Rep:Mod:Tompage
Toms Page
NH3 Molecule
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | NH3 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -56.6 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Point group | C3V |
| Bond distance | 1.01798 |
| Bond angle | 105.741 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986283D-10 Optimization completed.
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
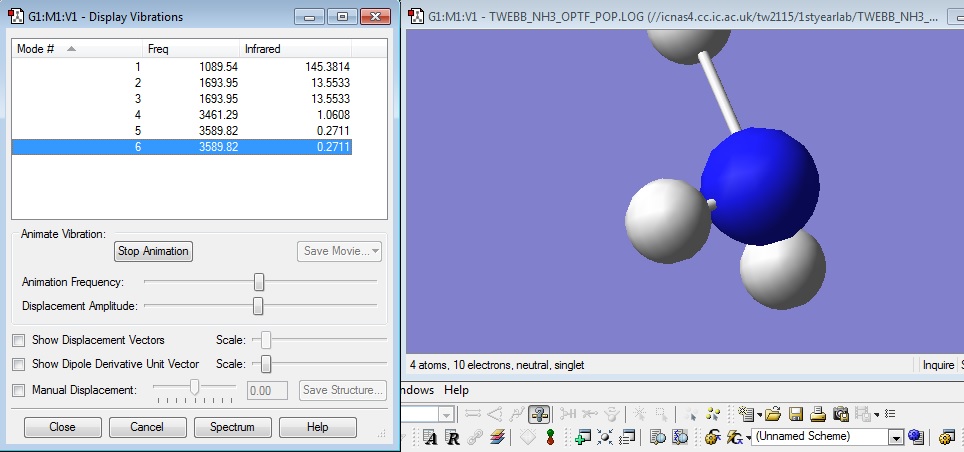
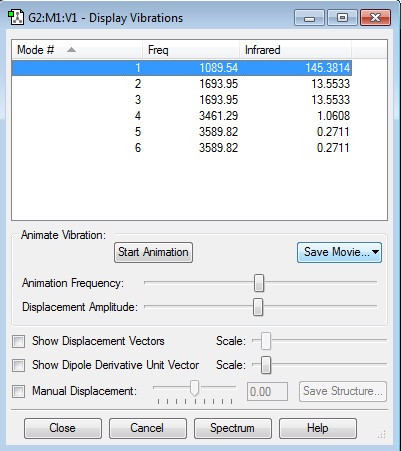
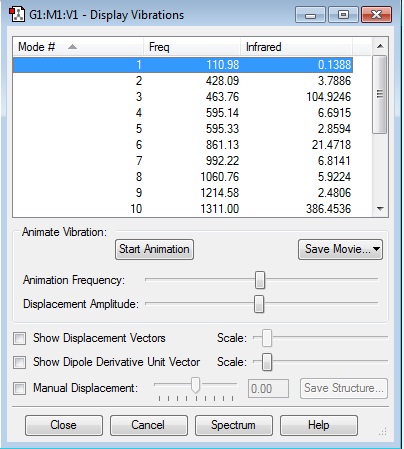
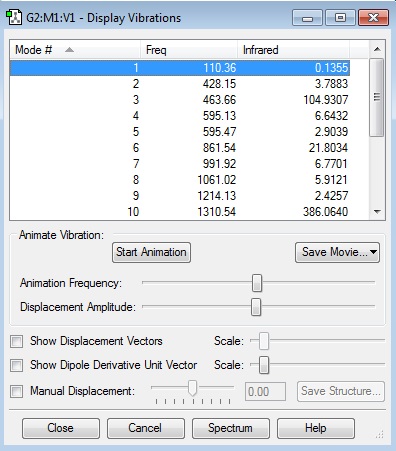
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
Using the 3N-6 rule there is an expected 6 vibrational frequencies which matches the data.
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate and also 5 and 6.
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
| Bend | Stretch |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 6 |
which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4 is highly symmetric
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
The Umbrella stretch is mode 4 as it gives an umbrella stretch shape.
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
There would be 2 bands. There are three values with a high enough absorption to register a peak in the infrared spectrum. However 2 of the bends have the same frequency and absorption making the bands indistinguishable leaving 2 distinct bands.
Charge on ammonia
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 0.375 |
| Nitrogen | -1.125 |
Explanation of the charges
The Nitrogen atom is more electronegative and has a drawing affect on the electrons pulling them close to its nucleus. This polar character in the band towards the nitrogen means it picks up a slight negative charge. The electrons are therefore pulled further from the hydrogen nucleus resulting in a small positive charge on each Hydrogen.
