Rep:Mod:VC2217
The Haber Process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
The combination of nitrogen a gas that is in surplus in our atmosphere and hydrogen results in the production of ammonia, this vital process allows for the industrial production of fertilizers.
NH3 Optimization
Ammonia |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -56.55776873 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Point Group | C3V |
| N-H Bond Length | 1.01798 |
| H-N-H Bond Angle | 105.741° |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986273D-10 Optimization completed.
Media:VIRGINIA_NH3_OPTIMIZATION.LOG
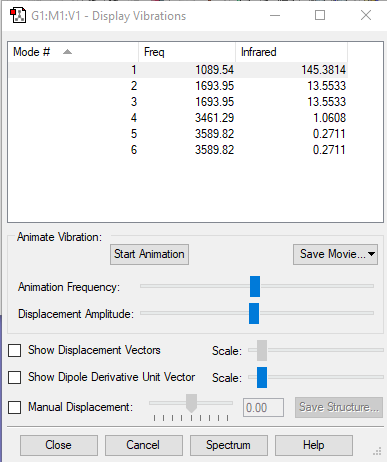
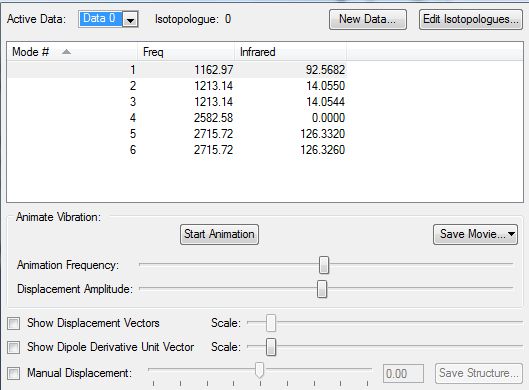
Vibrations
- From the 3N-6 rule 6 modes are expected
- Degenerate modes: 2&3, 5&6 as both pairs of modes have the same energy
- Bending vibrations: 1,2,3
- Bond stretch vibrations: 4,5,6
- 4 is a highly symmetric mode as all of the atoms move in the same direction
- The "umbrella" mode is mode 1
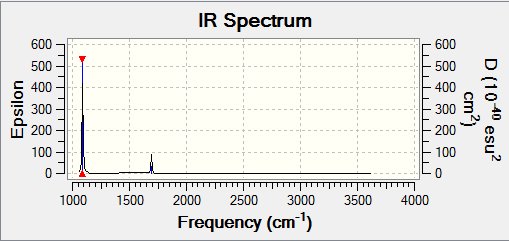
- You would expect to see 3 bands in the spectrum as the symmetric stretch does not result in a change in dipole hence would not show a band. However, only 2 can clearly be
seen in the spectra as the others that are degenerate (5&6) have very low intensities.
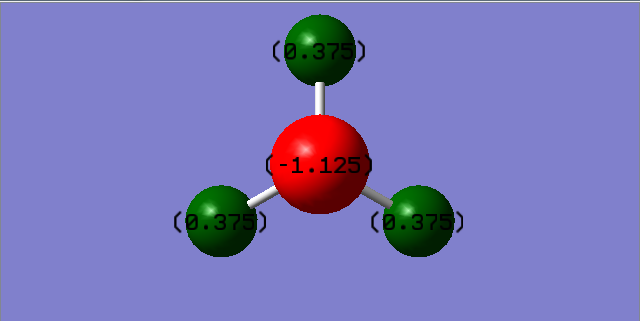
Charges
A negative charge was expected on the N atom and a more positive on the H atoms because Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen hence it withdraws electron density towards itself.
N2 Optimization
Nitrogen Molecule |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -109.52412868 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000060 |
| Point Group | DinfH |
| N-H Bond Length | 1.10550 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.400996D-13 Optimization completed.
