Rep:Mod:XYZ1379
Project molecule
NH3
Summary of NH3
| Molecule | NH3 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000485 au |
| Point Group | C3V |
Bond length and bond angle of NH3
Optimized bond distance N-H =1.01798 Å. Optimized H-N-H bond angle =105.741 degrees.
Final set of force and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Optimization file of NH3
The optimization file is linked to here
NH3 |
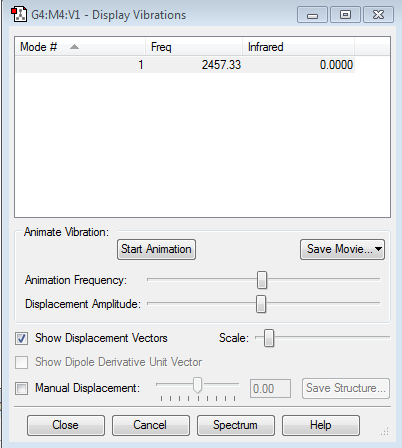
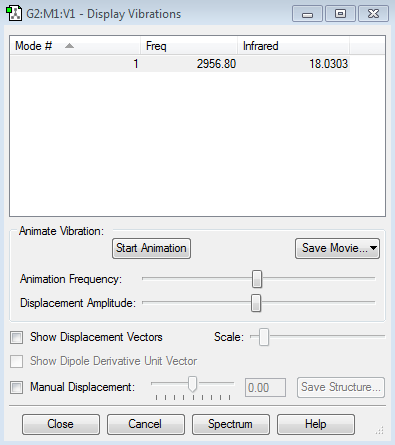
Display Vibrations and atomic charges
6 modes are expected from 3N-6 rule.
Mode 2&3 and mode 5&6 are degenerate .
Mode 1&2&3 are 'bending' vibrations, mode 4&5&6 are 'bond stretch' vibrations. Number 4 is the highly symmetric one because the point group doesn't change.
Mode 1 has the umbrella mode.
Two bands will be expected for ammonia in the spectrum. Because the infrared intensity of mode 4&5&6 are too small to be seen and mode 2&3 are degenerate therefore only two bands will be expected.
The charge on hydrogen is expected to be positive and the charge of nitrogen is expected to be negative because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. The charge on hydrogen is 0.375 and that on nitrogen is -1.125.
N2
Summary of N2
| Molecule | N2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -109.52412868 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000060 au |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Bond length and bond angle
Optimized bond distance N≡N =1.10550 Å, N2 is a linear molecule.
Final set of force and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Optimisation file of N2
The optimization file is linked to here
N2 |
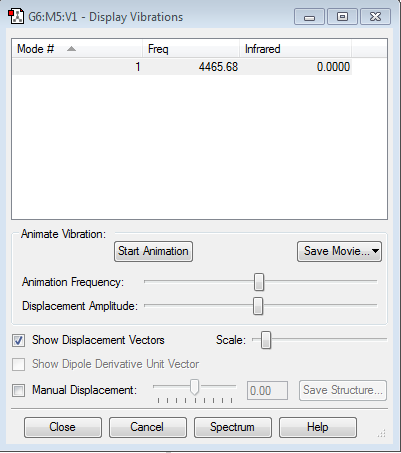
Display vibration and atomic charges
There is no change in the electronegativity in N2, therefore the charge is excepted to be zero.
H2
Summary of H2
| Molecule | H2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853936 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000017 au |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Bond length and bond angle
Optimized bond distance H-H =0.74279 Å, H2 is a linear molecule.
Final set of force and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Optimization file
The optimization file is linked to here
H2 |
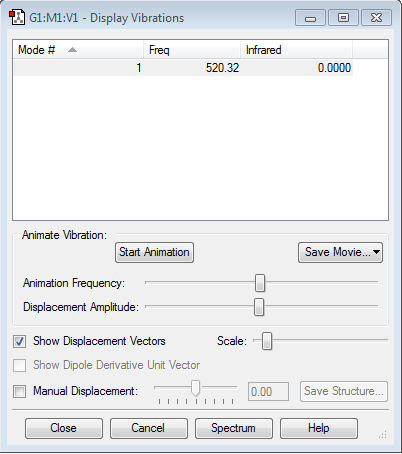
Display vibration and atomic charges
There is one mode expected according to the 3N-5 rule.
There is no change in the electronegativity in H2, therefore the charge is excepted to be zero.
Reaction energy
The energy of the haber process is shown as below.
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 au
E(N2)=-109.52412868 au
E(H2)=-1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579146 au =-146.480478 kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable because energy is released during the process since the sign of the energy change is negative.
Molecule of own choice
Cl2
Summary of Cl2
| Molecule | Cl2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -920.34987886 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00002511 au |
| Point Group | Dinfh |
Bond length and bond angle of Cl2
Optimized bond distance Cl-Cl =2.04174 Å, Cl2 is linear.
Final set of force and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Optimization file
The optimization file is linked to here
Cl2 |
Display vibration and atomic charges
There is no difference in the electronegativity between Cl and Cl in Cl2, therefore the charge is excepted to be zero. Since Cl2 is a linear molecule, therefore 3N-5 mode i expected which means only one mode is expected. And there is no change in dipole moment which means no band will be expected in the spectrum.
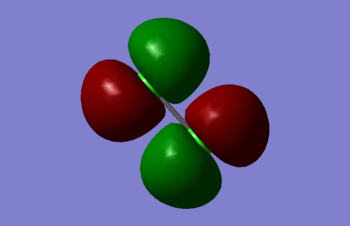
Molecular orbitals of Cl2
Calculation on another molecule
HCl
Summary of HCl
| Molecule | HCl |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basic Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP) | -460.80077875 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00005211 au |
| Point Group | CinfV |
Bond length and bond angle
Optimized bond distance H-Cl =1.28599 Å, HCl is a linear molecule.
Final set of force and displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
Optimisation file of HCl
The optimization file is linked to here
HCl |
Display vibration and atomic charges
The charge of H is 0.284 and that of Cl is -0.284. The charge of Cl is expected of be more positive compare to that of H because Cl is more electronegative than H.