N2 Molecule
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | N2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -109.5 |
| RMS gradient | 0.0247 |
| Point group | Dinf |
| Bond distance | 1.10550 |
| Bond angle | 180.00 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.400871D-13 Optimization completed.
N2 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2 Molecule
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | H2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -1.178 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Point group | Dinf |
| Bond distance | 0.6 |
| Bond angle | 180.00 |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
H2 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
| Molecule/Function | Energy (au) |
|---|---|
| E(NH3) | -56.557768 |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.115536 |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 |
| ΔE = 2*E(NH3) -[E(N2)+3*(H2)] | 0.634 |
| uni | Energy |
|---|---|
| au | -0.05578924 |
| KJ/mol | -146.475 |
Identify which is more stable the gaseous reactants or the ammonia product?
The Reactants are more stable than the products in this reaction. For the reaction to go forward there must be a positive increase in energy meaning the reactants where lower in energy and more stable. Energy is required to be put into the system to gain the products which have a higher energy.
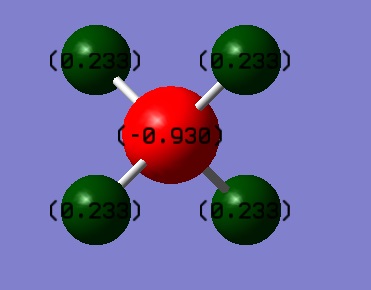
Methane Molecule (Own Molecule)
CH4 Molecule
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | CH4 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -40.524 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00003263 |
| Point group | Td |
| Bond distance | 1.09197 |
| Bond angle | 109.47 |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256043D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
CH4 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
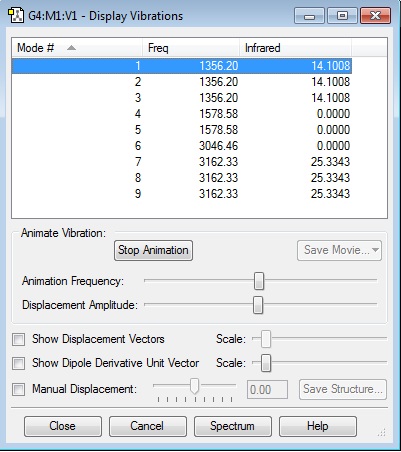
I would expect 2 bands in the infrared spectrum of this molecule as there are 6 modes which have an infrared intensity. But these go into 2 sets of 3 modes each identical.
| Frequency | Infrared 10-40esu2cm2 |
|---|---|
| 1356.2 | 14.1008 |
| 3162.33 | 25.3343 |
| Bend | Stretch |
|---|---|
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 8 |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 |
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Carbon | -0.93 |
| Hydrogen | 0.233 |
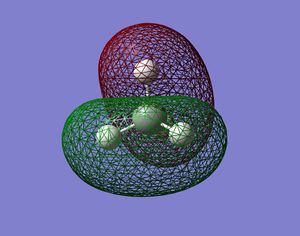
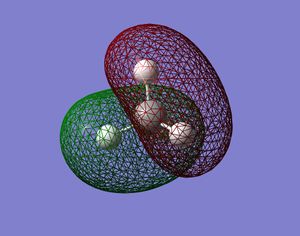
CH4 Orbitals
Independent Investigation into Acetone
optimization first ran with a torsion angle of 0 degrees.
0 degrees dihedral
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | C2H4O2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -229.081 |
| RMS gradient | 0.0001307 |
| Point group | CS |
| Dihedral Angle | 0 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000322 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000118 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001823 0.001800 NO RMS Displacement 0.000801 0.001200 YES <pre> NOTE its acceptable for the max deisplacement not to converge in organic molecules
Acetic |
The optimisation file is liked to here
The fact that all the infrared are evidence that the structure is optimized.
90° Torsion angle
| variable | Result |
|---|---|
| Molecule | C2H4O2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31(d.p) |
| Final energy (au) | -229.081 |
| RMS gradient | 0.00001289 |
| Point group | C1 |
| Dihedral Angle | 90 |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000018 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000008 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001389 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000660 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.108190D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Acetic |
Note structure was made mol file due to error in position when log used.
The optimization file is liked to here
The Molecule has been optimized and matches the structure when the dihedral is 0