Media:VIRGINIA_N2_OPTIMIZATION.LOG
Vibrations
- No band can be seen in the IR spectrum as the bond is not IR-active due to the molecule not having a dipole moment
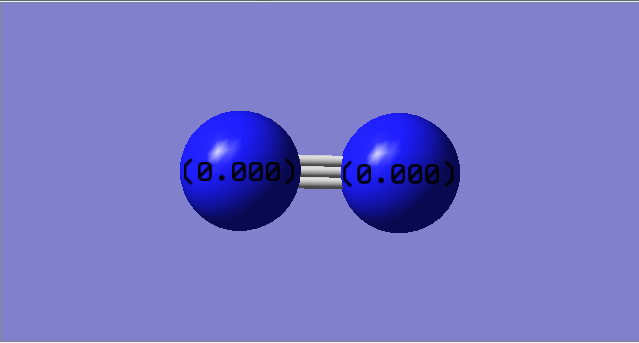
Charges
- No charge on N atoms
- Identical atoms hence both have the same electronegativity
- No dipole moment
H2 Optimization
Hydrogen Molecule |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -1.17853936 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Point Group | DinfH |
| H-H Bond Length | 0.74279 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13 Optimization completed.
Vibrations
- No band can be seen in the IR spectrum as the bond is not IR-active due to the molecule not having a dipole moment
Charges
- No charge on H atoms
- Identical atoms hence both have the same electronegativity
- No dipole moment
Media:VIRGINIA_H2_OPTIMIZATION.LOG
Energy Calculation
| E(NH3)= | -56.55776873 |
| 2*E(NH3)= | -113.1155375 |
| E(N2)= | -109.52412868 |
| E(H2)= | -1.17853936 |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= | -0.05579074 |
ΔE = -146.478599028 kJmol-1
The Ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants, this is because the change in energy for the conversion of the gases into ammonia is quite negative, hence a lot of energy is gained from the conversion, so the product is energetically more favourable.
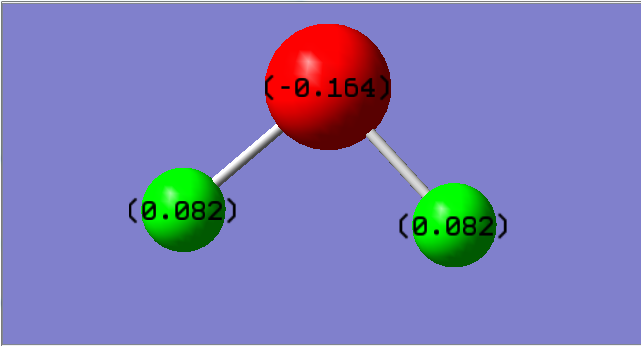
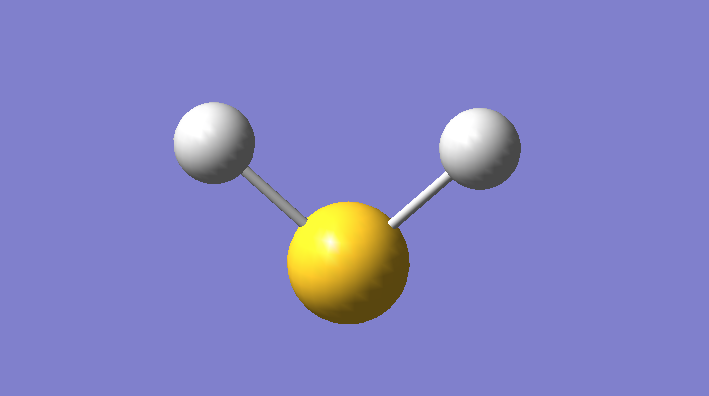
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen Sulfide Molecule |
Optimization
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -339.39162414 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00012068 |
| Point Group | C2v |
| S-H Bond Length | 1.34737 |
| H-S-H Bond Angle | 92.681° |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000175 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000145 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000472 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000386 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.208488D-07
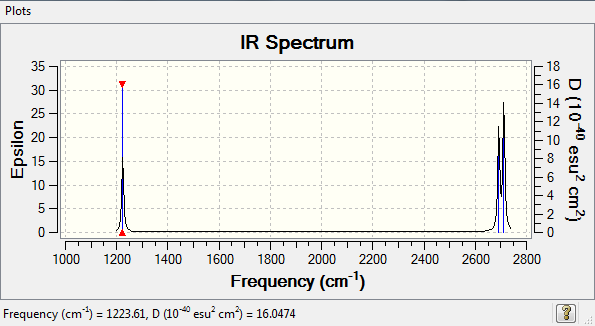
Vibrations
- From the 3N-6 rule 3 modes are expected
- Degenerate modes: None
- Bending vibrations: 1
- Bond stretch vibrations: 2&3
- 2 is a highly symmetric mode as all of the atoms move in the same direction
- You would expect to see 2 bands in the spectrum as the symmetric stretch (Mode 2) does not result in a change in dipole hence would not show a band
Charges
A negative charge was expected on the S atom and a more positive on the H atoms because Sulfur is more electronegative than hydrogen hence it withdraws electron density towards itself.
