap of 3py-3py and 3px-3px orbitals. Both of those orbitals are occupied.
LUMO orbital
This is an unoccupied antibonding orbital. This sigma* orbital is formed as a result of out of phase overlap of 3pz orbitals of Cl atoms. It is called LUMO because of being the lowest unoccupied orbital. This is relatively high in energy because of being further away from the nucleus, so it is not a good electrophile.
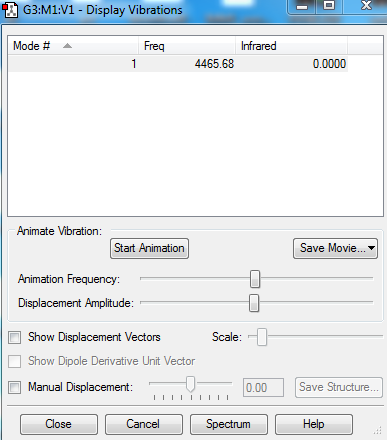
Vibration
The absence of any negative frequency value indicates optimisation. Since Cl2 is a linear diatomic molecule, its vibration gives no change in dipole moment which makes it IR inactive.
Charge
There is no charge associated with the Chlorine atoms confirming that the two electrons are equally shared resulting in a pure covalent bond.
Link to Optimization
The optimisation file is linked to Media:HKORKMAZHAN_CL2_OPTF_POP.LOG