Molecular Orbitals
1s
- Energy : -88.88741 au
- 1s Sulfur atom orbital
- Very deep in energy compared to valence electrons
- Cannot be seen as this orbital is too low in energy to be involved in chemical bonding
- Non Bonding
2s
- Energy: -7.9515
- 2s Orbital of sulfur
- Still quite low in energy and is not involved in chemical bonding
- Non Bonding
2Py
- Energy: -5.91588
- 2py orbital of S
- Non Bonding
2Pz
- Energy: -5.912688
- 2pz orbital of S
- Non Bonding
2Px
- Energy: -5.90552
- 2px orbital of S
- Non Bonding
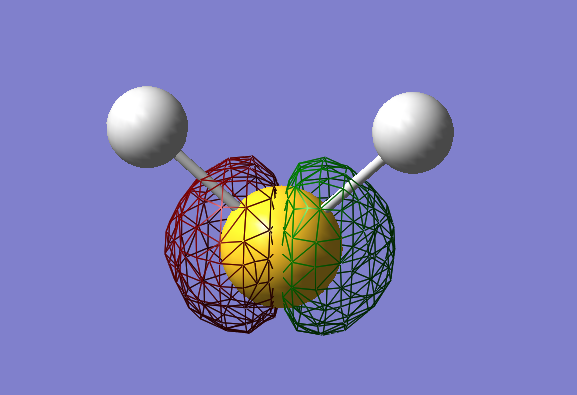
3s-1s
- Energy: -0.74654
- 3s orbital of S combined with 1s orbital of H
- Bonding
3py-1s
- Energy: -0.44963
- 3py orbital of S combined with 1s orbital of H
- Bonding
3pz-1s
- Energy: -0.36725
- 3pz orbital of S combined with 1s orbital of H
- Bonding
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital
- Energy: -0.26181
- HOMO
- Non Bonding
- Contains Lone Pair from 3px orbital of the S atom
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular orbital
- Energy: -0.02126
- LUMO
- 3py AO of S and 1s AO of H atom
- Antibonding
- Unoccuppied
Media:VIRGINIA_FINAL_H2S_OPTIMIZATION.LOG
Borane
Borane Molecule |
Optimization
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -26.61532364 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000211 |
| Point Group | D3h |
| B-H Bond Length | 1.19232 |
| H-B-H Bond Angle | 120° |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.053682D-10 Optimization completed.
Vibrations
- From the 3N-6 rule 6 modes are expected
- Degenerate modes: 2&3, 5&6 as both pairs of modes have the same energy
- Bending vibrations: 1,2,3
- Bond stretch vibrations: 4,5,6
- 4 is a highly symmetric mode as all of the atoms move in the same direction
- The "umbrella" mode is mode 1
- You would expect to see 3 bands in the spectrum due to the degenerate modes and because the symmetric stretch does not result in a change in dipole hence would not show a band. This can be seen in the IR spectrum.
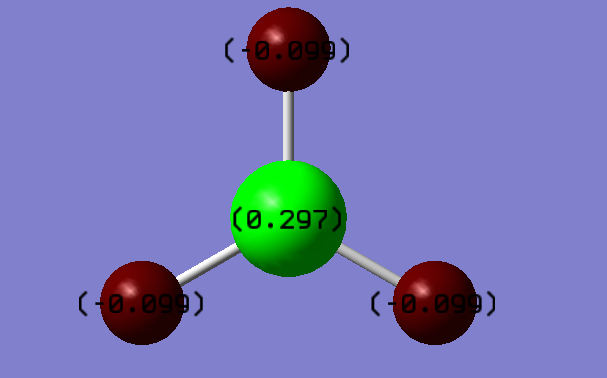
Charges
- Charge on Boron = 0.297
- Charge on Hydrogen atoms= -0.099
This is expected as hydrogen is more electronegative than Boron, this can be seen from their electronegativity literature values.
Literature Values:
Electonegativity of Boron (Pauling units): 2.04 [1]
Electonegativity of Hydrogen (Pauling units): 2.20 [2]